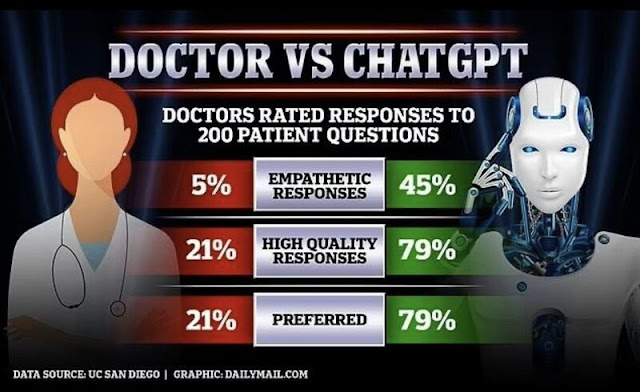
Age isn't the predominant cause of low testosterone and there are things you can do to maintain your levels

Many men accept as fact the idea that testosterone will inevitably decrease as they get older. However, new science is showing that diseases of lifestyle, rather than just age, are often the real culprits behind the decline. Testosterone levels have shown a stunning downward trend in the past several decades. The standard American diet is a nutritional wasteland. Environmental pollution and microplastics are wreaking havoc on our hormone levels with their endocrine-disrupting chemicals. Obesity, many drugs, and our sedentary lifestyle also undermine testosterone production. When so many aspects of our way of life can potentially sabotage testosterone levels—and by extension, good health—it becomes fundamental to a man’s well-being to understand how to preserve and boost levels of this vital hormone. In a study published in March 2023 in The Journal of Sexual Medicine, researchers examined 625 men with an average age of 65 years, aiming to determine how aging affects testosterone. The