Causes of Aging and Best Ways to Slow Down Aging: 1,000+ Studies Analyzed (2025)
The process of human aging is a complex and multifactorial process. NAD, stem
cells, nitric oxide, glutathione, vitamin B12, CoQ10, glycine, taurine and
testosterone decline as we age. Vitamin and mineral deficiencies are also common
in older individuals.
3. Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation, enable the immune system to
carry out its tasks, and help the brain and eyes to function
properly.
Published in 2021 in the Mayo Clinic Proceedings, omega-3 supplementation was associated with statistically
significant reductions in the risk of Myocardial Infarction (heart
attack) with a high GRADE certainty.
Many governments recommend eating omega-3 containing fatty fish, two times per week. But that is often not enough. Ideally, people would need to eat fatty fish four times per week, while also supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids, at least 1,000 mg of pure omega-3 (DHA and EPA) per day.
Make sure you buy high-quality omega-3 fatty acid supplements, meaning that the omega-3 fatty acids are pure and have not oxidized much (having low “TOTOX” value). TOTOX value stands for total oxidation value. The omega 3 fatty acids EPA and DHA from fish oil are highly sensitive to oxidation. This means that they are rapidly affected by contact with oxygen. Oxidised fatty acids are not beneficial to our health. For this reason, a good fish oil supplement has a low TOTOX value. The maximum TOTOX value is set at 26 by the Global Organization for EPA and DHA omega-3.
We show in this review evidence of the relationship of magnesium with all the hallmarks of aging (genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, deregulated nutrient sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, altered intercellular communication, disabled autophagy, dysbiosis, and chronic inflammation), which may positively affect the human healthspan. It is feasible to hypothesize that maintaining an optimal balance of magnesium during one’s life course may turn out to be a safe and economical strategy contributing to the promotion of healthy aging.
There are many ways in which magnesium deficiency can lead to accelerated aging. Magnesium is needed to build, maintain and repair DNA.
Magnesium reduces DNA damage and stabilizes the genome (R,R). For example, magnesium sticks to the DNA strand and stabilizes it, and it is also an essential cofactor for DNA repair proteins which need magnesium to function properly (R).
Magnesium can reduce inflammaging (low-grade inflammation that increases during aging). Low levels of magnesium have been linked to chronic low-grade inflammation, which is one of the drivers of aging (R).
Besides magnesium’s many effects on maintaining our cells, the mineral has various immediately noticeable effects. Athletes take magnesium to improve their physical performance, even when they are not magnesium deficient (R).
Magnesium supplements also improve sleep, and feelings of relaxation and wellbeing.
This is not surprising, given the important role of magnesium in the functioning of brain cells, such as excitation and neuronal metabolism.
Malate is often used in combination with magnesium to bring about health benefits, especially for improving energy and reducing fatigue.
It was also already discovered that hydrogen can prolong the life of stem cells by reducing oxidative stress (Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010).
Maintaining cells in low-oxygen conditions or in the presence of
hydrogen gas, matrix modification, and supplying the culture
medium with growth factors and antioxidants capable of
attenuating ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) accumulation can slow
done the telomere shortening and proliferative senescence.
Note: Most Molecular Hydrogen tablets have dual-ingredient formula and
use pure elemental magnesium as its carrier and provides you with
approximately 80 mg of magnesium per tablet. So, you receive also
highly bioavailable magnesium for a healthy brain, muscles, cells,
kidneys, and heart.
Glycine
Glycine can also help counteract adverse effects of Glyphosate. When
glyphosate enters your system, it can take the place of the glycine
molecule. While similar, (the "gly" in glyphosate stands for glycine) it's
not identical and does not work the same way as glycine. Hence, this
replacement causes all sorts of trouble.
"Your body only makes 3 grams of glycine per day, and if you only consume around 2 to 3 grams of glycine from foods then it means that almost all of us are in a 10-gram glycine deficit every day," he says.
"… I think most people would benefit for at least 5 to 10 grams of glycine a day, which is, uh kind of a moderate amount … if you are eating a lot of muscle meat … or you're just interested in getting more of the benefits of glycine then you can take even up to 20 grams a day."
Marios Kyriazis, M.D., a gerontologist nominated for the 2017 Nobel Prize in Medicine and
main contributor at For the Ageless, told Healthnews,
"NAC, the acetylated form of the amino acid cysteine, protects our brain by stimulating the activity of glutathione, which is a potent antioxidant that protects our mitochondria from free radical damage. NAC is also effective against viruses and it is used both for the prevention and treatment of some viral infections, including brain infections."
He added, "Conventional doctors use NAC to counteract the consequences of paracetamol overdose because it protects the liver from damage."
Kyriazis suggests the conventional dose is around 1000 mg to 1500 mg per day and says some doctors recommend taking NAC with vitamin C to prevent it from being destroyed in the body prematurely.
"500mg of NAC every morning is an effective dose for adults looking to use it daily as a longevity supplement," he explained. "It has an excellent safety profile and can be taken with any other supplements, including glutathione."
According to another research published in the June 2023 issue of the
journal Science, the semi-essential amino acid taurine appears to play an important
role in longevity and healthy aging.
*Umbrella review: An umbrella review, or a review of reviews, is a systematic review that only considers other systematic reviews as an eligible study type for inclusion.
Alpha-ketoglutarate also plays a role in maintaining stem cell health (Nature 2015), and in bone and gut metabolism (R).
Calcium alpha-ketoglutarate is also involved in collagen production, can reduce fibrosis, and can thus play a role in maintaining healthy, youthful skin (R,R).
CoQ10 is also part of Dr. David Sinclair’s supplement list.
Lastly, the interventions testing program (ITP) tested a similar compound,
MitoQ (a better absorbable nutrient based on coQ10), and didn’t find a
life extension effect (R).
Related: Best CoQ10 Supplements
Fisetin is a flavonoid. Flavonoids are substances that give fruits and vegetables their bright colors (like yellow, orange and blue) and play a major role in conferring the health benefits that we get from eating more vegetables and fruits.
Fisetin is probably most known for its impact on senescent cells: studies showed that this substance can reduce the accumulation of senescent cells (R). Fisetin is a senolytic, a compound that can clear away senescent cells.
Senescent cells accumulate everywhere in the body during aging. Senescent cells were previously normal cells that became too damaged. Normally, when a cell is too damaged, it kills itself, but senescent cells don’t do that.
Instead of dying, they keep lingering around in the body.
Senescent cells secrete all kinds of substances that damage the healthy surrounding cells, like inflammatory substances (cytokines and chemokines), substances that break down the glue that holds the cells together (matrix metalloproteinases), and growth factors that accelerate aging (R). Not only do senescent cells damage healthy surrounding cells, but they also damage stem cells, which are the foundational cells that create new cells, which build up and repair our organs and tissues.
Reducing the senescent cell burden can lead to reduced inflammaging (low-grade inflammation that increases during aging) and enhanced function of stem cells.
Substances that can eliminate senescent cells are called “senolytics”. Fisetin is a well-studied senolytic substance.
Fisetin versus quercetin
A 2021 research review suggests that resveratrol supplements may help protect
against age-related cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and
diabetic disorders.
Nearly two decades ago, it was discovered that resveratrol slowed
the process of cellular aging in yeast. In 2003, Harvard Medical
School Professor David Sinclair, PhD, found that resveratrol
activated a class of sirtuin proteins called SIRT1.
Note: You might have heard of “skinny genes” — genetic components
that can help us stay thin, age well, and live longer. Sirtuins
are a family of proteins that might do just that. Sirtuins aren’t
genes at all, they’re proteins. Humans have seven of them, called
SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT3, and so on.
The polyphenol is reported to be safe at doses up to 5 g/d, when
used either alone or as a combination therapy. Although the clinical
utility of resveratrol is well documented, the rapid metabolism and
poor bioavailability have limited its therapeutic use. In this
regard, the recently produced micronized resveratrol formulation
called SRT501, shows promise (Pratap Singh 2019).
Related: David Sinclair $720 Million Train Wreck!
The Minnesota Green Tea Trial (MGTT) is the largest and longest double-blind,
placebo-controlled, randomized intervention study that specifically
evaluated the effects of oral GTE (green tea extract) containing
defined quantities of EGCG on established biomarkers of breast cancer
risk.
EGCG can be consumed by drinking green tea or taking concentrated supplements.
Because scientists aren’t sure how much EGCG is safe to take in pill
form, the best way to incorporate it into the diet is by drinking
green tea. One cup of green tea usually contains about 50 to 100 mg of
EGCG.
A diet rich in fruits and vegetables should provide enough lutein for healthy adults, but there are no known side effects from supplementing for those who choose to do so. However, consuming lutein alongside beta carotene specifically might reduce the body’s absorption of both vitamins, and when taken with vitamin E, lutein can reduce the amount of vitamin E the body can absorb. Food sources of lutein include egg yolks, spinach and kale. It’s also important to consume lutein along with foods high in fat to facilitate better absorption.
An encouraging 2020 study shows that glucosamine and chondroitin, commonly used to
treat the pain and inflammation of arthritis, can also do “double
duty” in reducing the risk of heart disease and the risk of death
from cardiovascular disease conditions.
The study, conducted by researchers at West Virginia University
(WVU) and published in the Journal of the American Board of Family
Medicine, involved over 16,000 adults over age 40. After adjusting
for age, sex, race, education, smoking status, and physical
activity, the researchers came to a stunning conclusion.
They found that participants who took glucosamine and chondroitin daily for a year reduced the risk of death from any cause—by an astounding 39 percent. The supplementation also reduced cardiovascular deaths—including death from coronary artery disease, stroke, and other forms of heart disease—by 65 percent. In fact, glucosamine/chondroitin supplementation worked about as well as regular exercise in reducing the risk of death (although the researchers do not recommend that people forego exercising in favor of glucosamine).
Dr. King, the lead author of the WVU study not only strongly recommends
glucosamine and chondroitin, but goes a step further, acknowledging that
he regularly takes the supplement himself.
In one 2019 study published in the British Medical Journal, the scientists noted
that glucosamine/chondroitin given for arthritis pain also significantly
lowered the risk of heart disease and stroke. Specifically, the
supplementation lowered the risk of adverse cardiovascular events by 15
percent, cardiovascular-related deaths by 22 percent, and coronary heart
disease by 18 percent. For the WVU study, researchers took things a step
further by setting out to further explore the link between regular
consumption and mortality from cardiovascular conditions.
Most people are deficient, as they’re likely only consuming 0 to 1
gram of collagen protein daily. About one-third of total body
protein is collagen, so it's crucial to consume adequate collagen,
from foods like bone broth or grass fed ground beef, which contains
connective tissue, or glycine to support connective tissue health.
A
2023 meta-analysis
of 26 RCTs (randomized controlled trials), showed that Hydrolyzed
Collagen supplementation significantly improved skin hydration and
elasticity compared to the placebo group.
Collagen is the glue that holds us together. It’s great for skin, bones,
joints and muscles. The majority of people don’t eat enough collagen
foods, such as the skin of poultry and fish, organ meats and bone broth.
Therefore, older adults can benefit from a daily supplement of 10 to 15
grams of collagen peptides.
Consuming spermidine-rich food lowers mortality associated with cardiovascular diseases and cancer. Further, a study
published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found a diet rich in
spermidine, at levels commonly found in the Western diet, lowers the risk of all-cause mortality:
“Spermidine showed the strongest inverse relation with mortality among 146 nutrients studied. The reduction in mortality risk related to a diet rich in spermidine (top compared with bottom third of spermidine intake) was comparable to that associated with a 5.7-y younger age. All of the findings apply to spermidine from dietary sources and to amounts characteristically found in the Western diet …”
In humans, higher dietary intake of spermidine is also linked with a reduced risk of cognitive impairment.
A research team with Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences in India further suggested spermidine could be a useful therapeutic strategy for neurological disorders due to its autophagy-inducing properties. They noted that a healthy brain is dependent on its concentration of polyamines:
“Polyamines interact with the opioid system, glutamatergic signaling and neuroinflammation in the neuronal and glial compartments. Among the polyamines, spermidine is found highest in the human brain. Age-linked fluctuations in the spermidine levels may possibly contribute to the impairments in neural network and neurogenesis.”
Although the cocoa extract did not achieve statistical significance in reducing total cardiovascular events among these older adults, it did reduce CVD death by 27%. That should still encourage most adults to consume a bit more cocoa.
Source:
Effect of cocoa flavanol supplementation for the prevention of
cardiovascular disease events: the COcoa Supplement and Multivitamin
Outcomes Study (COSMOS) randomized clinical trial. (2022)
A 2024 meta-analysis of 16 randomised controlled trials (RCTs), suggests that creatine monohydrate supplementation may confer beneficial effects on cognitive function in adults, particularly in the domains of memory, attention time, and information processing speed.
In a 2023 research, published in Nutrition Reviews, found creatine supplementation enhanced memory performance in healthy adults, particularly those aged 66 to 76 years. The study concluded:
“These beneficial effects from creatine supplementation on memory performance may be related to creatine’s ability to influence brain bioenergetics. For example, creatine elevates phosphocreatine and ATP levels and increases oxidative phosphorylation in synaptosomes and isolated brain mitochondria. In hippocampal neuron cultures, creatine stimulates mitochondrial activity.”
To highlight, a 10-fold decrease in pineal melatonin production in octogenarians compared to teenagers was observed, which results in a significant attenuation of the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and mitochondrial optimizing effects of melatonin. This has important consequences for the immune changes common over the course of aging, including immune senescence and inflammaging (inflammation associated with aging), which may be mediated by the effects of night-time pineal melatonin in resetting and resynchronizing immune cell mitochondrial function...
Hence, a vicious circle between melatonin production levels and aging seems
to exist, since melatonin synthesis decreases with the age and, at the same
time, the aging is worsened as a consequence of the melatonin deficiency.
Related: Synthetic Progesterone Linked to Increased Risk of Brain Cancer
Can HRT Help Prevent Cardiovascular Disease in Women?
Cardiovascular disease is responsible for 1 in every 4 deaths in the U.S. It’s the leading cause of death in both men and women, and leads to more than 600,000 deaths across the country annually (CDC). It’s therefore critical that as the risk for cardiovascular disease increases with age, individuals find ways to optimize heart health.
HRT may not be prescribed for women primarily as a means for improving cardiovascular health, but this is indeed a powerful byproduct of the treatment. According to research published in the BMJ, women receiving HRT early after experiencing menopause had a significantly reduced rate of heart failure, myocardial infarction, and mortality overall. At the start of treatment, women on average were aged 50 and had been postmenopausal for seven months. Roughly half as many women using HRT experienced cardiovascular events compared to those in the control group. Additionally, these results did not correlate with an increased risk in any cancer [BMJ 2012].
Moreover, evidence shows that there is a clear benefit in using estrogen alone, with coronary calcium scores significantly reduced. This measures the buildup of calcium and other substances which can narrow or close the arteries, leading to cardiovascular issues. In particular, women under 60 who receive hormone therapy have a statistically significant reduction in coronary disease (Lobo 2013).
These aren’t the only positive outcomes of HRT, however. Hormone therapy has been commonly used as an osteoporosis preventative, which brings us to our next segment.
A meta-analysis (Lancet 2022) of 35 published studies that tracked
heart attacks and heart disease in men taking testosterone found
no association between testosterone and heart attacks and in fact
in most studies, men on testosterone had fewer heart attacks.
TRT is an acronym for testosterone replacement therapy, sometimes called androgen replacement therapy. It’s primarily used to treat low testosterone (T) levels, which can occur with age or as a result of a medical condition.
But it’s becoming increasingly popular for non-medical uses, including:
This is all part of a completely natural process that starts in your late 20s or early 30s.
This gradual decrease in Testosterone often doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms. But a significant drop in T levels may cause:
Your body can transform DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone) into
testosterone. Taking a DHEA may increase your testosterone levels. A
2013 study found that taking 50 milligrams (mg) of DHEA per day raised
the free testosterone levels of middle-aged adults undergoing
high-intensity interval training.
Why is mTOR important? mTOR is responsible for both intracellular and
extracellular signals and serves as a central regulator of cell
metabolism, growth, proliferation and survival. In simple words mTOR
activation causes cells to age faster. The good news is that there are
ways that you can slow your and even inhibit mTOR. We ALL know that severe
caloric restriction is one of the ways to inhibit mTOR but this is not
sustainable, nor is it good for your body long-term. Luckily, pioneers in
lifespan and longevity have made an amazing discovery called Rapamycin.
The following background information is from an organization that studies
human lifespan.
Metformin is arguably the most well-known, and the most common prescription drug that life-extension enthusiasts take in an effort to slow down aging and extend lifespan.
In humans, metformin has been in clinical use for over 60 years, studied extensively, has a high safety profile, and is uniquely positioned to intervene several crucial pathways responsible for aging and age-related diseases (Barzilai et al., 2016). As recommended by the American Diabetes Association, due to its glucose-lowering effects, metformin monotherapy is the preferred first-line pharmacological action against type 2 diabetes (American Diabetes Association, 2019).
Metformin is a prescription drug that has been used for decades to treat type 2 diabetes. It’s mechanism of action is different from most diabetes drugs, given it improves insulin sensitivity (or reduces insulin resistance).
In a 2024 study, published in Cell, gero-protective effects of metformin on monkeys were evaluated in a rigorous 40-month study. The results highlighted a significant slowing of aging indicators, notably a roughly 6-year regression in brain aging. Metformin exerts a substantial neuroprotective effect, preserving brain structure and enhancing cognitive ability. This research pioneers the systemic reduction of multi-dimensional biological age in primates through metformin, paving the way for advancing pharmaceutical strategies against human aging.
While some research suggests potential benefits from supplements, hormone therapy, or even stem cells in slowing aging, these shouldn't replace core healthy practices. A well-rounded approach is key for optimal well-being.
Remember, supplements are not magic bullets. They should complement, not replace, a healthy lifestyle. Consult your doctor before starting any new supplement program to ensure safety and suitability for your individual needs.
Multi-Faceted Aging Solutions
Aging is a complex process with various contributing factors. Ideally, an anti-aging supplement should address these factors synergistically, meaning the components work together for a stronger effect.
Reliable Research: Always prioritize credible sources for information. Look for research published in peer-reviewed journals, searchable through platforms like PubMed or Google Scholar.
Let age be just a number.
The Wellness Company's science-backed Longevity formula maintains youthful cellular function, helping you feel your best no matter the year you were born.
Target the root causes of aging with Liposomal Glutathione – the “master antioxidant," Nicotinamide Riboside (NR), and Resveratrol. This age-defying combination helps your cells clean up “dirty” DNA to increase energy production and reduce inflammation.
The Wellness Company combine these powerful ingredients with probiotics superior absorption. Feel like a younger version of yourself, everyday.
LONGEVITY FORMULA CONTAINS:
In September of 2019, the MIT Technology Review published “The Longevity
Issue” with a MASSIVE black heading on a snow-white cover and announced,
“OLD AGE IS OVER!” and in a font much smaller underneath are the following
words: “IF YOU WANT IT.”
Methodology: The selection or short-listing of the topics below is based on the available scientific evidence retrieved from scientific database such as PubMed and scientific search engine such as Google Scholar. The article will also be updated as and when there is a newly discovered major research publication related to anti-aging and longevity.
The most important way to negate the effects of sarcopenia is through
resistance exercise. Exercises such as walking are great for cardiovascular
fitness but they do very little to help with sarcopenia. Resistance exercise
means exercising against resistance, such as with weights or resistance
machines that you find in your local gym. Everybody is capable of doing some
form of resistance exercise and this is something you should not be
intimidated by.
Another important factors in slowing sarcopenia is diet. As we age our appetite declines, so as we eat less we naturally reduce the amount of protein that we consume. To slow sarcopenia we need to keep our protein intake high, and as we are eating less this means that a higher proportion of the food we eat needs to be protein. It is also important to spread this protein out through the day over three or meals as this produces more muscle protein synthesis when compared to one or two high protein meals.
It is also important to get your vitamin D levels checked as you age since deficiency is common due to reduced sun exposure. As well as weakening our bones, low vitamin D results in weaker muscles and accelerated sarcopenia. A low vitamin D level can be easily rectified with supplementation. When was the last time you had your vitamin D level checked?
Being aware that sarcopaenia affects us all is the first step in combating its effects. The earlier you commence resistance exercise, the greater the benefits, but it is never too late to start. If you are new to resistance exercise or intimidated by the gym environment, talk to your local gym about some personal training to help you learn.
Related: Muscle Mass - The Key to Longevity
Walking Is a Simple, Powerful Key to Longevity
A 2023 review published in GeroScience highlights the crucial role of regular physical activity, particularly walking, in promoting healthy aging and longevity.14 The researchers emphasize that walking is not just a basic exercise but a potent antiaging intervention. It has been shown to lower the risk of age-related chronic diseases such as heart disease, high blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes and cancer. Moreover, walking can alleviate pain and enhance function in musculoskeletal conditions.
A June 2022 study supports what immunologists have long suspected: A key stressor to
our immune system as we age may be stress itself.
“Immune aging may help explain why older people tend to benefit less from
vaccines and why they have more serious complications associated with
infections like COVID-19,” Erik Klopack, Ph.D., a lead author of the study and a postdoctoral scholar at the Leonard
Davis School of Gerontology at the University of Southern California. “Our
study suggests that social stress may accelerate immune aging,” he said.
As part of the Cardiovascular Health Study, 5,749 adults aged 65 years and older
from 4 US field centers for 25 years were followed. In older adults, higher
social network scores are significantly associated with longer life expectancy
and disability-free life expectancy. (Bhatia 2023)
This prospective cohort study included 6,670 women from the Women's Health
Initiative Memory Study who were cognitively unimpaired at enrollment;
showed that improving social support may reduce risk of MCI (mild cognitive
impairment) and dementia in older women. (Posis 2023)
Okinawa in Japan, Sardinia in Italy, Roseto in Pennsylvania, Loma Linda in California, Icaria in Greece and Nicoya in Costa Rica are some of the places with the highest proportions of people who live to be 100 years old.
All these places have the same thing in common. What is it?
Fasting can potentially starve cancer cells. When fasting, the body uses fats and produces ketones for energy. Cancer cells rely heavily on glucose, making them less efficient at using ketones.
Additionally, fasting reduces insulin levels. Elevated insulin levels are linked to an increased risk of breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers.
Food for Thought: Scurvy, pellagra, and beriberi were once thought to be infectious and were finally recognized as nutritionally linked. Scurvy is a deficiency of vitamin C, Pellagra is a deficiency of niacin, more commonly known as vitamin B3, and Beriberi is a deficiency of thiamine, more commonly known as vitamin B1.
Food for thought: The Sun powers photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy, fueling the entire ecosystem. Additionally, the sun’s rays also enable our bodies to produce vitamin D, essential for immune system, bone health and overall well-being.
Previous research found that a vitamin D level of 47 ng/ml was associated with a 50% lower risk of breast cancer (R). Further, researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine reported that raising your vitamin D level to at least 40 ng/ml can slash your risk of all invasive cancers by 67% (R).
Many governments advise 400 to 800 IU of vitamin D per day, while many vitamin D researchers claim you need at least 2000 to 4000 units per day.
We would recommend to take at least 2000 units per day. The risk of excess accumulation of vitamin D is negligible with this amount. Make sure it’s vitamin D3, and not vitamin D2 – the vitamin D3 variant works better.
NAD+ Precursors
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN)
A study in 2022 suggests that taking 250 mg/day of NMN can significantly increase and sustain the levels of NAD+ in
the blood, without adverse side effects.
Some brands have created a liposomal NMN formula with TMG* to
speed up NAD+ production. Combining NMN and TMG is proposed as one
of the potential ways to promote longevity.
Vitamin B12 is needed to form red blood cells and DNA. It is also a key player in the function and development of brain and nerve cells. However, we believe the most important function it provides is methylation. If you don’t know what methylation is, allow us to briefly explain. Methylation is a biochemical process which is involved in a wide range of bodily functions, and is essential to our overall well-being. When methylation is out of balance, many different health problems may arise.
This article has more than 18,000 words, more than 10 headings with
various sub-sections and more than 1,000 references. This practical
guide will help you to understand aging, longevity, and all that is
involved to “turn back the clock”. We are providing you with science,
knowledge, and best of all possibilities.
Current large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Google Gemini and
Microsoft Copilot might return generic answers to your questions. While
these can be a starting point, they often lack the depth you might
crave.
While your doctor may not delve deeply into diet, lifestyle and
anti aging supplements during consultations, these aspects can be crucial for your
well-being and longevity.
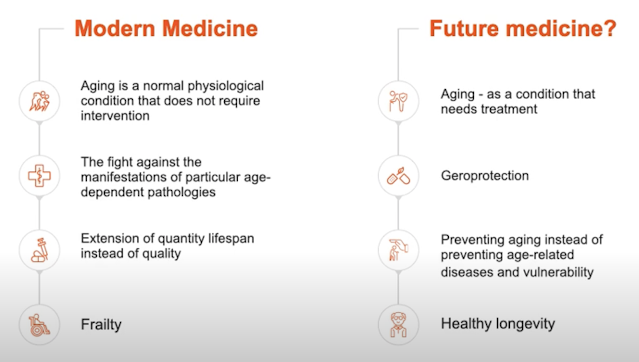
While aging is inevitable, increasing the human lifespan and slowing
the aging process has been a focus of scientific research for decades.
If aging is reversible, then maybe heart disease, cancer, diabetes,
Alzheimer's or other chronic disorders are reversible as well.
This guide is based on a comprehensive review of over 1,000 scientific
references and supporting studies. It explores the latest
science-backed interventions for promoting longevity and healthy
aging.
This long form article compiles research related to the anti-aging
space. This article will also reveal exciting new information about
a variety of immune-enhancing natural products and nutrients that
may help you maintain youthful immune system function into advancing
age.
Methodology: The selection or short-listing of the topics below is based on the available scientific evidence retrieved from scientific database such as PubMed and scientific search engine such as Google Scholar. The article will also be updated as and when there is a newly discovered major research publication related to anti-aging and longevity.
In this comprehensive guide you will learn about many aspects of
aging, longevity and age-reversal strategies.
Contents
- What is Aging?
- Biological Age vs Chronological Age
- Causes of Aging and Hallmarks of Aging
- What is Cell Senescence?
- What is Epigenetics?
- Diet and Lifestyle for Anti Aging
- Avoiding Sugar and Ultra-processed Foods
- Mediterranean Diet and Vegetables
- Avoiding Smoking and Alcohol
- Stress Management
- Avoiding Linoleic Acid (Omega-6 Fatty Acids) and Vegetable Oil
- Exercise, Resistance Training and Walking
- Sleep
- Social Support
- Caloric Restriction, Intermittent fasting (Time Restricted Eating) and Fasting
- Low-Fat High-Carbohydrate Heart Healthy Diet vs High-Fat Low-Carbohydrate Diet
- Best Scientifically Proven Anti Aging Supplements
- Vitamin D3 and K2
- B Vitamins, Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and NAD Boosting Supplements
- Glycine, NAC and Taurine
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Magnesium and Molecular Hydrogen
- Curcumin (Turmeric)
- Vitamin C and Alpha-KetoGlutarate (AKG)
- Fisetin and Quercetin
- CoQ10
- Resveratrol and Pterostilbene
- Zinc
- EGCG (Green Tea)
- L-Citrulline and L-Arginine (Nitric Oxide Boosters)
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin
- Protein Powder and Collagen
- Spermidine
- Crocin (Saffron)
- Cocoa
- Creatine
- Melatonin
- Other Promising Anti Aging Strategies
- Stem Cell Therapy for Anti-Aging
- Hormone Replacement Therapy
- Peptide Therapy for Anti Aging
- Exosomes for Anti Aging
- Does Metformin Increase Life Expectancy?
- Metabolic Manipulation (mTOR Inhibitors) and Rapamycin
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT)
- Conclusion and Key Takeaways
What is Aging?
The global anti-aging & longevity market size was estimated at USD
63.60 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual
growth rate (CAGR) of 21.5% from 2024 to 2030. (R)
We are interested in your 'biological age' and in Healthspan rather
than Lifespan, which means that you LIVE - HEALTHIER - LONGER. This
is better than chronologic age and Longevity because it just means a
long life with no regard to your quality and function.
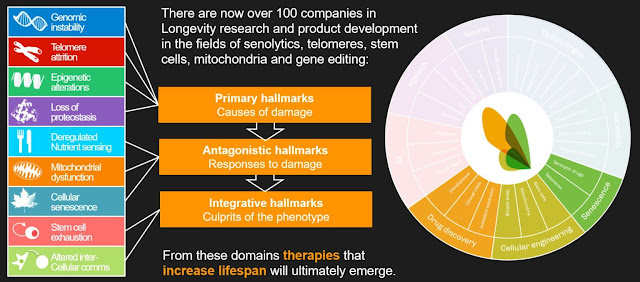 Image credit: Longevity.technology
Image credit: Longevity.technology
The term epi means above or in addition to and epigenetics
describes the study of gene expression regulation that cannot
be directly attributed to changes in the DNA sequence.
Epigenetics (the study of epigenomes) describes the way our
specific behaviors (e.g., lifestyle choices including how much
alcohol we drink, or whether we use a water filter) and
environmental factors (e.g., air pollution) can alter the way
our genes work. Epigenetic changes can be extremely impactful,
often passed on from generation to generation, yet they are
reversible, and do not alter the DNA sequence (although they
do change how our bodies READ a DNA sequence). A bit
confusing?
A
2024 review
aims to summarize recent findings on the dietary factors
influencing chronic diseases and longevity, primarily from
large cohort studies.
A 2019 study
found that healthy lifestyle choices could reduce the risk of
stroke—a cardiovascular event when blood supply to the brain is
cut off or when a blood vessel in the brain bursts—by 80
percent, with
diet identified as the most influential factor.
An article by the New York Times (2016) titled "How the Sugar Industry Shifted Blame to Fat" suggested that the sugar industry paid scientists in the 1960s to play down the link between sugar and heart disease and promote saturated fat as the culprit instead, newly released historical documents show. This article was based on the internal sugar industry documents, discovered by a researcher at the University of California, San Francisco, and published in JAMA Internal Medicine (2016) that suggested that five decades of research into the role of nutrition and heart disease, including many of today’s dietary recommendations, may have been largely shaped by the sugar industry.
Think Twice About Plant-Based Foods: Some Types Could
Heighten Cardiovascular Risks and Mortality
In June 2024,
The Lancet Regional Health–Europe
published a study indicating a positive association between
the intake of ultra-processed plant-based foods and the
risk of CVD and mortality. Conversely, consuming
non-ultra-processed plant-based foods was negatively
associated with these risks.
The study, which analyzed data from nearly 127,000 individuals aged 40 to 69 in the UK Biobank with a median follow-up of nine years, found that each 10 percent increase in the proportion of total energy intake from ultra-processed plant-based foods was associated with a 5 percent increase in the risk of CVD and a 6 percent increase in the risk of coronary heart disease. Moreover, the risk of mortality from CVD increased by 12 percent.
“Smoking is one of the strongest risk-factors for every
chronic disease, including heart disease and cancer,” says Susan Lakoski, M.D., associate professor of cancer prevention at MD
Anderson Cancer Center.
Smoking and secondhand smoke introduce harmful toxins to the body. There’s no such thing as a healthy smoker - especially when it comes to cancer prevention.
“The biggest myth I hear is that if someone exercises they can offset the negative effects from smoking, but that’s absolutely not the case,” says Susan Lakoski, M.D.
A 2022 study
in Experimental Gerontology shows that resistance exercise, such as
weightlifting, boosts immunity by activating key immune pathways and
reducing inflammation. Reviewing 30 studies, researchers found that just one
session of resistance exercise can enhance immune cell function, but regular
workouts over weeks are needed for lasting benefits.
Aging is a natural process that everyone goes through, and while
there is no magic potion to stop the clock. However, it's essential
to note that there is no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to
the effectiveness of anti-aging strategies, as they can vary
depending on individual health, age, and other factors.
|
| Longevity Medicine will become the New Primary Care |
Biological Age vs Chronological Age
When asked how old you are, you likely answer based on the number
of years that have passed since you were born. That would be your
chronological age.
But maybe your doctor says you have the physical conditioning of a 21-year-old. This would be considered your biological age, regardless of how many years ago you were born.
Your chronological age will always be an easy-to-determine number, while your biological age depends on a number of variables that can change on a continuing basis.
The basic idea behind biological aging is that aging occurs as
you gradually accumulate damage to various cells and tissues in
the body.
Also known as physiological or functional age, biological age differs from chronological age because it takes into consideration a number of factors other than just the day you were born.
The actual number comes down to different biological and physiological development factors. Some of these include:
But maybe your doctor says you have the physical conditioning of a 21-year-old. This would be considered your biological age, regardless of how many years ago you were born.
Your chronological age will always be an easy-to-determine number, while your biological age depends on a number of variables that can change on a continuing basis.
The difference between the two can be surprising and
definitely worthy of further exploration.
What is chronological aging?
What is chronological aging?
Your chronological age is the amount of time that has passed
from your birth to the given date. It’s your age in terms of
years, months, days, etc. This is the primary way people
define their age.
It’s also a primary risk factor for chronic diseases, mortality, and any impairments to bodily functions, such as hearing and memory.
What is biological aging?
It’s also a primary risk factor for chronic diseases, mortality, and any impairments to bodily functions, such as hearing and memory.
What is biological aging?
Also known as physiological or functional age, biological age differs from chronological age because it takes into consideration a number of factors other than just the day you were born.
The actual number comes down to different biological and physiological development factors. Some of these include:
- chronological age
- genetics (for example, how quickly your body’s antioxidant defenses kick in)
- lifestyle
- nutrition
- diseases and other conditions
Using these guidelines along with various mathematical models,
medical professionals can figure out what age your body “acts”
like it is.
While chronological age is a factor, you may not end up having the same biological age as your chronological age. For example, if you’re a 28-year-old male who doesn’t exercise, only eats high-fat foods, and has smoked five packs of cigarettes per day for the last 10 years, it’s likely you would have a biological age of greater than 28 years.
While chronological age is a factor, you may not end up having the same biological age as your chronological age. For example, if you’re a 28-year-old male who doesn’t exercise, only eats high-fat foods, and has smoked five packs of cigarettes per day for the last 10 years, it’s likely you would have a biological age of greater than 28 years.
 Image credit: Longevity.technology
Image credit: Longevity.technologyCauses of Aging
In order to guide and provide a framework for ageing research
and discussion, the landmark 2013 Hallmarks of Aging study identified 9 factors that contribute to health decline in
advancing age: genomic instability, telomere attrition,
epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, deregulated
nutrient-sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular
senescence, stem cell exhaustion, and altered intercellular
communication.
The review was updated (Cell 2023) by the same authors in 2023 to
include 12 hallmarks of aging:
- genomic instability,
- telomere attrition,
- epigenetic alterations,
- loss of proteostasis,
- deregulated nutrient-sensing,
- mitochondrial dysfunction,
- cellular senescence,
- stem cell exhaustion,
- altered intercellular communication,
- disabled macroautophagy, (new)
- chronic inflammation, and (new)
- dysbiosis. (new)
While aging is inevitable, increasing the human lifespan and
slowing the aging process has been a focus of scientific
research for decades. If aging is reversible, then maybe heart
disease, cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer's or other chronic
disorders are reversible as well. A comparison of the Hallmarks
of 'Aging' vs the Hallmarks of 'Cancer' (Cancer Discov 2022) reveals significant overlap between the two hallmarks.

|
| Source: Cell 2023 |
When interpreting scientific studies, let’s remember that
not all studies are created equal. Below is a list of study types ranked in descending order
based on their level of evidence quality:
- Umbrella Review, Meta-analysis and Randomised controlled trials (RCTs)
- Large clinical trials (phase 3)
- Small clinical trials (phase 2) and Case studies
- Mouse results and animal studies
- In Vitro, cell culture, commentary, review, expert opinions and anecdotal evidence
While mainstream media often portrays a lack of scientific
evidence to substantiate the efficacy of diet, lifestyle and
specific supplements, this narrative is not entirely accurate.
There are numerous anti-aging supplements backed by compelling
scientific research.

|
| Credit: ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024 |

|
| Credit: ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024 |
What is Cell Senescence?
Senescence is defined as biological aging and the gradual
deterioration of functional characteristics in a living
organism. There is a loss of the cell’s power to divide and
grow. This may seem like a natural life cycle pattern,
however, the problem is these cells are not alive, nor dead.
They are providing no benefit to your body, in fact, they
are creating destruction of healthy cells leading to
inflammation, the precursor to all dysfunction and disease.
For this reason, these cells are also referred to as “zombie
cells’’.
Below are a few examples of the damage these “zombie cells”
cause to your body:
- Interfere with organ function (heart, brain, liver, kidney, skin…)
- Create age related diseases (cardiovascular, kidney, diabetes…)
- Shorten healthy lifespan (decrease function and create disease)
- Accelerate degeneration (damage causes breakdown)
- Damage organs (colon, blood vessels, nervous system…)
- Triggers inflammation causing problems (high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol, elevated blood sugar….)
You have probably heard that inflammation is a precursor
to all diseases. In a nutshell, all healthy aging and
longevity strategies focus on countering chronic latent
inflammation. Chronic inflammation and an impaired immune
system accelerate cell death, which can be proven by
measuring biomarkers such as telomeres, inflammatory
markers, hormones, neurotransmitters, and many
others.
Senescent cells can be eliminated with a combination of
diet, specialized nutraceuticals, peptides, medications
and exosomes, since eliminating senescent cells is
critical to any effective longevity strategy when the goal
is to improve healthy lifespan, and quality of life.
The medications that are the key players in the clearing
of senescent cells are called SENOLYTICS. Senolytics, also
called geroprotectors, are substances that are used to
halt or reverse cellular aging. Researchers identified a
novel class of (senolytic) drugs that delay several
age-related symptoms in mice. The results demonstrate the
ability of compounds with potential to extend healthy
life. (NATIONAL Health Institute, September 12, 2017)
Studies published as early as 2018 ” reveal that just a
few senescent cells transplanted into young mice result in
persistent physical decline, a characteristic of aging.
There was an obvious acceleration of aging in these mice
just by inoculating them with “old” senescent cells.
When these mice were given senolytic compounds to remove
the senescent cells, there was an obvious alleviation of
physical decline and an extended lifespan, which equated
to living 36% longer. Imagine the opportunity to add 36%
more productive years to your life!
Let’s do the math. Say the average US lifespan is 76
years old; that means we could potentially add another
27 productive years? Now this is what we mean by
elongating your “HEALTHSPAN”!
What is Epigenetics?
Now science has learned genetics are responsible for only
10% of all human disease, while the remaining 90% are
triggered by environmental factors (Exposome and Exposomics, CDC).
Think of it this way: The way our epigenomes are affected by
our external environment represents the interaction between
our environment and the process of adaptation that all living
systems use to adapt and thrive. Still confused, let us
describe it to you in this way: Smokers have lower DNA
methylation than non-smokers (in the AHRR gene, which mediates
toxicity, and epigenetic adaptation). However, this
epigenetically-altered DNA response is often reversed after a
smoker kicks the habit.
The epigenetic marks, or modifications, that we each pick up
in life, do not cause any adaptations to DNA itself. Though
sometimes temporary, epigenetic marks can still be inherited
from cell to cell, as cells divide and reproduce, and that is
then passed down through generations, possibly to the
detriment of our offspring, depending on what those epigenetic
adaptations might be. Here is an example: a famed epigenetic
study conducted in the Netherlands studied children born
during “The Hunger Winter” of 1944-1945, where food was
severely rationed. Parents suffered a vastly decreased caloric
intake, which impacted their children, notably. Children
became significantly more likely to develop cardiovascular
disease, diabetes, and obesity, partly a result of the
epigenetic adaptations made to the fetus’s intrauterine
environment, because of these environmental stressors.
Did you know that six months of aerobic exercise, can
positively alter whole-genome DNA methylation in skeletal
muscle, and adipose (fat) tissue, directly influencing more
effective lipogenesis (fat loss). A body of evidence also
supports the idea that a clean diet can: Reverse abnormal gene
activation or gene silencing, using bioactive dietary
compounds (e.g., garlic, soy products, herbs, and cruciferous
vegetables), with clear indicators that many nutritional
compounds have epigenetic targets in cancer cells. Ultimately,
epigenetics represents one of the most fascinating and
exciting areas of modern medical research.
Diet and Lifestyle for Anti Aging
Nutrition, exercise, proper sleep and stress reduction
are also very important methods to extend
lifespan.
- First, maintaining a healthy weight throughout life is pivotal for healthy aging and longevity, mirroring the benefits of lifelong, moderate calorie restriction in today's obesogenic food environment.
- Second, the specific types or food sources of dietary fat, protein, and carbohydrates are more important in influencing chronic disease risk and mortality than their quantity.
- Third, some traditional diets (e.g., the Mediterranean, Nordic, and Okinawa) and contemporary dietary patterns, such as healthy plant-based diet index, the DASH (dietary approaches to stop hypertension) diet, and alternate healthy eating index, have been associated with lower mortality and healthy longevity. These patterns share many common components (e.g., a predominance of nutrient-rich plant foods; limited red and processed meats; culinary herbs and spices prevalent in global cuisines) while embracing distinct elements from different cultures.
- Fourth, combining a healthy diet with other lifestyle factors could extend disease-free life expectancies by 8-10 years.
Another research presented in July 2023 at the American Society for Nutrition’s annual
conference in Boston (SciTechDaily). Researchers examined the data of nearly 720,000 military
veterans ages 40–99, who were followed over time. Those who
adopted eight healthy habits saw a 13% reduction in mortality
compared to those who did not. The eight habits are: being
physically active, being free from opioid addiction, not
smoking, managing stress, having a good diet, not regularly
binge drinking, having good sleep hygiene, and having positive
social relationships.
Studies showed the critical role of diet in cardiovascular
health. An analysis by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation
attributed 30 percent of cardiovascular disease deaths in 2021
to poor diet. This finding aligns with broader research
suggesting that more than two-thirds of heart disease-related
deaths worldwide are linked to food choices, according to the European Society of Cardiology.
1. Avoiding Sugar and Ultra-processed Foods
At this point, there is simply no question that processed foods
that are high in sugar and low in fiber are unhealthy.
Evidence from a 2023 umbrella review (BMJ 2023) of more than 8,000 studies supports the limiting dietary
sugar recommendation.
A 2024 umbrella review* (BMJ) of the literature confirmed what multiple
studies have shown — the higher your intake of
ultraprocessed food, the higher your risk of adverse health
outcomes. The analysis, which included 14 meta-analysis
studies, 45 unique pooled analyses and 9,888,373
participants, found direct associations between 32 health
parameters and exposure to ultra processed food, including metabolic dysfunction, cancer, mental,
respiratory, cardiovascular and gastrointestinal issues, as
well as all-cause mortality.
*Umbrella review: An umbrella review, or a review of
reviews, is a systematic review that only considers other
systematic reviews as an eligible study type for
inclusion. An umbrella review compiles evidence from
multiple existing reviews and is one of the strongest and
highest levels of evidence.
The study, which analyzed data from nearly 127,000 individuals aged 40 to 69 in the UK Biobank with a median follow-up of nine years, found that each 10 percent increase in the proportion of total energy intake from ultra-processed plant-based foods was associated with a 5 percent increase in the risk of CVD and a 6 percent increase in the risk of coronary heart disease. Moreover, the risk of mortality from CVD increased by 12 percent.
2. Best Anti Aging Diet: Mediterranean Diet and Vegetables
A heart-healthy diet such as a Mediterranean based
diet or the DASH diet is recommended in order to
reduce risk and decrease inflammation in the body.
A high adherence to well-known anti-inflammatory dietary patterns (e.g., Mediterranean Diet and DASH) was associated with delayed biological aging (Clinical Nutrition 2022) and dietary polyphenols consumption was also associated with delayed biological aging (Nutrients 2021).
The Mediterranean diet (MedDiet) is one of the most
consistent dietary patterns analyzed in relation to
the prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and
other health outcomes, including reduction of
overall mortality and increased likelihood of
healthy aging (Silvia Canudas 2020). In a this review of 8 original studies, the meta-analysis
demonstrates that higher MedDiet adherence is
associated with longer Telomere Length (TL).
A 2022 umbrella review* of 41 systematic reviews and meta-analyses of 303
observational studies
revealed that CV (cruciferous vegetable intake might
be associated with beneficial effects on several
health-related outcomes (gastric cancer, lung cancer,
endometrial cancer, and all-cause mortality).
Another 2018 study, eating just one serving of green leafy vegetables
a day may help to slow cognitive decline associated
with aging, helping you to be 11 years younger, cognitively speaking, than your non-leafy
green-eating peers. They’re a rich source of
brain-protective nutrients like folate, vitamins E and
K, lutein and beta-carotene (source). Cruciferous vegetables, like broccoli and cauliflower, are equally impressive, in part because they’re
good sources of choline, a B vitamin known for its
role in brain development.
Caution: What are the nutrients of concern for vegetarians and vegans? Vitamin B12 and K2. Anybody who is eating a vegan diet or a vegetarian diet or just a mostly plant-based diet should be taking vitamin B12 and K2 supplements. Vitamin B12 is only found in significant amounts in animal products and fortified foods, and a deficiency can cause anemia, mood changes, or permanent neurological damage. Plant-based diets may also be low in vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and minerals like iodine, selenium, iron, and zinc.@lewis Biochemist Jessie Inchauspé aka @glucosegoddess_ shares incredible hacks in this episode to minimize glucose spikes without cutting sugar out of your diet - have you listened yet? #sugar #sciencetok #aging #reverseaging #glucose #glucosegoddess #jessieinchauspe #jessieinchauspé #biochemistry #nutrition #nutritiontips #healing #healingjourney #wellness #wellnesstips #healthandwellness #healthandwellnesstips #food #glycation #ageinreverse #nutritionhacks #biohack #biohackingsecrets ♬ Adventurer - Lux-Inspira
3. Avoiding Smoking and Alcohol
Avoid Smoking
Smoking and secondhand smoke introduce harmful toxins to the body. There’s no such thing as a healthy smoker - especially when it comes to cancer prevention.
“The biggest myth I hear is that if someone exercises they can offset the negative effects from smoking, but that’s absolutely not the case,” says Susan Lakoski, M.D.
Smoking has been linked to many types of cancer, including
cancer of the lung, mouth, throat, voice box, pancreas,
bladder, cervix and kidney. Even being around secondhand
smoke might increase the risk of lung cancer.
But it's not only smoking that's harmful. Chewing tobacco has been linked to cancer of the mouth, throat and pancreas.
Staying away from tobacco — or deciding to stop using it — is an important way to help prevent cancer. For help quitting tobacco, ask a health care provider about stop-smoking products and other ways of quitting.
But it's not only smoking that's harmful. Chewing tobacco has been linked to cancer of the mouth, throat and pancreas.
Staying away from tobacco — or deciding to stop using it — is an important way to help prevent cancer. For help quitting tobacco, ask a health care provider about stop-smoking products and other ways of quitting.
Avoid Alcohol
According to a study from the UK Biobank that examined brain scans of 36,678 middle-aged and older adults (Nature 2022), even just one to two alcoholic drinks per day is associated with negative changes in brain structure, including reductions in overall brain volume, gray matter and white matter integrity.
Drink alcohol only in moderation, if at all. Alcohol
increases the risk of various types of cancer, including
cancer of the breast, colon, lung, kidney and liver.
Drinking more increases the risk.
4. Avoiding Linoleic Acid and Vegetable Oil
Advice to substitute polyunsaturated fats for
saturated fats is a key component of worldwide dietary
guidelines for coronary heart disease risk reduction.
However, clinical benefits of the most abundant
polyunsaturated fatty acid, omega 6 linoleic acid,
have not been established.
In this cohort (BMJ 2013), substituting dietary linoleic acid in place of
saturated fats increased the rates of death from all
causes, coronary heart disease, and cardiovascular
disease. An updated meta-analysis of linoleic acid
intervention trials showed no evidence of
cardiovascular benefit. These findings could have
important implications for worldwide dietary advice to
substitute omega 6 linoleic acid, or polyunsaturated
fats in general, for saturated fats.
Another study (Women's Health Initiative Study), a dietary intervention that reduced total fat
intake and increased intakes of vegetables, fruits,
and grains did not significantly reduce the risk of
CHD, stroke, or CVD in postmenopausal women.
The Minnesota Coronary Experiment (MCE), a randomized
controlled trial conducted in 1968-73, was the largest
(n=9570) and perhaps the most rigorously executed
dietary trial of cholesterol lowering by replacement
of saturated fat with vegetable oil rich in linoleic
acid. A re-evaluation of the trial data (published
in BMJ 2016), add to growing evidence that incomplete
publication has contributed to overestimation of the
benefits of replacing saturated fat with vegetable
oils rich in linoleic acid. Available evidence from
randomized controlled trials shows that replacement of
saturated fat in the diet with linoleic acid
effectively lowers serum cholesterol but does not
support the hypothesis that this translates to a lower
risk of death from coronary heart disease or all
causes.
Over the last century, thanks to fatally flawed research suggesting saturated animal fat caused heart disease, the LA in the human diet has dramatically increased, from about 2 to 3 grams a day 150 years ago, to 30 or 40 grams a day.
On a side note, do not confuse LA with conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). While most think CLA and LA are interchangeable, they're not. CLA has many potent health benefits and will not cause the problems that LA does.
Like other nutrition experts, study author Nilson agreed that a healthy, balanced diet should be based on fresh and minimally processed foods, when possible, in addition to avoiding ultra-processed foods.
“The continuity of the current trends with gradual increases in ultra-processed food consumption will increase premature deaths,” Nilson said, adding that his research highlights a need for a shift in policy around ultra-processed foods.
While most have heard about the health risks of
eating processed sugars, net carbs and trans fats,
seed oils far surpass all of these in the damage
they cause to your health. If you were to make one change today to lower
your risk of chronic diseases, eliminating all
seed oils from your diet would be the highest
priority.
Over the last century, thanks to fatally flawed research suggesting saturated animal fat caused heart disease, the LA in the human diet has dramatically increased, from about 2 to 3 grams a day 150 years ago, to 30 or 40 grams a day.
On a side note, do not confuse LA with conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). While most think CLA and LA are interchangeable, they're not. CLA has many potent health benefits and will not cause the problems that LA does.
Another study builds on existing evidence
linking ultra-processed food consumption to
chronic disease and premature death. The study
published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine (Nov 2022) found that increased
consumption of ultra-processed foods (UPF) was
associated with a significant increase in
all-cause premature, preventable deaths in
Brazil in 2019.
Like other nutrition experts, study author Nilson agreed that a healthy, balanced diet should be based on fresh and minimally processed foods, when possible, in addition to avoiding ultra-processed foods.
“The continuity of the current trends with gradual increases in ultra-processed food consumption will increase premature deaths,” Nilson said, adding that his research highlights a need for a shift in policy around ultra-processed foods.
5. Enough Sleep
This is one of the most under-rated anti-aging strategies. Research has demonstrated sleep is a crucial component of a healthy lifestyle.
In a 2023 study (The Lancet), scientists looked at how the
relationship between sleep and exercise might impact
cognitive decline. Researchers from University College
London examined the association between physical
activity and sleep duration in 8,958 participants over
10 years. The data were collected from the English
Longitudinal Study of Aging, during which participants
were interviewed every two years.
The researchers evaluated episodic memory using recall
tasks and verbal fluency using animal naming tasks. They
found that participants with lower levels of physical
activity and suboptimal sleep had worse performance on
the cognitive tests and those who slept the least
exhibited faster cognitive decline. Interestingly, the
participants who had higher levels of physical activity
and shorter sleep times also had faster rates of
cognitive decline.
Those who had higher levels of physical activity and
slept an optimal number of hours had the slowest
cognitive decline. Overall, the data suggested that
higher-intensity physical activity was not enough to
mitigate the rapid cognitive decline that is associated
with insufficient sleep.
Lack of quality sleep can also weaken immune function
and increase susceptibility to respiratory infections,
including the common cold, and chronic lack of sleep may
be associated with an increased risk of death (Prather
2015; Ibarra-Coronado 2015; Wilder-Smith 2013; Aldabal
2011).
Sleep deprivation is associated with elevated cortisol
levels, as well as higher daytime levels of inflammatory
cytokines including IL-1, IL-6, and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha (Aldabal 2011; Hirotsu 2015). A study in
individuals aged 61‒86 found even a single night of
partial sleep deprivation induced patterns of gene
activation associated with biological aging (Carroll
2016).
6. Exercise, Resistance Training and Walking
In combination with a healthy diet, exercise is one of the most cost
effective, long term, and preventative measures you can take.
Physical exercise has been well validated as an effective antiaging
intervention. Regular physical activity of the elderly plays a vital role
at a multi-system level, avoiding muscle atrophy, mending or sustaining
cardiorespiratory health and cognitive performance, and enhancing
metabolic activity. Recommendations predicated on the most recent American
College of Sports Medicine Guidelines advise that physical exercises for
elderly need to involve aerobic exercise, muscle strengthening, and
endurance training, as well as flexibility and neuromotor exercises.
(ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024)
Physical exercise is also the most studied antiaging strategy as shown
below.

|
| Connecting the dots between Antiaging nutrients and drugs and (A) hallmarks of aging, and (B) antiaging strategies. Credit: ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024 |

|
|
Source:
Ancestral Diet Could Prevent Most
Diseases Including Blindness |

|
| Credit: ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024 |
A 2024 meta-analysis
from the European Society of Cardiology found that people who chose to take
the stairs saw a 39 percent lower likelihood of death from heart disease,
compared to those who always take the elevator or escalator.
In another study (Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2018), VO2 max is related to functional capacity and human performance
and has been shown to be a strong and independent predictor of all-cause and
disease-specific mortality.
Researchers have also analyzed 13 studies of sitting time and activity
levels. They found that those who sat for more than eight hours a day with
no physical activity had a risk of dying similar to that posed by obesity
and smoking. However, unlike some other studies, this analysis of data
from more than 1 million people found that 60 to 75 minutes of moderately
intense physical activity a day countered the effects of too much sitting.
Other studies have found that for people who are most active, sitting time
contributes little to their risk of death (Mayo Clinic).
It has also been evidenced recently that one of the best strategies for
healthy brain aging is regular aerobic exercise. It is suggested that
exercise likely remains the most effective intervention for healthy brain
aging because it stimulates strategic energy-sensing pathways that modulate
multiple hallmarks of aging. (Exerc Sport Sci Rev 2021)
According to Dr Murtaza Ahmed:
Another important factors in slowing sarcopenia is diet. As we age our appetite declines, so as we eat less we naturally reduce the amount of protein that we consume. To slow sarcopenia we need to keep our protein intake high, and as we are eating less this means that a higher proportion of the food we eat needs to be protein. It is also important to spread this protein out through the day over three or meals as this produces more muscle protein synthesis when compared to one or two high protein meals.
It is also important to get your vitamin D levels checked as you age since deficiency is common due to reduced sun exposure. As well as weakening our bones, low vitamin D results in weaker muscles and accelerated sarcopenia. A low vitamin D level can be easily rectified with supplementation. When was the last time you had your vitamin D level checked?
Being aware that sarcopaenia affects us all is the first step in combating its effects. The earlier you commence resistance exercise, the greater the benefits, but it is never too late to start. If you are new to resistance exercise or intimidated by the gym environment, talk to your local gym about some personal training to help you learn.
That said, if you're eating very small amounts of food, you are becoming very frail
and skinny. Exercise without proper nutrition is counter-productive. In
the actual world, we're starting to see right now that frailty is a huge
risk factor for early death and mortality. And malnutrition itself also
increases the risk of a lot of different diseases, all-cause mortality and
neuro-degeneration and heart disease events.
A 2023 review published in GeroScience highlights the crucial role of regular physical activity, particularly walking, in promoting healthy aging and longevity.14 The researchers emphasize that walking is not just a basic exercise but a potent antiaging intervention. It has been shown to lower the risk of age-related chronic diseases such as heart disease, high blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes and cancer. Moreover, walking can alleviate pain and enhance function in musculoskeletal conditions.
7. Stress Management
A big component of the longevity equation is the management of stress.
8. Social Support
Okinawa in Japan, Sardinia in Italy, Roseto in Pennsylvania, Loma Linda in California, Icaria in Greece and Nicoya in Costa Rica are some of the places with the highest proportions of people who live to be 100 years old.
All these places have the same thing in common. What is it?
In the 1950s, Roseto, Pennsylvania, shocked the medical community. From 1954
to 1961, Roseto had nearly no heart attacks for men ages 55 to 64. And for men
over 65, the death rate was half of that of the U.S. average.
Dr. Robert J. Waldinger, a Clinical Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical
School, conducted the longest scientific study on health and happiness in
history, the Harvard Study of Adult Development.
According to Prof. Waldinger:
We had more than 40 years of data. We began to find that when we looked at
our 80 year olds, and we looked back at what we knew about them when they
were 50, that the strongest predictor of who was going to be happy and
healthy at age 80, was the quality of their relationships at age 50.
9. Intermittent fasting, time restricted eating (TRE) and Calorie Restriction
Intermittent fasting is currently one of the most popular nutrition programs
around. Unlike diets that tell you what to eat, intermittent fasting focuses
on when to eat.
Limiting the hours you eat each day may help you consume fewer calories. It may also provide health benefits, including weight loss and improved heart health and blood sugar levels.
There are several forms of intermittent fasting, including a common form called time-restricted eating.
Research overwhelmingly supports the notion that ditching the three square
meals a day approach in favor of time-restricted feeding — can do wonders
for your health. Contrary to modern belief, your body isn't designed to be
fed throughout the day, and the near-continuous grazing that most engage in
can have serious health consequences.
Limiting the hours you eat each day may help you consume fewer calories. It may also provide health benefits, including weight loss and improved heart health and blood sugar levels.
There are several forms of intermittent fasting, including a common form called time-restricted eating.
Time-restricted eating is just what it sounds like. It's a form of
intermittent fasting where you eat all of your meals for the day within a
restricted window of time, ranging from two to eight hours. That means
you're avoiding food (fasting) for 16 to 22 consecutive hours. Eating within
a four- to six-hour window is likely close to metabolic ideal for most. As
noted in the paper "A Time to Fast," published in the November 2018 issue of Science:
"Adjustment of meal size and frequency have emerged as powerful tools to ameliorate and postpone the onset of disease and delay aging, whereas periods of fasting, with or without energy intake, can have profound health benefits.
The underlying physiological processes involve periodic shifts of metabolic fuel sources, promotion of repair mechanisms, and the optimization of energy utilization for cellular and organismal health …
In general, both prolonged reduction in daily caloric intake and periodic fasting cycles have the power to delay the onset of disease and increase longevity."
"Adjustment of meal size and frequency have emerged as powerful tools to ameliorate and postpone the onset of disease and delay aging, whereas periods of fasting, with or without energy intake, can have profound health benefits.
The underlying physiological processes involve periodic shifts of metabolic fuel sources, promotion of repair mechanisms, and the optimization of energy utilization for cellular and organismal health …
In general, both prolonged reduction in daily caloric intake and periodic fasting cycles have the power to delay the onset of disease and increase longevity."
Fasting, or reducing your calorie intake is also an excellent method for
indirectly boosting the body’s NAD levels. Fasting has been shown to
increase the levels of NAD+ and surtuins; the proteins which have been found
to slow the aging process.
While fasting is effective in increasing NAD+ levels, drastic reduction in
calorie intake or fasting can have a counterproductive effect. There is also
some speculation that intermittent fasting or adopting a low carb-ketogenic
diet may also provide similar positive results.
Research also suggests that caloric restriction and fasting might be helpful
to give your existing so-called endogenous stem cells a boost.
Fasting may also help reduce obesity-associated cancers. “There’s a lot of
obesity-associated cancers,” said Dr. Jason Fung, a nephrologist and
fasting expert. “There’s about 13 cancers that are well accepted that they are associated with obesity; fasting
might help decrease that.”
Fasting can potentially starve cancer cells. When fasting, the body uses fats and produces ketones for energy. Cancer cells rely heavily on glucose, making them less efficient at using ketones.
Additionally, fasting reduces insulin levels. Elevated insulin levels are linked to an increased risk of breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers.
Caloric Restriction
The goal of caloric restriction is to reduce total caloric intake while
maintaining optimal nutrition. This may be best accomplished by eating a diet
primarily composed of low-calorie, nutrient-dense foods such as vegetables,
fruits, legumes, nuts and seeds, and whole grains; limiting intake of animal
products; and avoiding calorie-dense, nutrient-poor foods (Rizza 2014).
Caloric restriction in animals has been shown to prolong lifespan and delay
aging, and to confer a more youthful profile of T cells (Ahmed 2009; Fernandes
1997; Michan 2014).
Caution:
Historically, many mistakes have been made in longevity research,
particularly the focus on extreme calorie, carbohydrate and protein restriction. If you're eating very small amounts of food, you are becoming very frail
and skinny. In the actual world, we're starting to see right now that
frailty is a huge risk factor for early death and mortality. And
malnutrition itself also increases the risk of a lot of different
diseases, all-cause mortality and neuro-degeneration and heart disease
events.
10. Low-Fat High-Carbohydrate Heart Healthy Diet vs High-Fat Low-Carbohydrate Diet
In a 2021 study published in
OpenHeart:
The Women’s Health Initiative Randomized Controlled Dietary Modification
Trial (WHIRCDMT) was designed to test whether the US Department of
Agriculture’s 1977 Dietary Guidelines for Americans protects against
coronary heart disease (CHD) and other chronic diseases. The only
significant finding in the original 2006 WHIRCDMT publication was that
postmenopausal women with CHD randomised to a low-fat ‘heart-healthy’
diet in 1993 were at 26% greater risk of developing additional CHD
events
compared with women with CHD eating the control diet.
A 2017 WHIRCDMT publication includes data for an additional 5 years of
follow-up. It finds that
CHD risk in this subgroup of postmenopausal women had increased further
to 47%–61%. The authors present three post-hoc rationalisations to explain why this
finding is ‘inadmissible’: (1) only women in this subgroup were less likely
to adhere to the prescribed dietary intervention; (2) their failure to
follow the intervention diet increased their CHD risk; and (3) only these
women were more likely to not have received cholesterol-lowering
drugs.
These rationalisations appear spurious. Rather these findings are better
explained as a direct consequence of postmenopausal women with features of
insulin resistance (IR) eating a low-fat high-carbohydrate diet for 13
years. All the worst clinical features of IR, including
type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in some, can be ‘reversed’ by the
prescription of a high-fat low-carbohydrate diet.
The Women’s Health Study has recently reported that T2DM (10.71-fold
increased risk) and other markers of IR (insulin resistance) including
metabolic syndrome (6.09-fold increased risk) were the most powerful
predictors of future CHD development in women; blood low-density
lipoprotein-cholesterol concentration was a poor predictor (1.38-fold
increased risk).
These studies challenge the prescription of the low-fat high-carbohydrate
heart-healthy diet, at least in postmenopausal women with IR, especially T2DM. According to
the medical principle of ‘first do no harm’, this practice is now shown to
be not evidence-based, making it scientifically unjustifiable, perhaps
unethical.
Best Anti-Aging Supplements
There are a lot of options out there, and we know it can be overwhelming.
Not all the supplements below are required. You are advised to consult
with your trusted medical provider before taking these supplements. Here
are the best supplements with anti-aging properties.
1. Vitamin D3 and K2
Can Vitamin D extend lifespan? Higher levels of vitamin D are
associated with less risk of heart disease, auto-immune
diseases, improved brain health and a better functioning immune
system.
Optimizing your vitamin D level is one strategy that can boost
your health in myriad ways. A deficiency in vitamin D has been
implicated in such problems as multiple sclerosis (R) and Parkinson’s disease (R), for instance. The link between Parkinson’s and vitamin D
is so strong that one study found people with high vitamin D
levels had a 65% lower risk of Parkinson’s compared to those
with low vitamin D levels (R).
A 2024 paper published in Nutrients by Italian scientists summarized the current knowledge of how vitamin D might modulate
some of the hallmarks of aging.
Another
2024 study in older adults, low vitamin D and inflammation (high hs-CRP*), both
independently and jointly, increase mortality risk in Chinese
community-dwelling older adults. Thus, priority should be
given to early detection and appropriate intervention in older
individuals with combined vitamin D deficiency and systemic
inflammation.
*hs-CRP: High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) is
widely used to reflect the degree of systemic inflammation
(source).
In a 2023 study, 80 RCTs (randomised controlled trials) were analyzed. The meta-analysis concluded that vitamin D supplementation appears to decrease the risk of ACM (all cause mortality i.e. death from all causes) (especially convincing in the fair- and good-quality RCTs), while not showing a decrease in the specific cardiovascular morbidity and death risk.
In a 2023 study, 80 RCTs (randomised controlled trials) were analyzed. The meta-analysis concluded that vitamin D supplementation appears to decrease the risk of ACM (all cause mortality i.e. death from all causes) (especially convincing in the fair- and good-quality RCTs), while not showing a decrease in the specific cardiovascular morbidity and death risk.
Another
2023 study, 116 randomised controlled trials were analysed. The
meta-analysis concluded that vitamin D reduces lung cancer
mortality. All-cause mortality is decreased in patients with
COVID-19 and liver diseases, especially in liver
cirrhosis.
The DO-HEALTH trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01745263), were published in Frontiers in Aging 2022. The first randomized-controlled trial (DO-HEALTH) trial to
investigate the combination of three complementary treatments
for the prevention of cancer and suggest that the combination
of daily vitamin D3, supplemental marine omega-3s, and a
simple home exercise program may be effective in the prevention of invasive cancer
among generally healthy and active adults aged 70 and older.
Findings from this 3 year Randomized Controlled Trial with
more than 2,000 participants observed a 61% reduction in the
risk of invasive cancer among patients who completed a home
exercise program and took vitamin D3 and omega-3 fatty acids daily.
Previous research found that a vitamin D level of 47 ng/ml was associated with a 50% lower risk of breast cancer (R). Further, researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine reported that raising your vitamin D level to at least 40 ng/ml can slash your risk of all invasive cancers by 67% (R).
Many governments advise 400 to 800 IU of vitamin D per day, while many vitamin D researchers claim you need at least 2000 to 4000 units per day.
We would recommend to take at least 2000 units per day. The risk of excess accumulation of vitamin D is negligible with this amount. Make sure it’s vitamin D3, and not vitamin D2 – the vitamin D3 variant works better.
Vitamin D ensures that your blood levels of calcium are high enough
to meet your body’s demands. However, vitamin D does not fully
control where the calcium in your body ends up. That’s where vitamin
K steps in. Vitamin K2 supplements have been proven to be more
effective than vitamin K1. That's why most of the top vitamin D
supplement brands do combine their vitamin D3 with K2.
Make sure to take 500 mg to 1000 mg of magnesium and 150 mcg of
vitamin K2, (not K1) which are important cofactors for optimizing
vitamin D function. And, remember the only way you know what your
vitamin D level is, is to test it. Most people are shocked how low
their level is when they finally get around to testing it.
Vitamin K2
In a 2022 study, researchers even revealed vitamin K2 modulates mitochondrial
dysfunction caused by neurotoxins. Vitamin K2 also inhibited the
accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and promoted mitophagy,
which is the removal of damaged mitochondria via autophagy — an
essential function to maintain cellular health. Writing in the journal
Nutrients, the scientists explained:
“… [V]itamin K2 can reduces mitochondrial damage, and … this effect
is related to the participation of vitamin K2 in the regulation of
the mitochondrial quality-control loop, through the maintenance of
the mitochondrial quality-control system, and repair mitochondrial
dysfunction, thereby alleviating neuronal cell death mediated by
mitochondrial damage.”
2. B Vitamins and NAD Boosting Supplements
B vitamins are necessary for proper brain function, research
suggests. People with low levels of vitamins B6 and B12 can
develop anemia as well. Older adults are often low in vitamin B12, and
as we age, it’s harder for us to absorb it and even use it because
it’s not as bioavailable.
B vitamins include:
B vitamins include:
- B1 (thiamine)
- B2 (riboflavin)
- B3 (niacin)
- B5 (pantothenic acid)
- B6
- B7 (biotin)
- B12
- Folic acid
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a vital molecule for most,
if not all, forms of life. The last decade has seen a strong
proliferation of therapeutic strategies for the treatment of metabolic
and age-related diseases based on increasing cellular NAD+
bioavailability. Among them, the dietary supplementation with NAD+
precursors—classically known as vitamin B3—has received most of the
attention. Multiple molecules can act as NAD+ precursors through
independent biosynthetic routes.
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a precursor to NAD+. NAD+ is a
very important substance in the cells. It provides energy for cells
and is also a cofactor for proteins that repair and maintain our
epigenome and our DNA.
The epigenome is the intricate machinery that surrounds the DNA and that determines which genes are active and not. During aging, the epigenome becomes more and more dysregulated.
The older we get, the less NAD+ is present in our cells. Taking in NMN can increase NAD+ levels.
Various animal and lab studies show that NMN has beneficial effects on aging diseases and symptoms (R,R,R,R).
For example, long term administration of NMN mitigated age-associated decline in mice: NMN reduced the typical age-associated increase in body weight, improved energy metabolism, improved lipids in the blood and insulin sensitivity and ameliorated eye function (R).
NMN can also improve aging-related decline in fertility (R), improve bone health (R) and vascular health (R,R,R).
The epigenome is the intricate machinery that surrounds the DNA and that determines which genes are active and not. During aging, the epigenome becomes more and more dysregulated.
The older we get, the less NAD+ is present in our cells. Taking in NMN can increase NAD+ levels.
Various animal and lab studies show that NMN has beneficial effects on aging diseases and symptoms (R,R,R,R).
For example, long term administration of NMN mitigated age-associated decline in mice: NMN reduced the typical age-associated increase in body weight, improved energy metabolism, improved lipids in the blood and insulin sensitivity and ameliorated eye function (R).
NMN can also improve aging-related decline in fertility (R), improve bone health (R) and vascular health (R,R,R).
NMN can also improve and protect stem cells such as mesenchymal stem
cells that form bone and fat tissue (R,R).
NMN (Nicotinamide MonoNucleotide) is a molecule found in various
foods such as broccoli, cabbage, avocado, mushrooms, meat, and
shrimp. However, obtaining sufficient amounts through diet alone
can be challenging.
Studies suggest that daily dosages of NMN range from 50mg to
250mg, and a 150-pound (68kg) person would require approximately
560mg per day. Unfortunately, obtaining these amounts solely
through diet would be impractical. For example, you would need to
consume about 100 pounds of edamame, 1,800 pounds of broccoli, or
unrealistic amounts of cucumber, cabbage, avocado, tomato,
mushrooms, raw beef, or shrimp to achieve the required intake.
Therefore, taking NMN supplements may be a more practical approach
to ensure adequate daily intake.
Related: Best NMN Supplements
NMN with TMG
*Trimethylglycine (TMG) is a form of the amino acid glycine
with three methyl groups that are attached to it. TMG is also
commonly known as betaine or betaine anhydrous. TMG functions as
a methyl donor. TMG methylates homocysteine, an amino acid that
can build up in the blood and raise the risk of heart disease,
and converts it into methionine.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is needed to form red blood cells and DNA. It is also a key player in the function and development of brain and nerve cells. However, we believe the most important function it provides is methylation. If you don’t know what methylation is, allow us to briefly explain. Methylation is a biochemical process which is involved in a wide range of bodily functions, and is essential to our overall well-being. When methylation is out of balance, many different health problems may arise.
3. Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation, enable the immune system to
carry out its tasks, and help the brain and eyes to function
properly.
According to a review (Nutrients, September 2022), data from scientific literature 'overwhelmingly' supports
beneficial effects of omega-3 fatty acids on the length of
telomeres, reported to be a marker of biological age.
The Framingham study group is one of the longest-running
longitudinal health data sets in existence. Since 1971, the
residents of this small Massachusetts town have given us everything
from heart health data to their knee annual MRI images. That’s where
the data for this new Omega-3 research originates.
The study, published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (Oct 2021), used data from a long-term study group, the Framingham Offspring Cohort, which has been monitoring residents of this Massachusetts town, in the United States, since 1971. The research looked at 2,200 people who were monitored for 11 years for their blood fatty acid levels. The researchers found that omega-3 levels in red blood cells are very good mortality risk predictors. That means that higher levels of Omega-3 in the blood from regularly eating oily fish, increased life expectancy by almost five years.
This research comes a few months after a meta-analysis of 17 prospective cohort studies was published in Nature Communications (2021). The analysis linked higher circulating omega-3 fatty acid levels to longevity. In a pooled analysis of the studies, participants in the highest fifth of combined blood DHA and EPA were 15 to 18 percent less likely to die from any cause over the follow-up period (median follow-up time is 16 years in these studies). Higher blood omega-3s were also associated with a reduced risk for death from cardiovascular disease and cancer.
The study, published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (Oct 2021), used data from a long-term study group, the Framingham Offspring Cohort, which has been monitoring residents of this Massachusetts town, in the United States, since 1971. The research looked at 2,200 people who were monitored for 11 years for their blood fatty acid levels. The researchers found that omega-3 levels in red blood cells are very good mortality risk predictors. That means that higher levels of Omega-3 in the blood from regularly eating oily fish, increased life expectancy by almost five years.
This research comes a few months after a meta-analysis of 17 prospective cohort studies was published in Nature Communications (2021). The analysis linked higher circulating omega-3 fatty acid levels to longevity. In a pooled analysis of the studies, participants in the highest fifth of combined blood DHA and EPA were 15 to 18 percent less likely to die from any cause over the follow-up period (median follow-up time is 16 years in these studies). Higher blood omega-3s were also associated with a reduced risk for death from cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Published in 2022, the Cognitive impAiRmEnt Study (CARES Trial 2), was designed to examine the potential
synergistic effects of a combination of omega-3 fatty acids
(namely DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid [EPA]), xanthophyll
carotenoids (specifically lutein, zeaxanthin and meso-zeaxanthin)
and vitamin E (d-α-tocopherol) on the cognitive performance of
cognitively healthy older adults. In conclusion, the CARES
research has shown improvements in working memory following
24-month supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids, xanthophyll
carotenoids (lutein and zeaxanthin) and vitamin E in
cognitively healthy older adults. This study provides Class II
evidence that 24-month supplementation with 430 mg DHA, 90 mg EPA,
10 mg lutein, 2 mg zeaxanthin, 10 mg meso-zeaxanthin and 15 mg
vitamin E (d-α-tocopherol) is effective in improving cognitive
performance, namely working memory, in cognitively healthy older
adults.
These results support a biologically plausible rationale whereby
these nutrients work synergistically, and in a dose-dependent
manner, to improve cognitive performance. These findings
illustrate the importance of nutritional enrichment in improving
cognition and enabling older adults to continue to function
independently, and highlight how a combination of omega-3 fatty
acids and xanthophyll carotenoids may prove beneficial in reducing
cognitive decline and/or delaying Alzheimer's disease onset in
later life. (Power 2022).
Many governments recommend eating omega-3 containing fatty fish, two times per week. But that is often not enough. Ideally, people would need to eat fatty fish four times per week, while also supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids, at least 1,000 mg of pure omega-3 (DHA and EPA) per day.
Make sure you buy high-quality omega-3 fatty acid supplements, meaning that the omega-3 fatty acids are pure and have not oxidized much (having low “TOTOX” value). TOTOX value stands for total oxidation value. The omega 3 fatty acids EPA and DHA from fish oil are highly sensitive to oxidation. This means that they are rapidly affected by contact with oxygen. Oxidised fatty acids are not beneficial to our health. For this reason, a good fish oil supplement has a low TOTOX value. The maximum TOTOX value is set at 26 by the Global Organization for EPA and DHA omega-3.
4. Magnesium and Molecular Hydrogen
Magnesium
Magnesium is a very important mineral in the human body.
Magnesium functions as a cofactor to hundreds of different enzymes, which need magnesium to function properly.
Magnesium functions as a cofactor to hundreds of different enzymes, which need magnesium to function properly.
In a 2024 study published in Nutrients, researchers dove deep into the effects of magnesium on the 12 Hallmarks of Aging. This is an important undertaking, as they noted that magnesium deficiency becomes more common as you age. According to the authors:
There are many ways in which magnesium deficiency can lead to accelerated aging. Magnesium is needed to build, maintain and repair DNA.
Magnesium reduces DNA damage and stabilizes the genome (R,R). For example, magnesium sticks to the DNA strand and stabilizes it, and it is also an essential cofactor for DNA repair proteins which need magnesium to function properly (R).
Magnesium can reduce inflammaging (low-grade inflammation that increases during aging). Low levels of magnesium have been linked to chronic low-grade inflammation, which is one of the drivers of aging (R).
Besides magnesium’s many effects on maintaining our cells, the mineral has various immediately noticeable effects. Athletes take magnesium to improve their physical performance, even when they are not magnesium deficient (R).
Magnesium supplements also improve sleep, and feelings of relaxation and wellbeing.
This is not surprising, given the important role of magnesium in the functioning of brain cells, such as excitation and neuronal metabolism.
Malate is often used in combination with magnesium to bring about health benefits, especially for improving energy and reducing fatigue.
Molecular Hydrogen
Molecular hydrogen is the smallest anti-oxidant. This paper (Mar 2022) reviews the basic research and recent application of hydrogen
in order to support hydrogen use in medicine for ageing prevention
and ageing-related disease therapy.
Molecular hydrogen has therapeutic and preventive effects on
various organs. It has antioxidative properties as it directly
neutralizes hydroxyl radicals and reduces peroxynitrite level.
It also activates Nrf2 and HO-1, which regulate many antioxidant
enzymes and proteasomes. Through its antioxidative effect,
hydrogen maintains genomic stability, mitigates cellular
senescence, and takes part in histone modification, telomere
maintenance, and proteostasis. In addition, hydrogen may prevent
inflammation and regulate the nutrient-sensing mTOR system,
autophagy, apoptosis, and mitochondria, which are all factors
related to ageing. Hydrogen can also be used for prevention and
treatment of various ageing-related diseases, such as
neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular disease, pulmonary
disease, diabetes, and cancer.
It was also already discovered that hydrogen can prolong the life of stem cells by reducing oxidative stress (Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010).
According to a review paper published in BioMedicines 2022:
Related: Best Molecular Hydrogen Tablets
5. Glycine, NAC and Taurine
Both Glycine and Taurine levels decline as we age.
Glycine
Glycine is an amino acid that occurs naturally in our body. When we
age, glycine levels decline.
Low glycine levels also have been associated with various aging-related diseases like cardiovascular disease and with type 2 diabetes.
Glycine extends lifespan in different species (R,R,R,R).
Glycine has many functions in the body. It improves the epigenome (the machinery that determines which genes are switched on or off, a process that goes increasingly awry when we get older). Glycine especially improves the epigenome of mitochondria, the power plants of our cells (R).
Glycine also functions as a chaperone. Chaperones are small molecules that gently stick to and protect the proteins. That is important, because one of the reasons why we age is due to proteins accumulating everywhere inside and outside our cells, eventually hampering the proper functioning of our cells.
Glycine also reduces inflammation (R) and has many other beneficial effects, especially for the cardiovascular system. People with higher glycine levels in the blood had less risk of a heart attack (R), and glycine can protect the blood vessels (R).
Low glycine levels also have been associated with various aging-related diseases like cardiovascular disease and with type 2 diabetes.
Glycine extends lifespan in different species (R,R,R,R).
Glycine has many functions in the body. It improves the epigenome (the machinery that determines which genes are switched on or off, a process that goes increasingly awry when we get older). Glycine especially improves the epigenome of mitochondria, the power plants of our cells (R).
Glycine also functions as a chaperone. Chaperones are small molecules that gently stick to and protect the proteins. That is important, because one of the reasons why we age is due to proteins accumulating everywhere inside and outside our cells, eventually hampering the proper functioning of our cells.
Glycine also reduces inflammation (R) and has many other beneficial effects, especially for the cardiovascular system. People with higher glycine levels in the blood had less risk of a heart attack (R), and glycine can protect the blood vessels (R).
In addition to supporting brain function, supplemental glycine may be
useful for the "prevention and control of atherosclerosis, heart failure,
angiogenesis associated with cancer or retinal disorders and a range of
inflammation-driven syndromes, including metabolic syndrome."(McCarty 2019)
People with higher glycine levels in the blood had less risk of a heart
attack (Ding 2016), and glycine can protect the blood vessels (DiNicolantonio 2014).
Note: Glyphosate is the active ingredient in Roundup and other common
weed killer formulations.
By taking a glycine supplement, you can counteract this chain of events by making sure there's enough glycine present to fill up those glycine slots. As noted by Stephanie Seneff, Ph.D., (a senior research scientist at MIT for over five decades), "If there's lots of glycine, you're going to be much less likely to pick up glyphosate."
By taking a glycine supplement, you can counteract this chain of events by making sure there's enough glycine present to fill up those glycine slots. As noted by Stephanie Seneff, Ph.D., (a senior research scientist at MIT for over five decades), "If there's lots of glycine, you're going to be much less likely to pick up glyphosate."
To gain all of glycine's healing potential, doses of 10, 15, or 20 grams
a day may be necessary. Land suggests you need at least 12 grams of
glycine daily for optimal collagen turnover, plus another 3 grams per
day to form glutathione and other compounds (YouTube):
"Your body only makes 3 grams of glycine per day, and if you only consume around 2 to 3 grams of glycine from foods then it means that almost all of us are in a 10-gram glycine deficit every day," he says.
"… I think most people would benefit for at least 5 to 10 grams of glycine a day, which is, uh kind of a moderate amount … if you are eating a lot of muscle meat … or you're just interested in getting more of the benefits of glycine then you can take even up to 20 grams a day."
Doses of 3 to 5 grams have been shown to improve sleep (R). One study estimated that most people are about 10 grams short of what their
bodies need for all metabolic uses on a daily basis, and in a study of people with metabolic syndrome, 15 grams of glycine a day for
three months reduced oxidative stress and improved systolic blood pressure.
NAC
"NAC, the acetylated form of the amino acid cysteine, protects our brain by stimulating the activity of glutathione, which is a potent antioxidant that protects our mitochondria from free radical damage. NAC is also effective against viruses and it is used both for the prevention and treatment of some viral infections, including brain infections."
He added, "Conventional doctors use NAC to counteract the consequences of paracetamol overdose because it protects the liver from damage."
Kyriazis suggests the conventional dose is around 1000 mg to 1500 mg per day and says some doctors recommend taking NAC with vitamin C to prevent it from being destroyed in the body prematurely.
"500mg of NAC every morning is an effective dose for adults looking to use it daily as a longevity supplement," he explained. "It has an excellent safety profile and can be taken with any other supplements, including glutathione."
Glycine and NAC (GlyNAC)
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine also looked into supplementation with a combination of glycine and N-acetylcysteine (NAC), two glutathione precursors known as GlyNAC when taken together.
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine also looked into supplementation with a combination of glycine and N-acetylcysteine (NAC), two glutathione precursors known as GlyNAC when taken together.
A pilot trial in older humans (Kumar 2021) with GlyNAC supplementation for 24 weeks corrected glutathione
deficiency and improved multiple measures of health, including:
- Mitochondrial dysfunction
- Oxidative stress
- Inflammation
- Endothelial dysfunction
- Insulin resistance
- Genomic damage
- Cognition
- Strength
- Gait speed
- Exercise capacity
- Body fat levels
- Waist circumference
How to get GlyNAC supplement >
Buy on Amazon
Taurine
This semi-essential amino acid is our latest addition and update to
our list of 'Best 10 Anti Aging Supplements'. When we age, taurine
levels decline as well.
In a 2024 meta-analysis of 25 RCTs (randomized controlled trials),
researchers from Taiwan (Nature 2024) concluded that taurine supplementation exhibits positive effects on
multiple Metabolic Syndrome related factors, making it a potential
dietary addition for individuals at risk of or already experiencing
Metabolic Syndrome.
This isn’t just another ordinary experiment and a report, but a series
of experiments at various levels of detail showing that taurine
may be the real deal and promote anti-aging.
Animals given supplemental taurine didn’t just live longer, they were
also healthier overall. In mice, taurine improved:
- Strength, coordination and endurance
- Bone mass and bone quality
- Glucose homeostasis and glucose tolerance
- Age-related inflammation
- Immune function
- Gut health
- Memory
- Function of all organs
- Mitochondrial function and health
Interestingly, according to the authors, taurine “cured” osteoporosis.
It’s not often you see the word “cure” being used in medical
literature. Taurine also “suppressed ovariectomy-induced body-weight
gain in a rodent model of menopause,” and reduced anxiety and
depression-like behavior in the mice.
Treated mice also had less body fat (approximately 10% less at 1,000 milligrams of taurine per day) and higher energy levels. According to the authors, “Fat-pad weight divided by body weight percentage was dose-dependently reduced in taurine-treated mice.” Taurine supplementation also improved several markers of aging, including Senescence, Intercellular communication, Telomere length, Epigenetic changes, Genomic stability, Mitochondrial function, Stem cell populations and Nutrient sensing.
The key to remember is that it's best to get taurine and other nutrients from whole foods and, if necessary, via high-quality supplements — not synthetic energy drinks. Energy drinks are not a safe source of taurine.
Taurine is found in animal foods such as seafood, red meat, poultry and dairy products. If you're a vegan, however, you may want to consider a high-quality taurine supplement, as you're not getting any from the foods you eat. While your body can synthesize some taurine, it's not going to be sufficient in the long run, especially as you get older and your body's ability to synthesize it diminishes.
Treated mice also had less body fat (approximately 10% less at 1,000 milligrams of taurine per day) and higher energy levels. According to the authors, “Fat-pad weight divided by body weight percentage was dose-dependently reduced in taurine-treated mice.” Taurine supplementation also improved several markers of aging, including Senescence, Intercellular communication, Telomere length, Epigenetic changes, Genomic stability, Mitochondrial function, Stem cell populations and Nutrient sensing.
The key to remember is that it's best to get taurine and other nutrients from whole foods and, if necessary, via high-quality supplements — not synthetic energy drinks. Energy drinks are not a safe source of taurine.
Taurine is found in animal foods such as seafood, red meat, poultry and dairy products. If you're a vegan, however, you may want to consider a high-quality taurine supplement, as you're not getting any from the foods you eat. While your body can synthesize some taurine, it's not going to be sufficient in the long run, especially as you get older and your body's ability to synthesize it diminishes.
Taurine Dosage: Most of the existing research used 1-3
grams daily, which is the amount most bodybuilders use.
Read More: Taurine May Be Key for Anti Aging and Healthier Lifespan
6. Curcumin (Turmeric)
Curcumin — the main active compound in turmeric — has been shown to
possess powerful anti-aging properties, which are attributed to its potent
antioxidant potential.
One 2020 research review in PharmaNutrition concluded that curcumin does have anti-inflammatory effects in the
body, and a 2019 research review in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences concluded that curcumin appears to both reduce inflammation and
suppress cancer cells.
As published in the European Journal of Pharmacology (Nov 2022), Abe and colleagues focused on testing the effects of
the curcumin prodrug TBP1901. They found that TBP1901 metabolized to its
active form most greatly in bone marrow, leading them to use the drug on a
multiple myeloma mouse model — a model for age-related bone marrow cancer.
The researchers found that TBP1901 had significant anti-tumor effects,
effectively shrinking tumors in mice. However, TBP1901 did not have strong
effects in preventing cancer cell growth in a dish (in vitro). Still,
regular curcumin had anti-tumor effects in vitro.
Cellular senescence occurs when cells stop dividing. As you age, senescent cells accumulate, which is believed to accelerate aging and disease progression (Source, Source).
Research demonstrates that curcumin activates certain proteins, including sirtuins and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which helps delay cellular senescence and promotes longevity (Source, Source).
Plus, curcumin has been shown to combat cellular damage and significantly increase the lifespan of fruit flies, roundworms, and mice. This compound has been shown to postpone age-related disease and alleviate age-related symptoms as well (Source, Source).
This may be why turmeric intake has been associated with a reduced risk of age-related mental decline in humans (Source). You can increase your curcumin intake by using turmeric in recipes or taking curcumin supplements.
Cellular senescence occurs when cells stop dividing. As you age, senescent cells accumulate, which is believed to accelerate aging and disease progression (Source, Source).
Research demonstrates that curcumin activates certain proteins, including sirtuins and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which helps delay cellular senescence and promotes longevity (Source, Source).
Plus, curcumin has been shown to combat cellular damage and significantly increase the lifespan of fruit flies, roundworms, and mice. This compound has been shown to postpone age-related disease and alleviate age-related symptoms as well (Source, Source).
This may be why turmeric intake has been associated with a reduced risk of age-related mental decline in humans (Source). You can increase your curcumin intake by using turmeric in recipes or taking curcumin supplements.
Studies have come forward that in addition to its anti-aging and
anti-inflammatory properties, it may also have anti-cancer properties.
However, the bioavailability — ability to be used in the body — of
curcumin may not be ideal. Thus, to help enhance its known positive
benefits, researchers out of Kyoto University in Japan modified curcumin
into a prodrug – an inactive compound that requires metabolism by the body
before becoming biologically active.
A 2022 review paper, analysed 21 human studies. Sixteen out of 21 clinical trials were
associated with the effectiveness of curcumin or turmeric on various types
of cancer, and the other five clinical trials were related to the evaluation
of the efficacy of curcumin or turmeric in relieving the side effects of
cancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The emerging data from the clinical
trials confirm that curcumin has the potential for cancer prevention and
intervention. Interestingly, curcumin appears to be universally useful for
just about every type of cancer (Arslan 2022), which is really odd since cancer consists of a wide variety of different
molecular pathologies.
7. Vitamin C and Calcium Alpha-KetoGlutarate (AKG)
Vitamin C can help to maintain a proper epigenome, especially in
combination with another longevity ingredient, alpha- ketoglutarate.
An umbrella review* (Xu 2022) to assess the existing systematic reviews and meta-analyses for
the association between vitamin C intake and multiple health outcomes;
showed that vitamin C intake was associated with reduced risk of
all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease (CVD), oesophageal cancer,
gastric cancer, cervical cancer and lung cancer with an increment of
50–100 mg per day. Beneficial associations were also identified for
respiratory, neurological, ophthalmologic, musculoskeletal, renal and
dental outcomes. A total of 76 meta-analyses (51 papers) of randomised
controlled trials and observational studies with 63 unique health
outcomes were identified. Harmful associations were found for breast
cancer and kidney stones for vitamin C supplement intake.
*Umbrella review: An umbrella review, or a review of reviews, is a systematic review that only considers other systematic reviews as an eligible study type for inclusion.
Alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) extends lifespan and healthspan in different
species. In humans, alpha-ketoglutarate has shown to protect cells
against damage and stressors. Alpha-ketoglutarate supports a healthy
metabolism and a healthy epigenome.
Alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) is a small molecule naturally present in our
body. During aging, levels of AKG decline.
Alpha-ketoglutarate is used by the mitochondria, which convert this substance into energy, but alpha-ketoglutarate has various other functions in the body.
Numerous studies show that alpha-ketoglutarate can extend lifespan in various organisms. AKG extended lifespan in C elegans worms (R) and fruit flies (R,R,R) and mice.
Alpha-ketoglutarate is used by the mitochondria, which convert this substance into energy, but alpha-ketoglutarate has various other functions in the body.
Numerous studies show that alpha-ketoglutarate can extend lifespan in various organisms. AKG extended lifespan in C elegans worms (R) and fruit flies (R,R,R) and mice.
Alpha-ketoglutarate also plays a role in maintaining stem cell health (Nature 2015), and in bone and gut metabolism (R).
Calcium alpha-ketoglutarate is also involved in collagen production, can reduce fibrosis, and can thus play a role in maintaining healthy, youthful skin (R,R).
8. CoQ10
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is an antioxidant that your body produces. It
plays an essential role in energy production and protects against
cellular damage (Source).
Research suggests that levels of CoQ10 decline as you age. Supplementing with it has been shown to improve certain aspects of health in older individuals.
For instance, a 4-year study in 443 older adults demonstrated that supplementing with CoQ10 and selenium improved overall quality of life, reduced hospital visits, and slowed physical and mental deterioration (Source).
CoQ10 supplements may work by reducing oxidative stress, a condition characterized by an accumulation of free radicals that accelerates the aging process and the onset of age-related disease (Source).
Additionally, CoQ10 supplements may benefit heart health by reducing stiffness in your arteries, lowering blood pressure, and preventing the buildup of oxidized cholesterol in your arteries (Trusted Source).
Research suggests that levels of CoQ10 decline as you age. Supplementing with it has been shown to improve certain aspects of health in older individuals.
For instance, a 4-year study in 443 older adults demonstrated that supplementing with CoQ10 and selenium improved overall quality of life, reduced hospital visits, and slowed physical and mental deterioration (Source).
CoQ10 supplements may work by reducing oxidative stress, a condition characterized by an accumulation of free radicals that accelerates the aging process and the onset of age-related disease (Source).
Additionally, CoQ10 supplements may benefit heart health by reducing stiffness in your arteries, lowering blood pressure, and preventing the buildup of oxidized cholesterol in your arteries (Trusted Source).
However, various studies show that coenzyme Q10 does not extend
lifespan (R,R,R,R). Some studies show that coenzyme Q10 can actually shorten
lifespan (R).
There are of course also some studies showing that co-enzyme Q10 can
extend lifespan, but often these studies have not been well conducted,
or they use organisms that are not ideal representation of normal aging,
like using co-enzyme Q10 deficient mice.
That said, CoQ10 decline as you age and it plays an essential role in
energy production and protects against cellular damage. Supplementing with
CoQ10 might allow for more physical activity and therefore more likely to
have a protective effect than a negative one.
9. Fisetin and Quercetin
Quercetin and Fisetin have been grouped together due to their similar
molecular structure, with only minor differences. Both are flavonoids
and senolytics.
Fisetin, a molecular cousin to the more popular Quercetin, is also a
naturally occurring substance found in fruits and vegetables, such as
strawberries, apples, grapes, onions, and cucumbers.
Fisetin is a flavonoid. Flavonoids are substances that give fruits and vegetables their bright colors (like yellow, orange and blue) and play a major role in conferring the health benefits that we get from eating more vegetables and fruits.
Fisetin is probably most known for its impact on senescent cells: studies showed that this substance can reduce the accumulation of senescent cells (R). Fisetin is a senolytic, a compound that can clear away senescent cells.
Senescent cells accumulate everywhere in the body during aging. Senescent cells were previously normal cells that became too damaged. Normally, when a cell is too damaged, it kills itself, but senescent cells don’t do that.
Instead of dying, they keep lingering around in the body.
Senescent cells secrete all kinds of substances that damage the healthy surrounding cells, like inflammatory substances (cytokines and chemokines), substances that break down the glue that holds the cells together (matrix metalloproteinases), and growth factors that accelerate aging (R). Not only do senescent cells damage healthy surrounding cells, but they also damage stem cells, which are the foundational cells that create new cells, which build up and repair our organs and tissues.
Reducing the senescent cell burden can lead to reduced inflammaging (low-grade inflammation that increases during aging) and enhanced function of stem cells.
Substances that can eliminate senescent cells are called “senolytics”. Fisetin is a well-studied senolytic substance.
Fisetin versus quercetin
Besides fisetin, another senolytic is quercetin. Quercetin and fisetin
look very similar. However, fisetin seems to be the most potent and
safest of natural senolytics (Lancet 2018).
The conclusion of the researchers was the following:
“Fisetin had the most potent senotherapeutic effects in several
cell types in vitro and showed strong anti-geronic effects in
vivo”.
Quercetin reduces glutathione and inhibits sirtuin-6 and NRF-2. All
of these will hurt your longevity (see this clip, 2:30).
Lifespan extension effects of fisetin
Scientists demonstrated that fisetin can extend median and maximum
lifespan in mice, even when taken late in a mouse’s life (equivalent
to 50 or 60 years old for a human) (R).
More than a senolytic: other anti-aging effects of fisetin
Fisetin has many other beneficial effects on the aging process besides
eliminating senescent cells.
For example, fisetin inhibits the mTOR pathway (R), which plays an important role in aging and is where many of the health benefits behind fasting are derived. Fisetin can also reduce oxidative stress (R).
Fisetin can reduce inflammaging (aging-related low-grade inflammation) by inhibiting pro-inflammatory enzymes and substances, like lipoxygenases and NF-kB (R, R).
Interestingly, fisetin can also have various beneficial effects on the skin. For example, fisetin can reduce the formation of skin wrinkles and appearance of skin aging.
For example, fisetin inhibits the mTOR pathway (R), which plays an important role in aging and is where many of the health benefits behind fasting are derived. Fisetin can also reduce oxidative stress (R).
Fisetin can reduce inflammaging (aging-related low-grade inflammation) by inhibiting pro-inflammatory enzymes and substances, like lipoxygenases and NF-kB (R, R).
Interestingly, fisetin can also have various beneficial effects on the skin. For example, fisetin can reduce the formation of skin wrinkles and appearance of skin aging.
10. Resveratrol and Pterostilbene
Resveratrol and pterostilbene have been grouped together due to
their similar molecular structure, with only minor
differences.
Resveratrol is a polyphenol in grapes, berries, peanuts, and red
wine that may promote longevity by activating certain genes
called sirtuins. It has been shown to increase the lifespan of
fruit flies, yeasts, and nematodes (Source).
It displays powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and
antitumor properties in clinical trials. Resveratrol also
enhances sirtuin function (R).
Then, the same mechanism was studied and found to be true in mice.
An animal study published in 2013 found that resveratrol does extend the life
of obese mice, but not of mice that maintain a healthy weight. Not
even if they’re give more resveratrol from a very young age. That
suggests that resveratrol can help reduce the damage caused by
lifestyle factors like diet and fitness levels, but it doesn’t add
any extra benefit you can’t already get from leading a healthy
lifestyle in the first place.
Investigations into resveratrol then turned toward its effects on
human health. Resveratrol was found to support cardiovascular
health, antioxidant defenses, glucose metabolism, healthy
inflammatory balance, and more. As results of these reported
studies, people became more interested in drinking resveratrol-rich
red wine and taking resveratrol supplements.
The efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of resveratrol have
been documented in over 244 clinical trials, with an additional 27
clinical trials currently ongoing (Pratap Singh 2019). Resveratrol is reported to potentially improve the
therapeutic outcome in patients suffering from diabetes mellitus,
obesity, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, multiple myeloma,
metabolic syndrome, hypertension, Alzheimer's disease, stroke,
cardiovascular diseases, kidney diseases, inflammatory diseases,
and rhinopharyngitis.
Pterostilbene vs Resveratrol
Some of the biggest hurdles for reaping the benefits of
resveratrol in humans appear to be its limited bioavailability and
rapid elimination from the body. But those hurdles might be
overcome by a compound that has more recently gained some notice.
PubMed has indexed more than 12,000 research studies on
resveratrol, but only 500 on pterostilbene. However, the sheer
number of scientific studies on a compound doesn’t necessarily
mean the compound is superior. It’s also important to note that
pterostilbene research lags about 10 years behind resveratrol
research.
The slight difference in molecular structure between resveratrol and pterostilbene provides a sound rationale for the superiority of pterostilbene. Pterostilbene should be more stable and bioavailable in theory, and preclinical studies so far validate the assumption.
The slight difference in molecular structure between resveratrol and pterostilbene provides a sound rationale for the superiority of pterostilbene. Pterostilbene should be more stable and bioavailable in theory, and preclinical studies so far validate the assumption.
11. Zinc
Zinc is an essential trace mineral that is critical to healthy immune
function. Zinc is an important mineral for proper immune system
function, brain health and skin health, among many other effects.
Ideally, one takes 10 to 15 mg of zinc per day.
Zinc deficiency is common in older individuals, and causes changes in
immune function that resemble those seen in immune senescence (Cabrera
2015; Maywald 2015). Immunological alterations associated with zinc
deficiency include diminished thymus function, decreased antibody
response to vaccines, and impaired function of phagocytic and NK cells
(Haase 2009; Cabrera 2015).
In a study in healthy older volunteers, daily intake of 45 mg zinc for one year resulted in a 67% reduction versus placebo in incidence of infections. Levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, an inflammatory cytokine, were also greatly reduced in those taking zinc (Prasad 2007). In a study of older individuals in nursing homes, residents with normal zinc levels had a significantly lower incidence of pneumonia compared with zinc-deficient individuals. Zinc-replete individuals also had shorter pneumonia duration and 50% lower usage of antibiotics, as well as lower all-cause mortality (Meydani 2007). A controlled clinical trial in aged individuals showed supplementation with 45 mg zinc per day for six months decreased plasma markers of inflammation, including IL-6 and C-reactive protein (Bao 2010).
Combining zinc with other important vitamins and minerals may also aid immune function. In a randomized controlled trial that enrolled 42 subjects between 55 and 75 years of age, those who took a multivitamin/mineral supplement containing 10 mg zinc and 1,000 mg vitamin C, along with other vitamins and minerals, for 12 weeks experienced fewer self-reported sick days and less severe symptoms than those who took placebo. The number of sick days decreased by nearly 65% with supplement use (Fantacone 2020).
In a study in healthy older volunteers, daily intake of 45 mg zinc for one year resulted in a 67% reduction versus placebo in incidence of infections. Levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, an inflammatory cytokine, were also greatly reduced in those taking zinc (Prasad 2007). In a study of older individuals in nursing homes, residents with normal zinc levels had a significantly lower incidence of pneumonia compared with zinc-deficient individuals. Zinc-replete individuals also had shorter pneumonia duration and 50% lower usage of antibiotics, as well as lower all-cause mortality (Meydani 2007). A controlled clinical trial in aged individuals showed supplementation with 45 mg zinc per day for six months decreased plasma markers of inflammation, including IL-6 and C-reactive protein (Bao 2010).
Combining zinc with other important vitamins and minerals may also aid immune function. In a randomized controlled trial that enrolled 42 subjects between 55 and 75 years of age, those who took a multivitamin/mineral supplement containing 10 mg zinc and 1,000 mg vitamin C, along with other vitamins and minerals, for 12 weeks experienced fewer self-reported sick days and less severe symptoms than those who took placebo. The number of sick days decreased by nearly 65% with supplement use (Fantacone 2020).
Be careful, too much zinc can have negative effects. Also, if you take
zinc supplements, make sure you take copper, given zinc inhibits the
absorption of copper.
More and more studies show the importance of copper to reduce the risk
of heart disease and diabetes. Copper also plays an important role in
collagen production, skin health and skin appearance.
Ideally, one takes 2 mg of copper per day.
Ideally, one takes 2 mg of copper per day.
12. EGCG (Green Tea Extract)
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is a well-known polyphenol compound
concentrated in green tea.
Studies have confirmed numerous health benefits of green tea
including prevention of cancer (R, R) and cardiovascular disease, as well as anti-inflammatory,
antioxidant, antiarthritic, antibacterial, and antiviral effects.
(R, R, R, R). Plus, animal studies have shown that it can protect against skin
aging and wrinkles caused by ultraviolet (UV) light (Source).
Among EGCG’s diverse array of potential health-promoting properties
is its ability to promote longevity and protect against age-related
disease development.
EGCG may slow aging by restoring mitochondrial function in cells and acting on pathways involved in aging, including the AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway (AMPK). It also induces autophagy, the process by which your body removes damaged cellular material (Source).
Green tea may protect against EMF exposure as well. A 2011 study published in Neurotoxicity Research reported that green tea can protect neurons in the brain against cell phone radiation. Cell phone exposure for 24 hours resulted in neuronal cell death in cultured rat cells. Green tea, however, prevented cell death.
EGCG may slow aging by restoring mitochondrial function in cells and acting on pathways involved in aging, including the AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway (AMPK). It also induces autophagy, the process by which your body removes damaged cellular material (Source).
Green tea may protect against EMF exposure as well. A 2011 study published in Neurotoxicity Research reported that green tea can protect neurons in the brain against cell phone radiation. Cell phone exposure for 24 hours resulted in neuronal cell death in cultured rat cells. Green tea, however, prevented cell death.
They randomized and stratified 1075 healthy postmenopausal women at
high risk of breast cancer according to their breast tissue density
and catechol-O-methyltransferase genotypes and divided them into two
groups: 537 placebo and 538 green tea groups. Green tea group
participants took 4 capsules that contained 843 mg EGCG, whereas the
placebo group took capsules without green tea extracts.
Researchers measured changes in percent mammographic density,
circulating endogenous sex hormones, and proteins of the
insulin-like growth factor axis. Their results showed
that supplementation with green tea extract could modify and
reduce mammographic density (MD) and protect against breast cancer,
even though it was only significant in younger women (50–55 years)
and had no effect in older women (R), an age-dependent effect similar to those of tamoxifen.
EGCG can be consumed by drinking green tea or taking concentrated supplements.
Buy on Amazon > EGCG supplement
13. L-Citrulline and L-Arginine (Nitric Oxide Boosters)
Nitric oxide deficiency is a primary driver of hypertension (Biochemical Pharmacology 2022).
L-citrulline is a naturally occurring amino acid found in some
foods like watermelons and is also produced naturally by the body.
Citrulline can promote heart health by widening your blood vessels. It
can also improve your exercise performance and may play a role in
muscle building (Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2017). After citrulline is consumed, some is converted to another amino
acid called arginine. Arginine is converted into a molecule called
nitric oxide, which causes vasodilation of blood vessels by
relaxing the smooth muscle cells that constrict them (Nitric Oxide. 2015).
Though research has found both arginine and citrulline to boost levels
of nitric oxide (NO) in the body, research—like this The Journal of Nutrition study (2017)—shows that citrulline actually delivers the most benefit.
The body use arginine for a variety of functions, so it doesn’t use all
of the arginine it absorbs to produce Nitric Oxide. Plus, unlike
citrulline, higher doses of arginine have been linked to
gastrointestinal problems. Because it tends to be poorly absorbed,
arginine can even lead to diarrhea when consumed in large amounts.
Related: Best Nitric Oxide Supplements
14. Lutein and Zeaxanthin
Known as the “eye vitamin,” lutein is one of two carotenoids thought to
help filter light and protect the eye from sun damage. Oral supplements
containing lutein can help prevent age-related macular degeneration.
Dietary lutein might help prevent cataracts, but research has yet to
confirm whether supplements can have the same effect as food.
Lutein works hand in hand with another antioxidant [called] zeaxanthin. Both of those [nutrients] are usually found together [in the same supplement].
Lutein works hand in hand with another antioxidant [called] zeaxanthin. Both of those [nutrients] are usually found together [in the same supplement].
Published in 2022, the Cognitive impAiRmEnt Study (CARES Trial 2), was designed to examine the potential
synergistic effects of a combination of omega-3 fatty acids (namely
DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid [EPA]), xanthophyll carotenoids
(specifically lutein, zeaxanthin and meso-zeaxanthin) and vitamin E
(d-α-tocopherol) on the cognitive performance of cognitively healthy
older adults.
In conclusion, the CARES research has shown improvements in working
memory following 24-month supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids,
xanthophyll carotenoids (lutein and zeaxanthin) and vitamin E in
cognitively healthy older adults. This study provides Class II
evidence that 24-month supplementation with 430 mg DHA, 90 mg EPA, 10
mg lutein, 2 mg zeaxanthin, 10 mg meso-zeaxanthin and 15 mg vitamin E
(d-α-tocopherol) is effective in improving cognitive performance,
namely working memory, in cognitively healthy older adults.
A diet rich in fruits and vegetables should provide enough lutein for healthy adults, but there are no known side effects from supplementing for those who choose to do so. However, consuming lutein alongside beta carotene specifically might reduce the body’s absorption of both vitamins, and when taken with vitamin E, lutein can reduce the amount of vitamin E the body can absorb. Food sources of lutein include egg yolks, spinach and kale. It’s also important to consume lutein along with foods high in fat to facilitate better absorption.
15. Glucosamine and Chondroitin
Large studies found that people who take glucosamine live
longer. Glucosamine intake was also associated with better heart
health. In animals, glucosamine extends lifespan. Glucosamine
targets inflammaging at the cellular level, and helps the body
to manage oxidative stress and support autophagy.
They found that participants who took glucosamine and chondroitin daily for a year reduced the risk of death from any cause—by an astounding 39 percent. The supplementation also reduced cardiovascular deaths—including death from coronary artery disease, stroke, and other forms of heart disease—by 65 percent. In fact, glucosamine/chondroitin supplementation worked about as well as regular exercise in reducing the risk of death (although the researchers do not recommend that people forego exercising in favor of glucosamine).
Glucosamine and chondroitin supplements are made from chitin, a
compound found in shellfish. Natural healthcare providers typically
recommend supplementation with 1,500 mg a day of glucosamine and 1,200
mg a day of chondroitin (many products conveniently feature these two
compounds together). Note: Most experts feel that glucosamine sulfate
is superior to other formulations, such as glucosamine hydrochloride
and N-acetyl glucosamine. Of course, check first with your integrative
doctor before supplementing. And, if you are allergic to shellfish,
don’t use glucosamine or chondroitin.
You can also increase your dietary intake of glucosamine and chondroitin with nourishing bone broth.
Remember, long-term, regular use of these supplements seems to yield the most benefits. Be aware that it may take eight to twelve weeks before improvements begin to appear.
You can also increase your dietary intake of glucosamine and chondroitin with nourishing bone broth.
Remember, long-term, regular use of these supplements seems to yield the most benefits. Be aware that it may take eight to twelve weeks before improvements begin to appear.
16. Protein Powder and Collagen
Protein Powder
Muscle mass optimizes you for longevity, and dietary protein,
especially animal-based protein, is essential for muscle
maintenance and muscle building. The greater your muscle mass, the
higher your survivability against all diseases, including cancer.
Cachexia, for example — the loss of muscle mass — accounts for 20%
of all cancer deaths. (source)
One of the reasons for this is because muscle acts as a reservoir for amino acids, which are crucial during illness when your body’s demand for them increases. Additionally, muscle regulates metabolism and is integral for glucose disposal, which helps you manage conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Your muscle also interfaces with your immune system.
One of the reasons for this is because muscle acts as a reservoir for amino acids, which are crucial during illness when your body’s demand for them increases. Additionally, muscle regulates metabolism and is integral for glucose disposal, which helps you manage conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Your muscle also interfaces with your immune system.
It’s not only protein quantity that’s important but also its
quality and amino acid balance. Glycine and collagen, which are
often overlooked, are among the most important. Siim Land, author
of "The Collagen Cure" explains:
"Glycine is conditionally essential, not essential, but that's
because your body makes 3 grams of glycine per day. But those 3
grams would be used for things, like creatine synthesis. But
then you have 12 grams of glycine for collagen turnover, like
optimal collagen turnover." (source)
Collagen and Skin Anti-Aging
Research suggests that collagen supplements may help increase skin
elasticity, hydration and dermal collagen density. Collagen is also an
outstanding source of glycine. Preferably, use a less denatured
(unhydrolyzed) organic collagen supplement, as it has a more balanced
amino acid profile or, better yet, simply boost your collagen intake
by making homemade bone broth using bones and connective tissue from
grass fed, organically raised animals.
There are no known interactions between collagen supplements and
medications, foods or other supplements.
Though these results are promising, keep in mind that many collagen
studies are funded by companies that manufacture collagen products,
which may influence study results.
Many types of collagen supplements are on the market, including powders and capsules.
Many types of collagen supplements are on the market, including powders and capsules.
17. Spermidine
While spermidine was first found in semen, it has various metabolic functions in many types of cells and is naturally found in all living
organisms. It’s also found in common foods, including aged cheese and
fermented soy products, as well as mushrooms, pears and potatoes. A review
published in the journal Autophagy details some of spermidine’s benefits:
“This chemical affects numerous biological processes, including cell growth and proliferation, tissue regeneration, DNA and RNA stabilization, enzymatic modulation, and regulation of translation, among others. Furthermore, spermidine exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, enhances mitochondrial metabolic function and respiration, promotes chaperone activity and improves proteostasis.”
“This chemical affects numerous biological processes, including cell growth and proliferation, tissue regeneration, DNA and RNA stabilization, enzymatic modulation, and regulation of translation, among others. Furthermore, spermidine exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, enhances mitochondrial metabolic function and respiration, promotes chaperone activity and improves proteostasis.”
“Spermidine showed the strongest inverse relation with mortality among 146 nutrients studied. The reduction in mortality risk related to a diet rich in spermidine (top compared with bottom third of spermidine intake) was comparable to that associated with a 5.7-y younger age. All of the findings apply to spermidine from dietary sources and to amounts characteristically found in the Western diet …”
A research team with Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences in India further suggested spermidine could be a useful therapeutic strategy for neurological disorders due to its autophagy-inducing properties. They noted that a healthy brain is dependent on its concentration of polyamines:
“Polyamines interact with the opioid system, glutamatergic signaling and neuroinflammation in the neuronal and glial compartments. Among the polyamines, spermidine is found highest in the human brain. Age-linked fluctuations in the spermidine levels may possibly contribute to the impairments in neural network and neurogenesis.”
In humans, a diet high in spermidine is associated with reduced blood
pressure and lower incidence of cardiovascular disease (Nature Medicine 2016). It also reverses arterial aging, which is characterized by stiffening of
large arteries and the development of arterial endothelial dysfunction,
which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
This benefit may be due to its interactions with nitric oxide (NO) and other factors, according to researchers with the University of Colorado, Boulder:
“Our results indicate that spermidine exerts a potent anti-aging influence on arteries by increasing NO bioavailability, reducing oxidative stress, modifying structural factors and enhancing autophagy. Spermidine may be a promising nutraceutical treatment for arterial aging and prevention of age-associated CVD.”
This benefit may be due to its interactions with nitric oxide (NO) and other factors, according to researchers with the University of Colorado, Boulder:
“Our results indicate that spermidine exerts a potent anti-aging influence on arteries by increasing NO bioavailability, reducing oxidative stress, modifying structural factors and enhancing autophagy. Spermidine may be a promising nutraceutical treatment for arterial aging and prevention of age-associated CVD.”
According to The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition study:
“Spermidine is the polyamine most readily absorbed from the human gut. A broad and diverse palette of foods contain high amounts of spermidine, such as fresh green pepper, wheat germ, cauliflower, broccoli, mushrooms, and a variety of cheeses, whereas even higher amounts are found in soybean products such as natto, shitake mushrooms, amaranth grain, and durian.”
Polyamines like spermidine are also present in aged (fermented) cheese, including blue cheese, Brie, cheddar, Swiss, Gouda, Gruyere, Manchego and Parmesan. Intake of spermidine-rich foods is important at any age but may be particularly useful as you get older, when spermidine levels tend to decline.
“Spermidine is the polyamine most readily absorbed from the human gut. A broad and diverse palette of foods contain high amounts of spermidine, such as fresh green pepper, wheat germ, cauliflower, broccoli, mushrooms, and a variety of cheeses, whereas even higher amounts are found in soybean products such as natto, shitake mushrooms, amaranth grain, and durian.”
Polyamines like spermidine are also present in aged (fermented) cheese, including blue cheese, Brie, cheddar, Swiss, Gouda, Gruyere, Manchego and Parmesan. Intake of spermidine-rich foods is important at any age but may be particularly useful as you get older, when spermidine levels tend to decline.
18. Crocin (Saffron)
Crocin is a yellow carotenoid pigment in saffron, a popular, pricey spice that’s commonly used in Indian and Spanish
cuisine.
Saffron is the most expensive spice in the world — with 1 pound (450 grams) costing between 500 and 5,000 U.S. dollars. Saffron contains an impressive variety of plant compounds that act as antioxidants — molecules that protect your cells against free radicals and oxidative stress.
Human and animal studies have shown that crocin offers many health benefits, including anticancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, and antidiabetic effects (Source).
Aside from the properties listed above, crocin has been researched for its potential to act as an anti-aging compound and protect against age-related mental decline (Source).
Crocin has also been shown to help prevent aging in human skin cells by reducing inflammation and protecting against UV-light-induced cellular damage (Source, Source).
Given that saffron is the most expensive spice in the world, a more cost-effective way to boost your crocin intake is by taking a concentrated saffron supplement.
Saffron is the most expensive spice in the world — with 1 pound (450 grams) costing between 500 and 5,000 U.S. dollars. Saffron contains an impressive variety of plant compounds that act as antioxidants — molecules that protect your cells against free radicals and oxidative stress.
Human and animal studies have shown that crocin offers many health benefits, including anticancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, and antidiabetic effects (Source).
Aside from the properties listed above, crocin has been researched for its potential to act as an anti-aging compound and protect against age-related mental decline (Source).
Crocin has also been shown to help prevent aging in human skin cells by reducing inflammation and protecting against UV-light-induced cellular damage (Source, Source).
Given that saffron is the most expensive spice in the world, a more cost-effective way to boost your crocin intake is by taking a concentrated saffron supplement.
19. Cocoa
Howard Sesso et al conducted a large randomized double blind, placebo-controlled trial of cocoa extract supplementation for prevention of CVD and cancer that involved 21,442 older US adults (12,66 women) between 2015 and 2020. Participants were randomly assigned to cocoa extracts [500 mg flavanols/d, including 80 mg (-)-epicatechin] or placebo.Although the cocoa extract did not achieve statistical significance in reducing total cardiovascular events among these older adults, it did reduce CVD death by 27%. That should still encourage most adults to consume a bit more cocoa.
20. Garlic supplements
Garlic, well known for its ability to improve cardiovascular risk factors,
also has immune-modulating and immunostimulatory properties, as well as
anti-tumor effects (Ebrahimi 2013; Purev 2012).
A detailed review of data from published clinical trials found garlic
supplements significantly reduce the number, duration, and severity of
upper respiratory tract infections. This review also found garlic
supplements stimulate immune function by increasing macrophage activity,
numbers of NK cells, and production of T and B cells (Ried 2016).
In a clinical trial, 120 healthy participants, 21–50 years old, were
assigned to use 2.56 g aged garlic extract or placebo daily for 90 days
during cold and flu season. Garlic supplementation was associated with
reduced cold and flu severity, as well as increased cytotoxic T-cell and
NK-cell proliferation and activity (Percival 2016). In animal research,
garlic has been shown to increase antibody production and enhance the
cell-killing activity of macrophages, cytotoxic T cells, and NK cells
(Ghazanfari 2000).
Interestingly, garlic has also been demonstrated to suppress the overactive immune response associated with allergic reactions. Data from experimental studies indicate aged garlic extract may reduce histamine release and modify the function of immune cells involved in allergic reactions (Kyo 2001).
Interestingly, garlic has also been demonstrated to suppress the overactive immune response associated with allergic reactions. Data from experimental studies indicate aged garlic extract may reduce histamine release and modify the function of immune cells involved in allergic reactions (Kyo 2001).
21. Creatine
What is creatine? Creatine, a nitrogenous organic acid naturally occurring in vertebrates, plays a critical role in the energy metabolism of brain cells. Synthesized primarily from arginine, glycine, and methionine, creatine is produced endogenously and obtained through dietary intake.
“These beneficial effects from creatine supplementation on memory performance may be related to creatine’s ability to influence brain bioenergetics. For example, creatine elevates phosphocreatine and ATP levels and increases oxidative phosphorylation in synaptosomes and isolated brain mitochondria. In hippocampal neuron cultures, creatine stimulates mitochondrial activity.”
22. Melatonin
In a 2022 study:To highlight, a 10-fold decrease in pineal melatonin production in octogenarians compared to teenagers was observed, which results in a significant attenuation of the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and mitochondrial optimizing effects of melatonin. This has important consequences for the immune changes common over the course of aging, including immune senescence and inflammaging (inflammation associated with aging), which may be mediated by the effects of night-time pineal melatonin in resetting and resynchronizing immune cell mitochondrial function...
Most officially recommended daily doses are too low
You should know that the official recommended dietary allowances of
vitamins and minerals, as defined by government agencies, are often
just the bare minimum you need to take in to not become sick. They do
not tell you what are the best amounts for a long, optimal, healthy
life.
Most of these official recommendations are also based on old studies in which volunteers were deprived of a specific vitamin or mineral. Scientists then waited a while until people became sick, and then determined the minimum dose you would need to prevent this.
So these recommended daily intakes are what you need to take on a daily basis in order not to become sick after a number of months (the duration of the study). They do not tell you the ideal amounts you need to stay healthy and slow down aging for decades to come.
Take for example vitamin B12. The recommended dietary allowance is around 2.4 mcg in many countries. But that’s in fact the “minimum” amount you need to not become sick after a few months or years, getting serious complications, like anemia, fatigue or cognitive problems. This doesn’t mean this is the optimal amount for a long, healthy life.
For example, we see in studies that you need at least 20 mcg of vitamin B12 to optimally protect the DNA against DNA strand breaks – more than 8 times greater than the recommendation!
Also, many people do not take up vitamin B12 well, especially as we get older. For example, atrophic gastritis affects at least 10 to 30 percent of people older than 60, leading to malabsorption of vitamin B12. So, they would need far more vitamin B12 than advised by governments.
In fact, The Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University recommends that all people older than 50 take at least 100 to 400 ug/day of supplemental vitamin B12 (R). That’s considerably more than the 2.4 mcg many governments advise.
It’s interesting to see that many foods rich in vitamin B12 (clams, mussels, crab, and fish like mackerel and salmon) are water-borne foods. Scientists speculate that people evolved for tens of thousands of years living close to shorelines and rivers and lakes and consumed high amounts of sea food and thus vitamin B12 (R), probably reaching daily intake levels far more than a meagre 2.4 mcg per day.
These are just a few examples demonstrating that yes, we need to take supplements for optimal aging. And this for the rest of our lives, and even more when we are older and suffer from age-related malabsorption issues and changes that hinder us to properly use these important vitamins and minerals.
Most of these official recommendations are also based on old studies in which volunteers were deprived of a specific vitamin or mineral. Scientists then waited a while until people became sick, and then determined the minimum dose you would need to prevent this.
So these recommended daily intakes are what you need to take on a daily basis in order not to become sick after a number of months (the duration of the study). They do not tell you the ideal amounts you need to stay healthy and slow down aging for decades to come.
Take for example vitamin B12. The recommended dietary allowance is around 2.4 mcg in many countries. But that’s in fact the “minimum” amount you need to not become sick after a few months or years, getting serious complications, like anemia, fatigue or cognitive problems. This doesn’t mean this is the optimal amount for a long, healthy life.
For example, we see in studies that you need at least 20 mcg of vitamin B12 to optimally protect the DNA against DNA strand breaks – more than 8 times greater than the recommendation!
Also, many people do not take up vitamin B12 well, especially as we get older. For example, atrophic gastritis affects at least 10 to 30 percent of people older than 60, leading to malabsorption of vitamin B12. So, they would need far more vitamin B12 than advised by governments.
In fact, The Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University recommends that all people older than 50 take at least 100 to 400 ug/day of supplemental vitamin B12 (R). That’s considerably more than the 2.4 mcg many governments advise.
It’s interesting to see that many foods rich in vitamin B12 (clams, mussels, crab, and fish like mackerel and salmon) are water-borne foods. Scientists speculate that people evolved for tens of thousands of years living close to shorelines and rivers and lakes and consumed high amounts of sea food and thus vitamin B12 (R), probably reaching daily intake levels far more than a meagre 2.4 mcg per day.
These are just a few examples demonstrating that yes, we need to take supplements for optimal aging. And this for the rest of our lives, and even more when we are older and suffer from age-related malabsorption issues and changes that hinder us to properly use these important vitamins and minerals.
Other Promising Interventions for Longevity
If you are an anti aging, longevity or biohacking space enthusiast, chances are you have heard about many more advanced and emerging anti aging interventions mentioned below. We will review few of the popular ones below. However, do note that some of them might be too overwhelming for an average layperson and will require medical supervision to proceed.
Stem Cell Therapy for Anti-Aging
Stem cell therapy for anti aging is an ongoing topic for cutting edge
life-science research and is considered experimental by the medical
community at the moment. Is there any evidence that stem cell therapy
for anti aging is effective and safe?
The global stem cells market size was valued at USD 15.07 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 17.02 billion in 2024 to USD 56.15 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of 16.1% during the forecast 2024-2032. (Source)
As of May 2025, there are more than 300 scientific publications
related to stem cell and anti-aging on PubMed.gov.
Despite the fact that there are many published studies on stem cell therapy for anti-aging, major media has been slow to report the findings.
Despite the fact that there are many published studies on stem cell therapy for anti-aging, major media has been slow to report the findings.
Exosome Therapy for Anti Aging
Exosomes are small vesicles released by all the cells, but especially by stem cells. They are, essentially, little messengers carrying important signaling proteins and genetic information from cell to cell. Or in other words, a fat bubble with a message.
The exosomes market size was valued at USD 250.8 million in 2022 and is expected to reach USD 3.2 billion in 2032 with a CAGR of 29.9% from 2023 to 2032 (source).
Exosomes' primary job is to act as a connection between all our cells, facilitating communication whether cells are near or far to one another. The information they carry tells our cells to turn on or off certain functions or to react in a certain way. Exosomes are being heralded as the next frontier of cell therapy. While not being cells at all, they play a vital role in the communication and rejuvenation of all the cells in our body. Science has shown that the cell-to cell communication is important in maintaining a healthy cellular terrain.
Exosomes therapy is responsible, among other things, for assisting both the T-cells and NK cells in our immune system. T-cells are responsible for calming an immune response, while NK cells are responsible for ramping up that response. We need both, but when NK cells aren’t “turned off” or T-cells aren’t “turned on,” pain and inflammation are often the result.
Generally speaking, exosomes carry healthy and lost information and insert this into target cells. Exosomes released by young stem cells have been shown to be very powerful in regulating regenerative processes in the body and assisting in rejuvenation. You may be wondering the difference between exosomes and stem cells. The number one difference is that exosome therapy DOES cross the blood brain barrier and get to places whole stem cells cannot.
Few of the important benefits of Exosomes:
- Manage degenerative conditions
- Repair degenerated and damaged tissue
- Powerful anti-inflammatory effects
- Promising anti-aging capabilities
- Improve pain control
- Decrease brain inflammation
Hormone Replacement Therapy
HRT for Women
The media has been slow to report the findings which indicate
that not only is hormone replacement therapy not an identifiable
causative agent of breast cancer, but that when begun early,
hormone therapy actually has a collective mortality risk
reduction of 40%. [BMJ 2012]
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for women has been a topic of much debate in recent decades. This is due largely to the fact that the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) study in 2002 was halted prematurely because of a reported increase in the instance of breast cancer in women participating in the hormone replacement arm of the study. Thereafter, thousands of women were taken off or stopped taking HRT unnecessarily, despite the fact that many studies have debunked the WHI conclusions.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for women has been a topic of much debate in recent decades. This is due largely to the fact that the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) study in 2002 was halted prematurely because of a reported increase in the instance of breast cancer in women participating in the hormone replacement arm of the study. Thereafter, thousands of women were taken off or stopped taking HRT unnecessarily, despite the fact that many studies have debunked the WHI conclusions.
HRT for women has indeed developed a bad reputation, but any
fears surrounding the treatment are unfounded. Here, we examine
the relationship among HRT and breast cancer, colon cancer,
cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and brain health to dispel
the myths once and for all. Discover how this powerful treatment
helps, rather than harms, postmenopausal women in tremendous
ways below.
HRT & Breast Cancer: What’s the Connection?
One of the major flaws of the WHI was the confusion and fear it spread by projecting its results to all women receiving HRT. In the original study, more women who took estrogen plus progestin (E+P) developed breast cancer than those taking placebos.
Further research published in a 2013 article in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism shows that breast cancer rates were actually found to decrease significantly with estrogen alone. Moreover, the article goes on to say that even though there isn’t a significant increase with E+P used together versus estrogen alone, for illustrative purposes, any increased risk of breast cancer associated with E+P originally publicized with the WHI trial is less than the risk conferred by obesity, being a flight attendant, and many other common exposures.
Another noteworthy difference which can play a role in breast cancer risk is the use of synthetic progestins versus bioidentical progesterone. Synthetic progestins, which were used in the WHI, are hormones which are synthetically produced, and thus different in structure from bioidentical progesterone. Bioidentical progesterone, while produced from a plant source, is structurally and chemically identical to the progesterone produced by the ovaries. Synthetic progestins mimic some effects of the natural hormone, but react differently with progesterone receptors within the body and are felt to be responsible for the increase in breast cancer seen in WHI. On the other hand, bioidentical progesterone does not increase, and may actually reduce the risk of breast cancer.
HRT & Breast Cancer: What’s the Connection?
One of the major flaws of the WHI was the confusion and fear it spread by projecting its results to all women receiving HRT. In the original study, more women who took estrogen plus progestin (E+P) developed breast cancer than those taking placebos.
Further research published in a 2013 article in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism shows that breast cancer rates were actually found to decrease significantly with estrogen alone. Moreover, the article goes on to say that even though there isn’t a significant increase with E+P used together versus estrogen alone, for illustrative purposes, any increased risk of breast cancer associated with E+P originally publicized with the WHI trial is less than the risk conferred by obesity, being a flight attendant, and many other common exposures.
Another noteworthy difference which can play a role in breast cancer risk is the use of synthetic progestins versus bioidentical progesterone. Synthetic progestins, which were used in the WHI, are hormones which are synthetically produced, and thus different in structure from bioidentical progesterone. Bioidentical progesterone, while produced from a plant source, is structurally and chemically identical to the progesterone produced by the ovaries. Synthetic progestins mimic some effects of the natural hormone, but react differently with progesterone receptors within the body and are felt to be responsible for the increase in breast cancer seen in WHI. On the other hand, bioidentical progesterone does not increase, and may actually reduce the risk of breast cancer.
For many women, HRT is a powerful means of regaining quality of
life and maintaining optimal wellness through the postmenopausal
years. In fact, avoiding estrogen therapy can actually have
serious implications. One article published in the American
Journal of Public Health indicates that as many as 91,610
postmenopausal women died prematurely because of the avoidance
of hormone therapy. Estrogen therapy, especially when used in
younger postmenopausal women (aged 50-59), is linked to a
decisive reduction in all-cause mortality.
Yet the use of HRT in this group continues to fall. If the
potential for reducing breast cancer risk isn’t compelling
enough to take another look at hormone therapy, consider how it
could also combat colon cancer, below.
Can HRT Help Prevent Cardiovascular Disease in Women?
Cardiovascular disease is responsible for 1 in every 4 deaths in the U.S. It’s the leading cause of death in both men and women, and leads to more than 600,000 deaths across the country annually (CDC). It’s therefore critical that as the risk for cardiovascular disease increases with age, individuals find ways to optimize heart health.
HRT may not be prescribed for women primarily as a means for improving cardiovascular health, but this is indeed a powerful byproduct of the treatment. According to research published in the BMJ, women receiving HRT early after experiencing menopause had a significantly reduced rate of heart failure, myocardial infarction, and mortality overall. At the start of treatment, women on average were aged 50 and had been postmenopausal for seven months. Roughly half as many women using HRT experienced cardiovascular events compared to those in the control group. Additionally, these results did not correlate with an increased risk in any cancer [BMJ 2012].
Moreover, evidence shows that there is a clear benefit in using estrogen alone, with coronary calcium scores significantly reduced. This measures the buildup of calcium and other substances which can narrow or close the arteries, leading to cardiovascular issues. In particular, women under 60 who receive hormone therapy have a statistically significant reduction in coronary disease (Lobo 2013).
Women who were given hormone therapy during early menopause
also experienced reduced atherosclerosis progression (buildup
of fats and cholesterol in the artery walls) (Sriprasert 2019).
These aren’t the only positive outcomes of HRT, however. Hormone therapy has been commonly used as an osteoporosis preventative, which brings us to our next segment.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) for Men
Testosterone is a male steroid hormone that does a lot more for men
than just promote a healthy sex drive. The hormone affects several
other factors in your health, including body fat, muscle mass, bone
density, red blood cell count, and mood.
In a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled (NEJM 2023), 5246 men 45 to 80 years of age who had preexisting or a high
risk of cardiovascular disease and who reported symptoms of
hypogonadism and had two fasting testosterone levels of less than
300 ng per deciliter were enrolled. The study concluded that
testosterone-replacement therapy was non inferior to placebo with
respect to the incidence of major adverse cardiac events.
Normal testosterone levels are between 300 and 1,000 ng/dL. If a blood test shows that your levels are far below the norm,
your doctor may suggest testosterone injections. These are a form
treatment called testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).
Testosterone injections are most often given by your doctor. The injection site is typically in the gluteal muscles in the buttocks.
Testosterone injections are most often given by your doctor. The injection site is typically in the gluteal muscles in the buttocks.
TRT is an acronym for testosterone replacement therapy, sometimes called androgen replacement therapy. It’s primarily used to treat low testosterone (T) levels, which can occur with age or as a result of a medical condition.
But it’s becoming increasingly popular for non-medical uses, including:
- enhancing sexual performance
- achieving higher energy levels
- building muscle mass for bodybuilding
This is all part of a completely natural process that starts in your late 20s or early 30s.
This gradual decrease in Testosterone often doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms. But a significant drop in T levels may cause:
- low sex drive
- fewer spontaneous erections
- erectile dysfunction
- lowered sperm count or volume
- trouble sleeping
- unusual loss of muscle and bone density
- unexplained weight gain
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is a steroid hormone that plays a major
role in healthy immune system functioning (Buford 2008; Weksler 1993).
DHEA levels decline markedly with age. By age 80, DHEA levels fall to
10‒20% of their peak values (Kroll 2015; UMMC 2014).
DHEA plays a critical role by serving as a counterweight to cortisol. Cortisol is an adrenal hormone with immunosuppressive properties, while DHEA may have direct immunostimulating properties: in a laboratory study of white blood cells from donors who were at least 65 years old, DHEA treatment reversed the age-related reduction of specific receptors on immune cells and increased immune cell responsiveness (Corsini 2005). Although DHEA levels decline dramatically with age, cortisol levels remain relatively constant, leading to an imbalance of these two hormones that is believed to contribute to immune senescence (Buford 2008; Buoso 2011).
DHEA plays a critical role by serving as a counterweight to cortisol. Cortisol is an adrenal hormone with immunosuppressive properties, while DHEA may have direct immunostimulating properties: in a laboratory study of white blood cells from donors who were at least 65 years old, DHEA treatment reversed the age-related reduction of specific receptors on immune cells and increased immune cell responsiveness (Corsini 2005). Although DHEA levels decline dramatically with age, cortisol levels remain relatively constant, leading to an imbalance of these two hormones that is believed to contribute to immune senescence (Buford 2008; Buoso 2011).
Cautionary Note: Don't use DHEA with testosterone. Combining DHEA
and testosterone might cause symptoms such as low sperm count and
enlarged breasts in men (gynecomastia) and the development of
typically male characteristics in women.
What is mTOR?
Mechanistic (previously referred to as mammalian) Target Of Rapamycin
(mTOR) is a protein kinase that regulates protein synthesis and cell
growth in response to growth factors, nutrients, energy levels, and stress
(Marin et al., 2011).
We found it interesting enough to share, verbatim:
Rapamycin was first discovered in 1972 in the soil of Easter Island,
produced by a bacterium called Streptomyces hygroscopicus. It takes its
name from Rapa Nui, the indigenous name for the island. In the early
2000s, researchers discovered its potential to increase lifespan. In low
doses, rapamycin reliably increases the lifespan of worms, yeast, flies,
and mice. In one study, researchers gave a group of 20-month-old mice
(roughly equivalent to that of 60-year-old humans) rapamycin in small
doses over three months. They then simply observed the mice until they
died naturally.
They were astonished at what they observed! Normally, these 20-month-old
mice would have died of agerelated diseases around the 30-month mark.
But they didn’t! They lived another 2-months on average, which would be
equal to a human living to 140 years old! There are many other research
examples in multiple species of increased lifespan resulting from
rapamycin periodic dosing. In October 2021, Steve Hill published a
review of the Rapamycin literature in a popular Longevity Medicine
Journal.
In his Summary of Rapamycin he found the following:
Late-life mice treated with Rapamycin for three months showed:
- Significant benefits in cardiovascular function with reversal or attenuation of age-related changes in the heart
- Beneficial behavioral, skeletal and motor changes compared with mice fed a control diet
- Reduced indicators of inflammatory, metabolic, and hypertrophic expression of cardiac tissues
From these findings, we propose that late-life rapamycin therapy not
only extends the lifespan of mammals, but also confers functional
benefits to a number of tissues. In July 2013, James M Flynn published
in the journal, Aging Cell reporting that Late-life Rapamycin Treatment
Reverses Age-related Heart Dysfunction. Much has been learned about
Rapamycin since the mouse study mentioned here. The important news? All
signs pointed to increased lifespan in humans.
Some of the benefits of periodic dosing of Rapamycin found through
scientific exploration are:
- A decrease in cancer incidence
- Improvement of cardiac function (heart function)
- Improvement in bone marrow function (immune system)
- Metabolizes cellular fat stores (weight and body composition)
- Increases lifespan by inhibiting mTOR (slows down rate of aging)
Matt Kaeberlein’ research gives us information on the benefits of
Targeting mTOR Signaling to promote Healthy longevity. He reports that
Rapamycin is a viable option, especially when combined with:
- A highly-optimized diet
- Individualized power supplements
- A healthy sleep routine
- Stress management techniques
Note: There are more than 2,900 search results on rapamycin and aging on PubMed.
Peptide Therapy for Anti Aging
Peptide therapy has become quite a familiar term with those who are on a
quest for health and wellness. However, knowing what peptide to use and
for a specific outcome is quite confusing. This is where you need an
expert in the field to guide you.
There are over 7,000 known peptides within the human body and though
some may be similar, each is responsible for facilitating a different
response and action within the body. All are very important to the
health and wellness of your body. In fact, there are so many peptides
that we have decided to dedicate an entire eBook to just peptide
therapy. However, for the purposes of longevity, we will review 3
essential peptides that we believe are paramount in one’s quest to live
longer, at optimal function:
- BPC-157
- CJC-1295 with Ipamorelin
- Epithalon (Epitalon)
Before we go into the amazing benefits these 3 peptides have, let’s
first define what a peptide actually is. Pep·tide - / ’peptīde/noun a
compound consisting of two or more amino acids linked in a chain, the
carboxyl group of each acid being joined to the amino group of the next
by a bond of the type -OC-NH-. Put simply, a small group of small chain
amino acids (protein building blocks) that when linked together target a
specific function in the body. Now that you have a very basic
understanding of what a peptide chain is, let’s get into the specifics.
BPC-157, The body protection compound (BPC), is a very versatile
peptide. (This happens to be one of our favorite ones as well) Not only
is it used for overall gastrointestinal (GI) health or to heal your
leaky gut, it also has additional properties to promote the health of
your connective tissue. When used for gut health, BPC-157, is amazing at
balancing your flora, and protecting the very vulnerable lining of the
intestine. When the gut is not the focus, BPC157 is prescribed to help
protect active individuals from injuries or to accelerate the overall
healing process. Few of the important benefits of BPC-157:
- Alleviate aches and pain
- Promoting tissue healing
- Heal and unhealthy gut
- Maintain a newly healed healthy gut
CJC-1295 with Ipamorelin is used to stimulate your growth hormone to
help build muscle, lean out, improve sleep, and improve recovery time.
CJC-1295 can increase serum growth hormone (GH) levels by
200-1000%, by stimulating your body’s own natural production. The
elevated growth hormone production and release continue for up to 6
days because CJC-1295 has a half-life of about 6-8 days. Ipamorelin
has an added effect because of its own ability to facilitates the
release of growth hormone (GH). This dynamic duo boosts the amount of
circulating GH in your body, making you feel and look younger. The
combination is just fantastic.
Some of the amazing benefits of CJC 1295 with Ipamorelin:
- Increase in lean muscle mass
- Decrease in body fat percentage
- Increased collagen, elastin, and fibrin production for younger skin
- Increase in restful sleep
- Increase in energy levels
- Improved cardiovascular function
- Stronger immunity
- Decreased joint and muscle pain
- Enhanced healing after injury
EPITHALON has a primary role to increase the natural production of
telomerase, a natural enzyme that helps cells reproduce telomeres,
which are the protective parts of our DNA. In essence, this allows the
replication of our DNA so the body can grow new cells and rejuvenate
old ones. In addition, it is used to improve specific aging mechanisms
like gene expression and autophagy. Short peptides like EPITHALON
regulate different cellular levels by embedding themselves into the
DNA chain. By being part of the DNA, Epithalon expands gene
expression. Epithalon also increases energy levels through autophagy,
the body’s mechanism of cleaning worn-out and damaged cells,
regenerating newer and healthier ones. Some of the show-stopping
benefits of Epithalon:
- Increases telomerase
- Improving telomere health
- Cellular regeneration
- Improves autophagy
- Expands gene expression
Does Metformin Increase Life Expectancy?
Metformin, a biguanide that combats age-related disorders and improves health span, is the first drug to be tested for its age-targeting effects in the large clinical trial—TAME (targeting aging by metformin). A 2020 review (Cell 2020) focuses on metformin’s mechanisms in attenuating hallmarks of aging and their interconnectivity, by improving nutrient sensing, enhancing autophagy and intercellular communication, protecting against macromolecular damage, delaying stem cell aging, modulating mitochondrial function, regulating transcription, and lowering telomere attrition and senescence. These characteristics make metformin an attractive gerotherapeutic to translate to human trials.
In humans, metformin has been in clinical use for over 60 years, studied extensively, has a high safety profile, and is uniquely positioned to intervene several crucial pathways responsible for aging and age-related diseases (Barzilai et al., 2016). As recommended by the American Diabetes Association, due to its glucose-lowering effects, metformin monotherapy is the preferred first-line pharmacological action against type 2 diabetes (American Diabetes Association, 2019).
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) increases telomere length
According to a 83 Year Old Doctor, HBOT lengthens telomere by 100% (YouTube 2024). A 2020 study, also concluded that HBOT may induce significant senolytic effects including significantly increasing telomere length and clearance of senescent cells in the aging populations.Conclusion and Key Takeaways
The best way to promote longevity and overall health is to engage in healthy practices like consuming a nutritious diet, engaging in regular exercise, improving your sleep and reducing stress.While some research suggests potential benefits from supplements, hormone therapy, or even stem cells in slowing aging, these shouldn't replace core healthy practices. A well-rounded approach is key for optimal well-being.
Focus on Fundamentals:
- Nutritious Diet: Prioritize a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for consistent physical activity, incorporating different types like cardio and strength training.
- Quality Sleep: Get enough restful sleep for optimal body and brain function.
- Stress Management: Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as meditation or spending time in nature.
Remember, supplements are not magic bullets. They should complement, not replace, a healthy lifestyle. Consult your doctor before starting any new supplement program to ensure safety and suitability for your individual needs.
Multi-Faceted Aging Solutions
Aging is a complex process with various contributing factors. Ideally, an anti-aging supplement should address these factors synergistically, meaning the components work together for a stronger effect.
- Epigenetics: Look for substances supporting a healthy epigenome, like alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) and NMN.
- Mitochondrial Health: Consider ingredients like AKG, fisetin, and malate to support healthy mitochondrial function.
Reliable Research: Always prioritize credible sources for information. Look for research published in peer-reviewed journals, searchable through platforms like PubMed or Google Scholar.
Age Defying Longevity (Now Available)
Let age be just a number.
The Wellness Company's science-backed Longevity formula maintains youthful cellular function, helping you feel your best no matter the year you were born.
Target the root causes of aging with Liposomal Glutathione – the “master antioxidant," Nicotinamide Riboside (NR), and Resveratrol. This age-defying combination helps your cells clean up “dirty” DNA to increase energy production and reduce inflammation.
The Wellness Company combine these powerful ingredients with probiotics superior absorption. Feel like a younger version of yourself, everyday.
LONGEVITY FORMULA CONTAINS:
- NR (Nicotinamide Riboside) - The best booster of your body’s natural production of NAD+, the key coenzyme required for hundreds of vital cellular processes.
- Liposomal Glutathione - Optimizes the body for healthy detoxification, supports tissue repair, and protects your cells from free radical.
- Resveratrol - A potent polyphenol that combats aging by activating sirtuin proteins to promote heart, cognitive and cellular health.
- Betaine HCl - Promotes healthy digestion
- Probiotics BL21, LRa05 and LC86 - Help your digestive system work more efficiently, supporting muscle, immune and cognitive health.









.png)


.png)
Comments
Post a Comment