Benefits of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids 2021: COVID-19, Heart Health, Diabetes and Knee Pain

Fish oil and flaxseed oil each contain an impressive amount of omega-3 fatty acids. The main types of omega-3s in fish oil are eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) (NIH).
On the other hand, flaxseed oil contains the omega-3 fatty acid known as alpha-linoleic acid (ALA) (Trusted Source). Flaxseed oil also contains linoleic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid. Linoleic acid and arachidonic acid (AA) are the Omega-6 fatty acids that have been found to possess potential cancer protective properties. The human body converts linoleic acid into GLA (Gamma-Linoliec Acid), and the latter get converted into AA.
However, ALA isn’t biologically active and needs to be converted to EPA and DHA to be used for something other than just stored energy like other types of fat (Trusted Source).
While ALA is still an essential fatty acid, EPA and DHA are linked to many more health benefits (Trusted Source). Additionally, the conversion process from ALA to EPA and DHA is quite inefficient in humans (Trusted Source). For example, one study found that only 5% of ALA is converted to EPA and less than 0.5% of ALA is converted to DHA in adults (Trusted Source).
EPA and DHA can reduce inflammation, which causes swelling and pain. Research has indicated that both acids might suppress the body’s immune system. However, a 2016 study suggests that DHA might enhance immune function instead. DHA is more effective at reducing inflammation than EPA, but both have a role.
Omega-3 and COVID-19
EPA and DHA have a direct influence in the immunological response to viral infections and can modulate immune response and function.
Animal-based omega-3 fats, especially DHA, also help prevent thrombosis (a blood clot within a blood vessel) by decreasing platelet aggregation. Hypercoagulation is another complication of severe COVID-19 infection that can have lethal consequences.
Omega-3 also lowers your risk of lung dysfunction, protects against lung damage and secondary bacterial infections, and improves mitochondrial function.
Research shows that by lowering triglycerides, the risk of developing a cytokine storm is diminished. Omega-3 supplementation is known to lower triglycerides, but krill oil does so more effectively than fish oil.
Omega-3 and Heart Health
Omega-3s - particularly EPA and DHA - are important for overall health, including heart health. Most people do not get enough EPA and CHA omega-3s, and new research suggests you may need even more than you think.
- Fatal Heart Attack - 35%
- Heart Attack (myocardial infarction)- 13%
- Risk of death form Coronary Heart Disease - 9%
Omega-3 and Knee Pain
EPA and DHA can reduce inflammation, which causes swelling and pain. Research has indicated that both acids might suppress the body’s immune system. However, a 2016 study suggests that DHA might enhance immune function instead. DHA is more effective at reducing inflammation than EPA, but both have a role.
For the omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil to work against arthritis, it’s necessary to consume a fairly large quantity of it each day. Fish oil — or cod liver oil — enclosed in capsules makes this fairly easy.
On the other hand, because cod liver oil contains very high amounts of vitamin A and vitamin D, taking too much can be toxic. For the purpose of treating arthritis, fish oil is the safer choice.
Omega-6 and COVID 19
One of the most notable characteristics of the virus is its spike proteins, which allows the virus to bind to the different cells in the body. It connects to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), known as the cellular gateway of the virus to invade and infect cells.
Now, a team of researchers at the Max Planck-Bristol Center for Minimal Biology and Bristol's School of Biochemistry has identified a druggable pocket in the virus's spike protein that can be used to prevent the infection of cells. The study findings, published in the journal Science, are a groundbreaking discovery that will help develop new therapies and drugs to stem the growing pandemic.
Omega-6 and COVID-19 study
To arrive at the findings of the study, the researchers, headed by Professor Imre Berger, and Professor Christiane Schaffitzel, utilized a powerful imaging technique, dubbed as the electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM), to study and explore the characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein at the atomic level. They produced the virus spike proteins in the laboratory to study them and determine their structure.
Powered by the Oracle high-performing cloud computing, the team has created a three-dimensional stricture of the virus spike protein, which allowed them to observe the structure and identify its molecular composition.
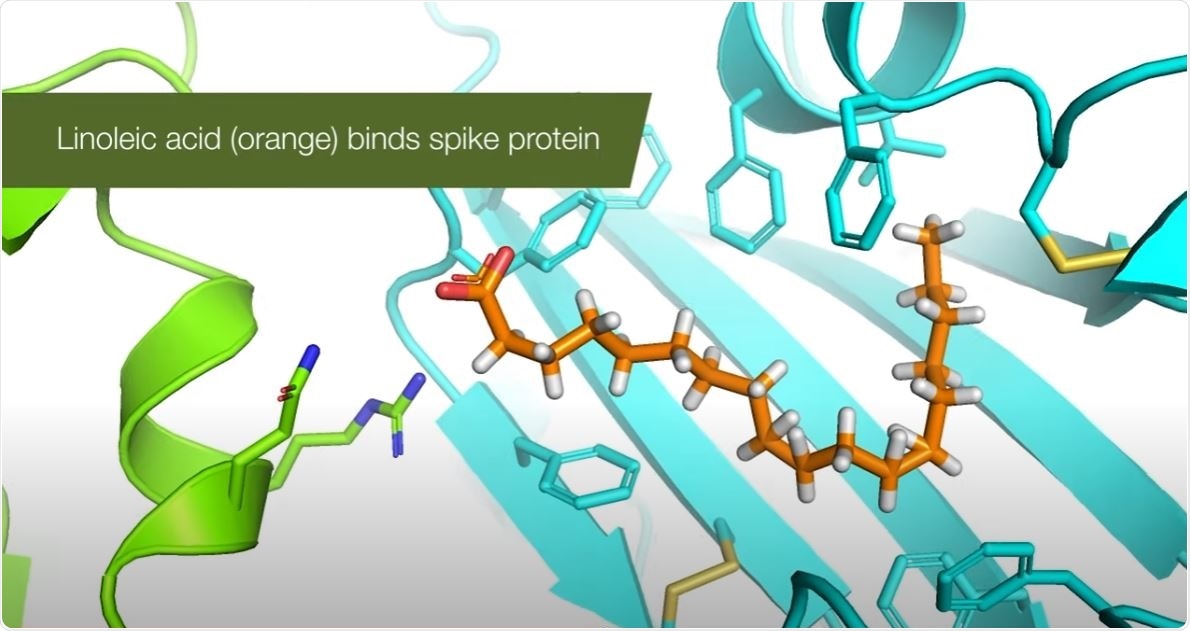
Upon the analysis of the molecular structure of the spike protein, the team has found something interesting. They revealed the presence of a small molecule, called linoleic acid (LA), which was discovered in a customized pocket within the spike protein.
What is linoleic acid?
The human body cannot produce linoleic acid, and it is found mainly in food. Intriguingly, LA plays a significant role in inflammation and immune modulation, which are key elements of the COVID-19 infection. Aside from that, these fatty acids are also essential to maintain cell membranes in the lungs to promote ventilation. LA also helps in the production of prostaglandins that protect against inflammation in the cardiovascular system. Linoleic acid is a small molecule and a free fatty acid essential for many cellular functions. Two fatty acids are essential in the diet – linoleic or omega-6 fatty acid and alpha-linolenic or omega-3 fatty acid. Both are polyunsaturated fatty acids, which means that they contain two or more double bonds."We were truly puzzled by our discovery and its implications. So here we have LA, a molecule which is at the center of those functions that go haywire in COVID-19 patients, with terrible consequences. And the virus that is causing all this chaos, according to our data, grabs and holds on to exactly this molecule – basically disarming much of the body's defenses," Professor Berger said.
The researchers also explained that in other illnesses, interfering with the metabolic pathways of the linoleic acid can induce systemic inflammation, pneumonia, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). All these health problems are seen in patients with COVID-19. The study findings provide the first direct link between LA, the health consequences, and the virus itself.
For instance, in the common cold virus, rhinovirus, scientists also discovered a similar pocket to develop molecules that attached firmly to the pocket to disrupt the structure, stemming from its infectivity. This same method can be used for SARS-CoV-2, potentially providing a method to combat the pandemic, which has now infected more than 32 million people, and killing at least 979,000.
Omega-3 and Diabetes
“Baseline plasma samples were analyzed for GAD65 antibodies and phospholipid n-3 PUFAs. Adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) for incident diabetes in relation to GAD65 antibody status and tertiles of plasma phospholipid n-3 PUFA or fish intake were estimated using Prentice-weighted Cox regression …
The hazard of diabetes in antibody-positive individuals with low intake of total and fatty fish, respectively, was significantly elevated (HR 2.52 and 2.48) compared with people who were GAD65 antibody negative and had high fish intake, with evidence of additive (AP 0.44 and 0.48) and multiplicative interactions.
Individuals with high GAD65 antibody levels (≥167.5 units/mL) and low total plasma phospholipid n-3 PUFAs had a more than fourfold higher hazard of diabetes …”








.png)
Comments
Post a Comment