Ivermectin, Hydroxychloroquine and Zinc for COVID-19: What are the Differences?
Ivermectin, hydroxychloroquine and zinc have received various media and social media attention for the past few months. 'No high quality evidence', "can only be used in a clinical trial setting', 'double blinded randomised controlled clinical trial needed', "insufficient data to recommend either for or against the use" are some of the medical and scientific technicalities that you might read in various social media channels. Confused?
The number of options for the treatment of COVID-19 has increased drastically in recent months, thus making it complicated when it comes to choosing the right combination. In general, there are 3 broad categories of medical interventions:
- Prevention or Prophylaxis e.g. vaccine
- Early out-patient treatment
- Hospital treatment
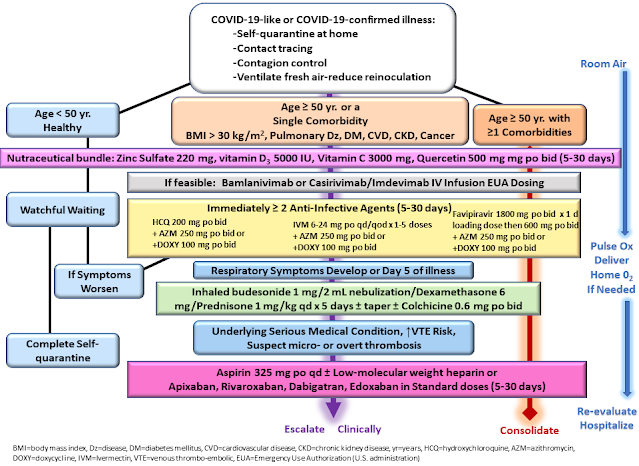
 |
| Image credit: Cleveland Clinic |
All these treatments come with various technical jargons, thus could be overwhelming and confusing for you as a consumer.
Generally, multiple treatments and strategies are used in combination to achieve the best possible outcome.
In this article, we would like to cover 3 popular treatments i.e. Ivermectin, Hydroxychloroquine and Zinc.
Ivermectin and COVID-19
Ivermectin and COVID-19 Updates:
“When the effectiveness of ivermectin for the COVID-19 pandemic is confirmed with the cooperation of researchers around the world and its clinical use is achieved on a global scale, it could prove to be of great benefit to humanity. It may even turn out to be comparable to the benefits achieved from the discovery of penicillin—said to be one of the greatest discoveries of the twentieth century.”—From Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19, published in the Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, March, 2021.
This international collaboration — comprised of physicians, like lead author Peter McCullough, MD, courageously treating patients despite the prevalence of “therapeutic nihilism” among government agencies like the NIH and FDA — outlines the urgency of, “prompt early initiation of sequenced multidrug therapy (SMDT) … to stem the tide of hospitalizations and death.”
The authors wrote:
The early stage of viral replication provides a therapeutic window of tremendous opportunity to potentially reduce the risk of more severe sequelae in high risk patients. Precious time is squandered with a ‘wait and see’ approach … resulting in unnecessary hospitalization, morbidity, and death. … In newly diagnosed, high-risk, symptomatic patients with COVID-19, SMDT has a reasonable chance of therapeutic gain with an acceptable benefit-to-risk profile.
Related Ivermectin and COVID-19 Publications:
- Review of the Emerging Evidence Demonstrating the Efficacy of Ivermectin in the Prophylaxis and Treatment of COVID-19 by Kory et al., provisionally accepted on American Journal of Therapeutics.
- Dr. Satoshi Ōmura, co-author of the newly published paper, “Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19” was one of the four researchers from Kitasato University in Tokyo, Japan who received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2015 for their discovery of ivermectin. Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19, published in the Japanese Journal of Antibiotics, March, 2021.
- A multi-centre randomised controlled study in Egypt (Elgazzar, Research Square) reported that the death rate was significantly lower in Ivermectin treated patients group (severe patients) vs non-Ivermectin group (2% vs 20%). 1,300 patients were included in this randomized controlled trial.
- This randomized controlled trial out of Iran (Hashim, pre-print) used Ivermectin and Doxycycline in mild, moderate, and severe hospitalized COVID-19 patients. No patients in the mild and moderate COVID-19 category died and 18% of the severe patients perished taking this medication combo. In the control group, no mild-moderate patients died, but 27% of the severe COVID patients died. The patients who also got Ivermectin had a shorter recovery.
- A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, phase 2 clinical trial at five hospitals (Iran) and 180 patients with mild to severe disease (Niaee, ResearchSquare, Nov 2020). Ivermectin as an adjunct reduced the rate of mortality, the duration of low oxygen saturation, and the duration of hospitalization.
- The ICON study in US, published in Chest, Oct 2020 reported that Ivermectin treatment was associated with lower death rate vs Control (13.3% vs 24.5%) during treatment of COVID-19, especially in patients with severe pulmonary involvement.
- A double-blinded randomised controlled study in Bangladesh (Mahmud et al) reported that the death rate was 0% (0/183) in the Ivermectin arm vs 1.67% (3/180) in the control arm in mild to moderate COVID-19 patients.
- The IDEA (Ivermectin, Dexamethasone, Enoxaparin and Aspirin) study from Argentina reported 1 death out of 167 patients studied. The patient that died was a severe COVID-19 patient that required ventilator support.
- The pre-AndroCoV trial from Brazil reported that early detection of COVID-19 followed by a pharmaceutical approach with different drug combinations (Azithromycin, Hydroxychloroquine, Nitazonide, Ivermectin) yielded irrefutable differences compared to non-treated controls in terms of clinical outcomes, ethically disallowing placebo-control randomized clinical trials in the early stage of COVID-19 due to the marked improvements.
- A retrospective study out of Bangladesh (Khan, Archivos de Bronconeumologia 2020). This retrospective study enrolled a total of 325 from April to June 2020. 248 adult COVID-19 patients were looked at in two groups, 115 received ivermectin plus standard care (SC), while 133 received only standard care (SC). This study showed that Ivermectin was efficient at rapidly clearing SARS-CoV-2 from nasal swabs (median 4 days). This was much shorter than in the COVID-19 patients receiving only SC (15 days) or receiving a combination of three antiviral drugs (7–12 days). In addition, fewer Ivermectin patients developed respiratory distress leading to ICU admission. In fact, with Ivermectin, there was a quick hospital discharge (median 9 days) in 114 out of 115 patients; the one remaining patient had been admitted with advanced disease.
Ivermectin for COVID-19: Real-time meta analysis of 50 studies
- 100% of the 50 studies to date report positive effects (25 statistically significant in isolation). Random effects meta-analysis for early treatment and pooled effects shows an 81% reduction, RR 0.19 [0.09-0.38], and prophylactic use shows 89% improvement, RR 0.11 [0.06-0.22]. Mortality results show 76% lower mortality, RR 0.24 [0.14-0.42] for all treatment delays, and 84% lower, RR 0.16 [0.04-0.63] for early treatment.
- 100% of the 26 Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) report positive effects, with an estimated 70% improvement, RR 0.30 [0.20-0.46].
- The probability that an ineffective treatment generated results as positive as the 50 studies to date is estimated to be 1 in 1 quadrillion (p = 0.000000000000001).
Related: List of Doctors that will prescribe Ivermectin
Hydroxychloroquine and COVID-19
- HCQ is effective for COVID-19. The probability that an ineffective treatment generated results as positive as the 231 studies to date is estimated to be 1 in 3 quadrillion (p = 0.0000000000000003).
- Early treatment is most successful, with 100% of 28 studies reporting a positive effect (12 statistically significant in isolation) and an estimated reduction of 64% in the effect measured (death, hospitalization, etc.) using a random effects meta-analysis, RR 0.36 [0.25-0.51].
- 92% of Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) for early, PrEP, or PEP treatment report positive effects, the probability of this happening for an ineffective treatment is 0.0032.
- There is evidence of bias towards publishing negative results. 88% of prospective studies report positive effects, and only 73% of retrospective studies do.
- Studies from North America are 3.9 times more likely to report negative results than studies from the rest of the world combined, p = 0.0000000013.
Hydroxychloroquine and COVID-19 Updates:
With the latest large Iranian study, we now have 13 studies on early hydroxychloroquine treatment with mortality data.
— Covid19Crusher (@Covid19Crusher) April 7, 2021
With unambiguous results. pic.twitter.com/FvYW7Y1egX
Zinc and COVID-19
Foods that are high in zinc include oysters, crab, lobster, mussels, red meat, and poultry. Cereals are often fortified with zinc. Most multivitamin and nutritional supplements contain zinc.As of April 2021, there are more than 50 studies that have been launched to investigate the benefits of Zinc against COVID-19. You can review the status of these trials on clinicaltrials.gov.
Taking zinc long term is typically safe for healthy adults, as long as the daily dose is under the set upper limit of 40 mg of elemental zinc (PubMed).
Excessive doses may interfere with copper absorption, which could negatively affect your immune system as it can cause copper deficiencies, blood disorders, impair the absorption of antibiotics and potentially permanent nerve damage or loss of smell.
Zinc Sulphate is also part of Dr. Vladimir Zelenko anti-coronavirus experimental protocol. Please take note that the protocol is experimental and has not been 100% proven. Do discuss with your doctor before taking the medication as per the protocol. You can check out his publication in the International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents.
Based on the statement released on 2 October by the U.S. president’s physician, zinc is also part of the treatment given to the US President. According to the president's physician, "Trump has been taking zinc, vitamin D, famotidine, melatonin and a daily aspirin.”
Ivermectin vs Hydroxychloroquine vs Zinc
Nutrients are safer alternatives especially if your risk is low e.g. age below 50 and no other chronic illness. Discuss with your doctor on the benefit vs risk for each treatment. If you are on multiple medications, be aware of supplement-drug interactions that might enhance the possibilities of adverse effects.
- Quercetin: 1 capsule daily (Amazon)
- Zinc, Vitamin D3 and Vitamin C: 1 lozenge daily (Amazon)
- Melatonin: 1 tablet before bedtime (causes drowsiness) (Amazon)
- treatment (therapeutic) dosages are normally higher than the RDA dosages and
- 'maintenance' or 'preventive' dosages that are normally based on the recommended daily value.

.png)





Comments
Post a Comment