This article compiles more than 200 references and supporting studies related
to the anti-aging or slowing the aging process. This article will also reveal
exciting new information about a variety of immune-enhancing natural products
and nutrients that may help you maintain youthful immune system function into
advancing age.
We created this article to help you find the top-rated supplements containing
vitamins and other ingredients for healthy aging.
Aging can be defined as the time-related deterioration of the physiological
functions necessary for survival and fertility. The characteristics of
aging—as distinguished from diseases of aging (such as cancer and heart
disease)—affect all the individuals of a species.
NAD, stem cells, nitric oxide, CoQ10, glutathione, glycine and taurine
decline as we age. Vitamin and mineral deficiencies are also common in older
individuals.
Methodology: The selection or short-listing of the list below is based on
the available scientific evidence retrieved from scientific database such
as PubMed and scientific search engine such as Google Scholar. The article
will also be updated as and when there is a newly discovered major
research publication related to anti-aging.
There are many supplements that claim to have anti-aging effects, but not
all of them are backed by scientific evidence. Not all the supplements below
are required. You are advised to consult with your trusted healthcare
provider before taking these supplements. Some of the most researched and
promising supplements for healthy aging include
How did we rank the best anti-aging supplements?
Choosing supplements can be difficult for consumers, and thorough
research into the product is necessary to ensure quality. The U.S. Food
and Drug Administration (FDA) only regulates dietary supplements as
food, not drugs, and considers them a product to supplement the diet.
Unlike drugs that must be proven safe and effective before marketing,
supplements only need their manufacturer’s verification for identity,
purity, strength, and composition, according to the FDA’s
Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP) regulations.
The FDA doesn’t require a
standardization process to ensure batch-to-batch consistency of the
products and identify specific chemicals or markers that qualify for
product consistency or product control.
Quality-control tests
are expensive, and many supplement companies don’t bother with them and
will put a product on the shelves anyway. Although quality issues have
resulted in lawsuits and trouble with the FDA, this is still a serious
problem in the industry.
Finding quality supplements takes
asking tough questions, including asking how many quality-control tests
they run and what kinds of tests they run.
Knowing the number
of tests is essential since the industry standard is to test for about
105 pesticides. However, the best companies use Pesticide Analytical
Manual (PAM) screening, which is more expensive but screens for 325
pesticides.
When asking a company how often it runs quality controls, Professor
Emeritus Steve Chaney from the University of North Carolina School of
Medicine, said the numbers should run into the tens of thousands each
year. He suggests asking the following questions about the analytic
methods used:
-
Does the company perform DNA testing for the authenticity of the raw
ingredients and non-GMO claims?
-
Does it use high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry
(HPLC/MS) testing? This analytic method identifies and quantifies the
final product’s chemical composition and ensures it contains the
correct amount of active ingredients without contaminants. Many
companies forego this test because of cost.
-
Does it use inductively coupled plasma/mass spectrometry (ICP/MS)
testing, a highly sensitive elemental testing technique to detect
heavy metal contamination? This test costs supplement companies even
more than HPLC/MS testing, and it is rarely used.
- Does it test for microbial contamination?
-
If the product doesn’t meet specifications, what does the company do
with it?
Supplements that have been independently tested and certified by a
nonprofit program, such as NSF® International or USP®, are likely to be of
high quality. These programs test supplements for content, purity, and
freedom from contaminants. An NSF or USP seal helps you know that products
contain what their labels say they contain, disintegrate properly in the
body, do not contain any contaminants, and have been manufactured in
accordance with current Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) in a
GMP-certified facility.
Best Anti-Aging Supplements in 2024: an overview
In the field of longevity products, we selected, in our opinion, the
best anti-aging supplements that might help you address processes resulting in
accelerated aging and the appearance of related symptoms.
Remember that while these supplements may propose some benefits, the sole
supplementation with them cannot be the only approach to healthy aging.
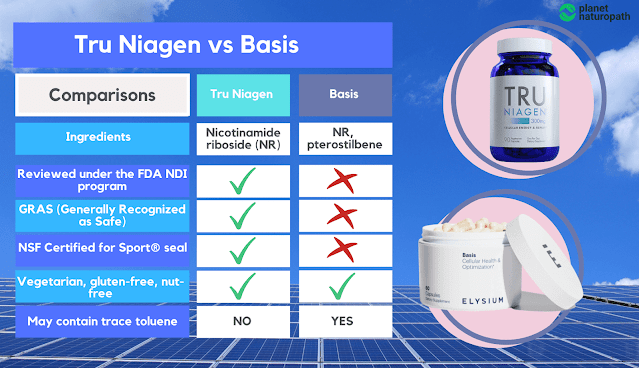
1. Tru Niagen — overall best longevity supplement

TRU Niagen NAD+ Supplement comes in 3 sizes:
Tru Niagen tops our list for a good reason — it's formulated with
nicotinamide riboside (NR) as its primary active ingredient. NR is
believed to be an effective precursor to Nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide (NAD+), a crucial co-enzyme involved in various
biological processes that may influence longevity.
Adding
to the appeal of this product is Niagen®, a form of NR that the
company has patented and safety-reviewed. It is generally
recognized as safe (GRAS).
ChromaDex markets TruNiagen, which is based on its branded Niagen
ingredient, which is a form of nicotinamide riboside (NR), the
form of nicotinamide that actively crosses into the cell to
participate in the NAD+ pathway (
R).
Creators claim that Niagen® can promote NAD+ production more
effectively than other precursors due to its design, which may
allow it to pass through cell walls easily.
Unlike NMN, the key ingredient Niagen was successfully notified
two times as an NDI (New Dietary Ingredient) and reviewed as GRAS
(Generally Recognized As Safe) under the United States
notification programs.
As per the brand, while you may
not notice changes immediately, Tru Niagen begins to boost NAD+
levels in your body starting from the first dose. They suggest
that after eight weeks of taking their 300 mg dose daily, your
baseline NAD+ levels should elevate by about 40 to 50%.
While
Tru Niagen's offering appears to have the right formulation
aligned with science, its inclusion at the top of our list isn't
solely due to this reason. This supplement also offers
convenience, with the brand offering the product in five different
sizes, including one available in powdered form — a convenient
solution for those who have trouble taking capsules.
While
various bottle sizes are available, Tru Niagen's 90-capsule
bottle, good for a 3-month supply, seems to strike the perfect
balance. It is priced at $119.95 for a one-time purchase.
Pros
- Contains GRAS NAD+ precursor
- Multiple sizing options to choose from
- Available in powder form
- Clinically evaluated dose
Cons: Perhaps not the most budget-friendly choice
While this is not a scientific review I have been taking Niagen in
one form or another non stop for several years. I have been
gradually increasing my doses with what I can only describe as a
profound effect. Without a doubt I feel younger than 46. I also
think I look younger than most people my age. I certainly don't feel
my age and have a ton of energy every single day. I also try to eat
plenty of vegetables with lots of non meat proteins along with
limited meat consumption. I am not a health nut but basically try to
stay away excess sugars and processed foods whenever I can. I also
do a hard bike ride once or twice a week. I think this also helps
the entire aging process some.
2. Nordic Naturals Omega-3
Amazon Reviews: 4.8 out of 5 - more than 49,000 global ratings
The fish oils used in Nordic Naturals’ products typically range between
TOTOX values of 5 and 14.
Recent tests of Nordic Naturals raw fish oils report TOTOX values of 7.0.
Note: TOTOX value stands for total oxidation value. The omega 3 fatty
acids EPA and DHA from fish oil are highly sensitive to oxidation. This
means that they are rapidly affected by contact with oxygen. Oxidised
fatty acids are not beneficial to our health. For this reason, a good fish oil supplement has a low TOTOX value. The maximum TOTOX value is set at 26 by the Global Organization for
EPA and DHA omega-3.
Best Fish Oil Supplements Consumer Reports:
"Nordic Naturals did meet every other quality measure in our study. The
pills, which cost about 67 cents per day, or $243 per year, contained
their labeled amount of omega-3 fatty acids and met other U.S.
Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Union standards, including those for
contaminants such as lead, mercury and dioxins. They also met the
stricter California Proposition 65 standard for total polychlorinated
biphenyls (PCBs)." -
Consumer Reports
NovosLabs.com:
"Ideally, you take an omega-3 oil supplement that contains both
fish-derived triglycerides and krill-derived phospholipids. Examples of
such brands are (not sponsored) Omega3 Innovations (sells fish oil with
very low oxidation / TOTOX values) and
Nordic Naturals."
-
NovosLabs.com
Related: Many common omega-3 fish oil supplements are ‘oxidized’
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation, enable the immune system to carry
out its tasks, and help the brain and eyes to function properly.
Best Evidence: A 2021 report (
Nature Communications) suggest that higher levels of omega 3 fatty acids in circulation
correlate with lower risk of premature death from age-associated
diseases such as cardiovascular disease and cancer.
The analysis was conducted with data from 17 prospective cohort studies examining the associations between blood omega-3 fatty acid
levels and risk for all-cause mortality. Over a median of 16 years of follow-up, 15,720 deaths occurred among
42,466 individuals. The researchers found that, after adjustment for relevant risk
factors, risk for death from all causes was significantly lower (by
15-18%, at least p < 0.003) in the highest vs the lowest quintile for
circulating long chain (20-22 carbon) omega-3 fatty acids
(eicosapentaenoic, docosapentaenoic, and docosahexaenoic acids). Similar
relationships were seen for death from cardiovascular disease, cancer
and other causes.
The DO-HEALTH trial, published in
Frontiers in Aging 2022. The first randomized-controlled trial (DO-HEALTH) trial to investigate
the combination of three complementary treatments for the prevention of
cancer and suggest that the combination of
daily vitamin D3, supplemental marine omega-3s, and a simple home
exercise program may be effective in the prevention of invasive cancer among generally
healthy and active adults aged 70 and older. Findings from this 3 year
Randomized Controlled Trial with more than 2,000 participants observed a 61%
reduction in the risk of invasive cancer among patients who completed a home
exercise program and took vitamin D
3 and omega-3 fatty acids daily.
3. Thorne — best longevity supplement for heart health
Ratings: 4.3 out of 5 - more than 4,000 global ratings.
Of the longevity supplements on our list, Thorne's offering is
advertised as a dual-action formula intended to support heart health and
healthy metabolism. The core active ingredient in the dietary supplement
is berberine, a botanical extensively studied for its potential to help
regulate blood sugar and keep cholesterol levels in a healthy range.
Not
just any berberine — Thorne uses the best-researched form of berberine,
berberine HCl, and combines it with the highly absorbable berberine
phytosome.
When it comes to quality, the brand’s defining trait
is that a large portion of its supplements bear the NSF Certified for
Sport® mark — a mark that ensures the products are free of substances
banned by major athletic organizations and safe for athletes to use.
Better
yet, Thorne's page states that they're the pick of champions and trusted
by professional sports teams. And these aren’t just buzzwords or a
marketing trick of sort — the brand is actually backed by the likes of
basketball Hall of Famer and Miami Heat legend Dwyane Wade, as well as NBA
champion guard Jrue Holiday.
Now, when discussing allergens,
you'll be glad to know that Thorne's Berberine is free from the major
ones. However, a detail worth noting is that while the product doesn't
contain peanuts, it does contain pea protein, which can still trigger
reactions in people with severe peanut allergies, so just keep that in
mind.
Pros
- Contains the well-researched berberine HCl
- NSF Certified for Sport®
- Brand trusted by sports legends
- Major allergen-free
Cons: Contains pea protein
I've been taking this supplement with several others for years to help
support my adrenal health and weight loss goals.
4. Nutricost Niacinamide (Best Affordable Anti-Aging Supplement)
Do not confused with Nutricost Niacin. Niacin is the form that may cause 'Niacin Flush'. Niacinamide
is the 'non-flush' form.
- Technically, Niacinamide is not the same molecule as NMN but
they are both NAD precursors and are categorised under Vitamin B3
(Niacin) supplements by Amazon.com.
- Niacinamide is a popular form of Vitamin B3, but without the often
uncomfortable feeling known as "Niacin Flush". Vitamin B3 is most
often found in meats like tuna and beef. However, in order to get a
similar amount of Vitamin B3, you would have to eat large amounts of
tuna and beef or other sources containing Vitamin B3.
- Technically, Niacinamide is not the same molecule as NMN but they
are both NAD precursors and are categorised under Vitamin B3
(Niacin) supplements by Amazon.com. Since, Niacinamide is the #2
best seller under this category, we have decided to feature them as
part of the best 10 list.
- 240 Capsules of Niacinamide Per bottle / 1 Capsule per serving
- 500mg of Vitamin B3 (Niacinamide) Per Capsule
- No "Niacin Flush"
- Non-GMO, Gluten Free, Soy Free, and Made in a GMP Compliant, FDA
Registered Facility
After a recent news article about this being a favorite supplement
in Australia for sun damage protection, I asked my dermatologist
about it. She said it might help prevent me getting as many
'barnacles' as she calls them. You know, those nasty, old-age,
sun-damage, crunchy brown or white patches all over your body. (I
have many). I'm still on my first bottle but after about two weeks
the most amazing thing happened. I happened to scratch an area near
one of my barnacles and it just flaked off in my hand. Since then,
many more have succumbed. Not all; just some. But I'm happy. Even
one less of those ugly bumps is an improvement.
Niacinamide Review
Dr. Conlon has concluded, and Dr Mercola thoroughly agree with her,
that the best single NAD+ precursor is niacinamide (also known as
nicotinamide), not niacin, NR or NMN. It is now beyond obvious to me
why no one is promoting niacinamide. This is because it costs less
than one cent a day and as a result there is simply no money to be
made in promoting it. Ideally you buy niacinamide powder and use 1 to 1/2 of 1/64th of a teaspoon three times a day
(25-50 mg). - Mercola.com.
5. Sports Research Vitamin D3 + K2
Created in 1980, Sports Research is a privately-owned business
born from a passion for fitness, wellness, and healing.
NEW SOFTGEL SHELL: Sports Research Vitamin D3+K2 Plant-gel capsules
now contain added Turmeric Root Powder in the outer softgel shell.
This added plant-based yellow color helps protect the active
ingredients inside against photo-degradation that may occur from
exposure to UV light. While the appearance has changed, we can
assure you that our Vitamin D3+K2 still contains the same great
ingredients you know and love
More than 100,000 customer reviews and a 4.8 out of 5 overall rating
on Amazon.
-
Contains 5000 IU (125mcg) of Vegan Vitamin D3 & 100 mcg of
Vitamin K2 as MK-7. Suitable for those whose vitamin D level is deficient or
insufficient.
-
Made with Vitashine D3 - a patent, plant based form of Vitamin D3
from Lichen and MenaQ7 - a patent form of MK7 from Chickpea
-
100% Plant based - Vegan Certified & Non-GMO Verified. Soy,
Gluten, Gelatin & Carrageenan free
Vitamin D supplements by Sports Research are available in
various dose strengths:
6. Paleovalley Essential C Complex (Best Whole Food Vitamin C
Supplement)
Ratings: 4.8 out of 5 - more than 1,700 global ratings.
Ascorbic acid vs whole food vitamin C? Ascorbic acid is NOT the same
as whole food vitamin C. If you were to compare the two to a car,
vitamin C would be the whole car, fully functional, and the engine is
an enzyme called tyrosinase, while ascorbic acid is the car frame,
with no moving parts.
Whole food vitamin C can also boost
your copper level, as vitamin C contains an enzyme called tyrosinase,
which has 2 atoms of copper in it. Acerola cherry is one excellent
source. A single acerola cherry contains about 80 mg of whole food
vitamin C. Ascorbic acid is prooxidant, while vitamin C complex is
actually an antioxidant. Anything that has copper is going to be
antioxidant.
An
umbrella review* (Xu 2022) to assess the existing systematic reviews and meta-analyses for
the association between vitamin C intake and multiple health outcomes;
showed that vitamin C intake was associated with reduced risk of
all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease (CVD), oesophageal cancer,
gastric cancer, cervical cancer and lung cancer with an increment of
50–100 mg per day. Beneficial associations were also identified for
respiratory, neurological, ophthalmologic, musculoskeletal, renal and
dental outcomes. A
total of 76 meta-analyses (51 papers) of randomised controlled trials and observational studies with
63 unique health outcomes were identified. Harmful associations were
found for breast cancer and kidney stones for vitamin C supplement
intake.
7. Optimized CoQ10 with PQQ from The Wellness Company (TWC)

Wouldn't it be natural to do everything possible to prevent your number one killer? Heart disease is the No. 1 killer for men and women (CDC), and according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about half of American adults have at least one of three key risk factors for heart disease (high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, and smoking).
CoQ10
CoQ10, also known as coenzyme Q10, is one of the most popular dietary supplements for heart health and overall wellness.
A study showed that ubiquinol-10 may enhance mitochondrial activity by increasing levels of SIRT1, PGC-1α, and SIRT3 that slow the rate of age-related hearing loss and protect against the progression of aging and symptoms of age-related diseases.
In studies using Alzheimer’s disease models, CoQ10 administration significantly delays brain atrophy and characteristic β-amyloid plaquing. In a 4 month clinical study on around 100 Alzheimer’s patients who took an oral mixture of vitamins E, C, CoQ10, and α-lipoic acid, the group receiving supplementation showed significant reductions in oxidative stress markers and subsequent DNA damage.
Individuals with Parkinson’s disease tend to show increased levels of oxidized (and by definition: damaged) CoQ10. They also have significant increases in markers of oxidative stress and damage in their brains, which is partially reversible with CoQ10 administration.
One last important clinical note: recall that the heart is filled with mitochondria which are partially powered by CoQ10. If you are taking a statin drug, please be aware that they deplete your body of CoQ10, so supplementation is a must.
CoQ10 Recommended Dosage
CoQ10 dosages of 90 to 200 mg per day are often advised, while larger doses of 300 to 600 mg may be necessary for specific illnesses. CoQ10 is a supplement is generally well-tolerated and safe.
Pyrroloquinoline Quinone (PQQ)
Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) also called methoxatin is contained in fruits and vegetables such as kiwi fruit and green peppers. It has received a lot of research attention in the past several years. PQQ can reduce reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and improve the apoptosis (death) of tumor cells. PQQ protects tissues by regulating the redox (electron transfer) reaction. Moreover, PQQ protects overall tissue function by improving the mitochondrial function of the liver, neurons, and other important tissues. It can also reduce atrophy in mouse skeletal muscles.
PQQ decreases oxidative stress (production of ROS) and inflammation which, by definition, will protect mitochondria. It also increases mitochondrial biogenesis, which is the formation of new, young-acting mitochondria. It is neuroprotective, too. Here’s how. Recall that you have read about GABA versus glutamate or inhibitory (relaxing) versus excitatory (too stimulating) neurotransmitter activity. We want more GABA than glutamate, plain and simple. Too much glutamate damages brain cells. PQQ protects neurons by preventing the long-term over-activation of the glutamate (NMDA) receptors, which results in toxic excitotoxicity of neurons. This over-stimulation of brain cells is associated with many neurodegenerative diseases and seizure disorders.
Recall again that you have the largest concentration of mitochondria in your brain, heart, and skeletal muscles. The brain “wins” pound for pound by a little edge, which is why you feel tired after using your brain all day. With this in mind, remember that when we protect the brain, we’re protecting brain mitochondria. PQQ protects the brain (to a certain extent) against neurotoxicity induced by mercury and other potent toxins such as mold mycotoxins. Lastly, it too helps to prevent the accumulation of amyloid tau and beta proteins associated with Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases.
What causes aging symptoms to appear?
The reasons for aging symptoms to appear may vary from person to person, depending on numerous factors.
Aging is a complex and multifaceted process characterized by a gradual decline in physical well-being and diminished health. This decline is typically linked to the time-dependent accumulation of cellular damage caused by various genetic pathways and biochemical processes.
These factors, individually or collectively, contribute to cell senescence, reducing their ability to repair, proliferate, and communicate effectively. Consequently, this leads to subsequent tissue damage. Over time, tissue damage may manifest in various physical, cognitive, sensory, or metabolic symptoms, resulting in visible signs of aging, an increased risk of age-related conditions, and reduced quality of life.
Although some of the above-mentioned causes of aging symptoms cannot be prevented, they may be slowed down with some anti-aging supplements containing micronutrients.
Most researched ingredients in supplements that might help with anti-aging
With the ongoing scientific research in the field of anti-aging supplements for longevity, scientists have differentiated some ingredients demonstrating potential benefits for promoting youthfulness while aging.
The ingredients described below can also be found in the best anti-aging supplements included on our list.
1. Vitamin D3, Omega-3 and K2
Vitamin D3 and K2
Can Vitamin D extend lifespan? Higher levels of vitamin D are associated with less risk of heart disease, auto-immune diseases, improved brain health and a better functioning immune system.
Best Meta-analysis Evidence: A meta-analysis of 18 randomized controlled trials (RCT) including over 57,000 subjects found that intake of daily doses of vitamin D supplements decreased total mortality rates (
Autier 2007).
The DO-HEALTH trial, published in
Frontiers in Aging 2022. The first randomized-controlled trial (DO-HEALTH) trial to investigate the combination of three complementary treatments for the prevention of cancer and suggest that the combination of
daily vitamin D3, supplemental marine omega-3s, and a simple home exercise program may be effective in the prevention of invasive cancer among generally healthy and active adults aged 70 and older. Findings from this 3 year Randomized Controlled Trial with more than 2,000 participants observed a 61% reduction in the risk of invasive cancer among patients who completed a home exercise program and took vitamin D
3 and omega-3 fatty acids daily.
Optimizing your vitamin D level is one strategy that can boost your health in myriad ways. A deficiency in vitamin D has been implicated in such problems as multiple sclerosis (
R) and Parkinson’s disease (
R), for instance. The link between Parkinson’s and vitamin D is so strong that one study found people with high vitamin D levels had a 65% lower risk of Parkinson’s compared to those with low vitamin D levels (
R).
In addition, optimizing your vitamin D levels is one of the absolute best affordable strategies to slash your cancer risk.
Previous research found that a vitamin D level of 47 ng/ml was associated with a 50% lower risk of breast cancer (
R). Further, researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine reported that raising your vitamin D level to at least 40 ng/ml can slash your risk of all invasive cancers by 67% (
R).
Many governments advise 400 to 800 IU of vitamin D per day, while many vitamin D researchers claim you need at least 2000 to 4000 units per day.
We would recommend to take at least 2000 units per day. The risk of excess accumulation of vitamin D is negligible with this amount. Make sure it’s vitamin D3, and not vitamin D2 – the vitamin D3 variant works better.
“We [in the medical community] are beginning to realize the anti-inflammatory effects of vitamin D,”
says Amanda Frick, a licensed naturopathic doctor and acupuncturist in Santa Monica, California. It builds bone, boosts immunity, guards against chronic ailments, and is responsible for increasing absorption of calcium and magnesium. If you’re still not sold on vitamin D as one of the anti-aging supplements to add to your regimen, Frick says it can also assist with
weight loss when combined with lifestyle intervention.
Theoretically, we should get enough vitamin D through our diet and from the sun, but for many of us, that’s not the case. In the United States, 35% of adults and 61% of people over the age of 65 are deficient in vitamin D.
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased risk of osteoporosis, weakness, and bone fractures in the elderly, among other things. Recent studies also show a link between vitamin D deficiency and cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer (
Sizar, 2020).
Vitamin D ensures that your blood levels of calcium are high enough to meet your body’s demands. However, vitamin D does not fully control where the calcium in your body ends up. That’s where vitamin K steps in. Vitamin K2 supplements have been proven to be more effective than vitamin K1. That's why most of the top vitamin D supplement brands do combine their vitamin D3 with K2.
Make sure to take 500 mg to 1000 mg of magnesium and 150 mcg of vitamin K2, (not K1) which are important cofactors for optimizing vitamin D function.
Data from nearly 3,000 individuals reveal you need 244% more oral vitamin D if you're not also taking magnesium and vitamin K2. What this means in practical terms is that if you take all three supplements in combination, you need far less oral vitamin D in order to achieve a healthy vitamin D level.
And, remember the only way you know what your vitamin D level is, is to test it. Vitamin D level should be in a therapeutic range of 50 to 70 ng/ml for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Most people are shocked how low their level is when they finally get around to testing it.
Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation, enable the immune system to carry out its tasks, and help the brain and eyes to function properly.
Best Evidence: A 2021 report (
Nature Communications) suggest that higher levels of omega 3 fatty acids in circulation correlate with lower risk of premature death from age-associated diseases such as cardiovascular disease and cancer.
The analysis was conducted with data from 17 prospective cohort studies examining the associations between blood omega-3 fatty acid levels and risk for all-cause mortality. Over a median of 16 years of follow-up, 15,720 deaths occurred among 42,466 individuals. The researchers found that, after adjustment for relevant risk factors, risk for death from all causes was significantly lower (by 15-18%, at least p < 0.003) in the highest vs the lowest quintile for circulating long chain (20-22 carbon) omega-3 fatty acids (eicosapentaenoic, docosapentaenoic, and docosahexaenoic acids). Similar relationships were seen for death from cardiovascular disease, cancer and other causes.
According to another review (
Nutrients, September 2022), data from scientific literature 'overwhelmingly' supports beneficial effects of omega-3 fatty acids on the length of telomeres, reported to be a marker of biological age.
The Framingham study group is one of the longest-running longitudinal health data sets in existence. Since 1971, the residents of this small Massachusetts town have given us everything from heart health data to their knee annual MRI images. That’s where the data for this new Omega-3 research originates.
The study, published in The
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (Oct 2021), used data from a long-term study group, the Framingham Offspring Cohort, which has been monitoring residents of this Massachusetts town, in the United States, since 1971.
The research looked at 2,200 people who were monitored for 11 years for their blood fatty acid levels. The researchers found that omega-3 levels in red blood cells are very good mortality risk predictors. That means that higher levels of Omega-3 in the blood from regularly eating oily fish, increased life expectancy by almost five years.
This research comes a few months after a meta-analysis of 17 prospective cohort studies was published in
Nature Communications (above). The analysis linked higher circulating omega-3 fatty acid levels to longevity. In a pooled analysis of the studies, participants in the highest fifth of combined blood DHA and EPA were 15 to 18 percent less likely to die from any cause over the follow-up period (median follow-up time is 16 years in these studies). Higher blood omega-3s were also associated with a reduced risk for death from cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Published in 2022, the
Cognitive impAiRmEnt Study (CARES Trial 2), was designed to examine the potential synergistic effects of a combination of omega-3 fatty acids (namely DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid [EPA]), xanthophyll carotenoids (specifically lutein, zeaxanthin and meso-zeaxanthin) and vitamin E (d-α-tocopherol) on the cognitive performance of cognitively healthy older adults.
In conclusion, the CARES research has shown improvements in working memory following 24-month supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids, xanthophyll carotenoids (lutein and zeaxanthin) and vitamin E in cognitively healthy older adults. This study provides Class II evidence that 24-month supplementation with 430 mg DHA, 90 mg EPA, 10 mg lutein, 2 mg zeaxanthin, 10 mg meso-zeaxanthin and 15 mg vitamin E (d-α-tocopherol) is effective in improving cognitive performance, namely working memory, in cognitively healthy older adults.
These results support a biologically plausible rationale whereby these nutrients work synergistically, and in a dose-dependent manner, to improve cognitive performance. These findings illustrate the importance of nutritional enrichment in improving cognition and enabling older adults to continue to function independently, and highlight how a combination of omega-3 fatty acids and xanthophyll carotenoids may prove beneficial in reducing cognitive decline and/or delaying Alzheimer's disease onset in later life. (
Power 2022).
Many governments recommend eating omega-3 containing fatty fish, two times per week. But that is often not enough. Ideally, people would need to eat fatty fish four times per week, while also supplementing with omega-3 fatty acids, at least 1,000 mg of pure omega-3 (DHA and EPA) per day.
Make sure you buy high-quality omega-3 fatty acid supplements, meaning that the omega-3 fatty acids are pure and have not oxidized much (having low “TOTOX” value).
TOTOX value stands for total oxidation value. The omega 3 fatty acids EPA and DHA from fish oil are highly sensitive to oxidation. This means that they are rapidly affected by contact with oxygen. Oxidised fatty acids are not beneficial to our health. For this reason, a good fish oil supplement has a low TOTOX value. The maximum TOTOX value is set at 26 by the Global Organization for EPA and DHA omega-3.
Vitamin K2
In a
2022 study, researchers even revealed vitamin K2 modulates mitochondrial dysfunction caused by neurotoxins. Vitamin K2 also inhibited the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and promoted mitophagy, which is the removal of damaged mitochondria via autophagy — an essential function to maintain cellular health. Writing in the journal Nutrients, the scientists explained:
“… [V]itamin K2 can reduces mitochondrial damage, and … this effect is related to the participation of vitamin K2 in the regulation of the mitochondrial quality-control loop, through the maintenance of the mitochondrial quality-control system, and repair mitochondrial dysfunction, thereby alleviating neuronal cell death mediated by mitochondrial damage.”
2. B Vitamins and NAD Boosting Supplements
B vitamins are necessary for proper brain function, research suggests. People with low levels of vitamins B6 and B12 can develop anemia as well. Older adults are often low in vitamin B12, and as we age, it’s harder for us to absorb it and even use it because it’s not as bioavailable.
B vitamins include:- B1 (thiamine)
- B2 (riboflavin)
- B3 (niacin)
- B5 (pantothenic acid)
- B6
- B7 (biotin)
- B12
- Folic acid
B vitamins are commonly found in meat, eggs, fish and leafy greens.
NAD+ Precursors
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a vital molecule for most, if not all, forms of life. The last decade has seen a strong proliferation of therapeutic strategies for the treatment of metabolic and age-related diseases based on increasing cellular NAD+ bioavailability. Among them, the dietary supplementation with NAD+ precursors—classically known as vitamin B3—has received most of the attention. Multiple molecules can act as NAD+ precursors through independent biosynthetic routes.
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN)
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a precursor to NAD+. NAD+ is a very important substance in the cells. It provides energy for cells and is also a cofactor for proteins that repair and maintain our epigenome and our DNA.
The epigenome is the intricate machinery that surrounds the DNA and that determines which genes are active and not. During aging, the epigenome becomes more and more dysregulated.
The older we get, the less NAD+ is present in our cells. Taking in NMN can increase NAD+ levels.
Various animal and lab studies show that NMN has beneficial effects on aging diseases and symptoms (
R,
R,
R,
R).
For example, long term administration of NMN mitigated age-associated decline in mice: NMN reduced the typical age-associated increase in body weight, improved energy metabolism, improved lipids in the blood and insulin sensitivity and ameliorated eye function (
R).
NMN can also improve aging-related decline in fertility (
R), improve bone health (
R) and vascular health (
R,
R,
R).
NMN can also improve and protect stem cells such as mesenchymal stem cells that form bone and fat tissue (
R,
R).
NMN (Nicotinamide MonoNucleotide) is a molecule found in various foods such as broccoli, cabbage, avocado, mushrooms, meat, and shrimp. However, obtaining sufficient amounts through diet alone can be challenging.
Studies suggest that daily dosages of NMN range from 50mg to 250mg, and a 150-pound (68kg) person would require approximately 560mg per day. Unfortunately, obtaining these amounts solely through diet would be impractical. For example, you would need to consume about 100 pounds of edamame, 1,800 pounds of broccoli, or unrealistic amounts of cucumber, cabbage, avocado, tomato, mushrooms, raw beef, or shrimp to achieve the required intake. Therefore, taking NMN supplements may be a more practical approach to ensure adequate daily intake.
A study in 2022 suggests that
taking 250 mg/day of NMN can significantly increase and sustain the levels of NAD+ in the blood, without adverse side effects.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is needed to form red blood cells and DNA. It is also a key player in the function and development of brain and nerve cells. However, we believe the most important function it provides is methylation. If you don’t know what methylation is, allow us to briefly explain. Methylation is a biochemical process which is involved in a wide range of bodily functions, and is essential to our overall well-being. When methylation is out of balance, many different health problems may arise.
3. Glycine, NAC and Taurine
Both Glycine and Taurine levels decline as we age.
Glycine
Glycine is an amino acid that occurs naturally in our body. When we age, glycine levels decline.
Low glycine levels also have been associated with various aging-related diseases like cardiovascular disease and with type 2 diabetes.
Glycine extends lifespan in different species (
R,
R,
R,
R).
Glycine has many functions in the body. It improves the
epigenome (the machinery that determines which genes are switched on or off, a process that goes increasingly awry when we get older). Glycine especially improves the epigenome of
mitochondria, the power plants of our cells (
R).
Glycine also functions as a chaperone. Chaperones are small molecules that gently stick to and protect the proteins. That is important, because one of the reasons why we age is due to proteins accumulating everywhere inside and outside our cells, eventually hampering the proper functioning of our cells.
Glycine also reduces inflammation (
R) and has many other beneficial effects, especially for the cardiovascular system. People with higher glycine levels in the blood had less risk of a heart attack (
R), and glycine can protect the blood vessels (
R).
In addition to supporting brain function, supplemental glycine may be useful for the "prevention and control of atherosclerosis, heart failure, angiogenesis associated with cancer or retinal disorders and a range of inflammation-driven syndromes, including metabolic syndrome."(
McCarty 2019)
People with higher glycine levels in the blood had less risk of a heart attack (
Ding 2016), and glycine can protect the blood vessels (
DiNicolantonio 2014).
Glycine can also help counteract adverse effects of Glyphosate. When glyphosate enters your system, it can take the place of the glycine molecule. While similar, (the "gly" in glyphosate stands for glycine) it's not identical and does not work the same way as glycine. Hence, this replacement causes all sorts of trouble.
Note: Glyphosate is the active ingredient in Roundup and other common weed killer formulations.
By taking a glycine supplement, you can counteract this chain of events by making sure there's enough glycine present to fill up those glycine slots. As noted by Stephanie Seneff, Ph.D., (a senior research scientist at MIT for over five decades), "If there's lots of glycine, you're going to be much less likely to pick up glyphosate."
To gain all of glycine's healing potential, doses of 10, 15, or 20 grams a day may be necessary. Land suggests you need at least 12 grams of glycine daily for optimal collagen turnover, plus another 3 grams per day to form glutathione and other compounds (
YouTube):
"Your body only makes 3 grams of glycine per day, and if you only consume around 2 to 3 grams of glycine from foods then it means that almost all of us are in a 10-gram glycine deficit every day," he says.
"… I think most people would benefit for at least 5 to 10 grams of glycine a day, which is, uh kind of a moderate amount … if you are eating a lot of muscle meat … or you're just interested in getting more of the benefits of glycine then you can take even up to 20 grams a day."
Doses of 3 to 5 grams have been shown to improve sleep (
R).
One study estimated that most people are about 10 grams short of what their bodies need for all metabolic uses on a daily basis, and in a
study of people with metabolic syndrome, 15 grams of glycine a day for three months reduced oxidative stress and improved systolic blood pressure.
NAC
Marios Kyriazis, M.D., a gerontologist nominated for the 2017 Nobel Prize in Medicine and main contributor at For the Ageless, told Healthnews,
"NAC, the acetylated form of the amino acid cysteine, protects our brain by stimulating the activity of glutathione, which is a potent antioxidant that protects our mitochondria from free radical damage. NAC is also effective against viruses and it is used both for the prevention and treatment of some viral infections, including brain infections."
He added, "Conventional doctors use NAC to counteract the consequences of paracetamol overdose because it protects the liver from damage."
Kyriazis suggests the conventional dose is around 1000 mg to 1500 mg per day and says some doctors recommend taking NAC with vitamin C to prevent it from being destroyed in the body prematurely.
"500mg of NAC every morning is an effective dose for adults looking to use it daily as a longevity supplement," he explained. "It has an excellent safety profile and can be taken with any other supplements, including glutathione."
Glycine and NAC (GlyNAC)
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine also looked into supplementation with a combination of glycine and N-acetylcysteine (NAC), two glutathione precursors known as GlyNAC when taken together.
A pilot trial in older humans (
Kumar 2021) with GlyNAC supplementation for 24 weeks corrected glutathione deficiency and improved multiple measures of health, including:
- Mitochondrial dysfunction
- Oxidative stress
- Inflammation
- Endothelial dysfunction
- Insulin resistance
- Genomic damage
- Cognition
- Strength
- Gait speed
- Exercise capacity
- Body fat levels
- Waist circumference
Further, GlyNAC supplementation improved four of nine hallmarks of aging associated with most age-related disorders — mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, insulin resistance and genomic damage (
Kumar 2021). Glycine, the team noted, is an important methyl-group donor. "Methyl groups are abundant in DNA and are important components of multiple cellular reactions. Glycine is also important for normal brain function."
Taurine
This semi-essential amino acid is our latest addition and update to our list of 'Best 10 Anti Aging Supplements'. When we age, taurine levels decline as well.
According to research published in the June 2023 issue of the journal
Science, the semi-essential amino acid taurine appears to play an important role in longevity and healthy aging.
This isn’t just another ordinary experiment and a report, but a series of experiments at various levels of detail showing that taurine may be the real deal and promote anti-aging.
Animals given supplemental taurine didn’t just live longer, they were also healthier overall. In mice, taurine improved:
- Strength, coordination and endurance
- Bone mass and bone quality
- Glucose homeostasis and glucose tolerance
- Age-related inflammation
- Immune function
- Gut health
- Memory
- Function of all organs
- Mitochondrial function and health
Interestingly, according to the authors, taurine “cured” osteoporosis. It’s not often you see the word “cure” being used in medical literature. Taurine also “suppressed ovariectomy-induced body-weight gain in a rodent model of menopause,” and reduced anxiety and depression-like behavior in the mice.
Treated mice also had less body fat (approximately 10% less at 1,000 milligrams of taurine per day) and higher energy levels. According to the authors, “Fat-pad weight divided by body weight percentage was dose-dependently reduced in taurine-treated mice.” Taurine supplementation also improved several markers of aging, including Senescence, Intercellular communication, Telomere length, Epigenetic changes, Genomic stability, Mitochondrial function, Stem cell populations and Nutrient sensing.
4. Molecular Hydrogen and Magnesium
Molecular hydrogen is the smallest anti-oxidant. This paper (
Mar 2022) reviews the basic research and recent application of hydrogen in order to support hydrogen use in medicine for ageing prevention and ageing-related disease therapy.
Molecular hydrogen has therapeutic and preventive effects on various organs. It has antioxidative properties as it directly neutralizes hydroxyl radicals and reduces peroxynitrite level. It also activates Nrf2 and HO-1, which regulate many antioxidant enzymes and proteasomes. Through its antioxidative effect, hydrogen maintains genomic stability, mitigates cellular senescence, and takes part in histone modification, telomere maintenance, and proteostasis. In addition, hydrogen may prevent inflammation and regulate the nutrient-sensing mTOR system, autophagy, apoptosis, and mitochondria, which are all factors related to ageing. Hydrogen can also be used for prevention and treatment of various ageing-related diseases, such as neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular disease, pulmonary disease, diabetes, and cancer.
It was also already discovered that hydrogen can prolong the life of
stem cells by reducing oxidative stress (
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010).
Maintaining cells in low-oxygen conditions or in the presence of hydrogen gas, matrix modification, and supplying the culture medium with growth factors and antioxidants capable of attenuating ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) accumulation can slow done the telomere shortening and proliferative senescence.
Note: Most Molecular Hydrogen tablets uses pure elemental magnesium as its carrier and provides you with approximately 80 mg of magnesium per tablet. So, you receive also highly bioavailable magnesium for a healthy brain, muscles, cells, kidneys, and heart.
Magnesium
Magnesium is a very important mineral in the human body.
Magnesium functions as a cofactor to hundreds of different enzymes, which need magnesium to function properly.
Magnesium also regulates the excitation and inhibition of cells, and plays an important role in muscle relaxation, including of the heart muscle.
Given the role of magnesium in a myriad of cellular processes, it should not be surprising that magnesium deficiency leads to accelerated aging (
R).
There are many ways in which magnesium deficiency can lead to accelerated aging. Magnesium is needed to build, maintain and repair DNA.
Magnesium reduces DNA damage and stabilizes the genome (
R,
R). For example, magnesium sticks to the DNA strand and stabilizes it, and it is also an essential cofactor for DNA repair proteins which need magnesium to function properly (
R).
Magnesium can reduce inflammaging (low-grade inflammation that increases during aging). Low levels of magnesium have been linked to chronic low-grade inflammation, which is one of the drivers of aging (
R).
Besides magnesium’s many effects on maintaining our cells, the mineral has various immediately noticeable effects. Athletes take magnesium to improve their physical performance, even when they are not magnesium deficient (
R).
Magnesium supplements also improve sleep, and feelings of relaxation and wellbeing.
This is not surprising, given the important role of magnesium in the functioning of brain cells, such as excitation and neuronal metabolism.
Malate is often used in combination with magnesium to bring about health benefits, especially for improving energy and reducing fatigue.
5. Curcumin (Turmeric)
Curcumin — the main active compound in turmeric — has been shown to possess powerful anti-aging properties, which are attributed to its potent antioxidant potential.
As published in the
European Journal of Pharmacology (Nov 2022), Abe and colleagues focused on testing the effects of the curcumin prodrug TBP1901. They found that TBP1901 metabolized to its active form most greatly in bone marrow, leading them to use the drug on a multiple myeloma mouse model — a model for age-related bone marrow cancer. The researchers found that TBP1901 had significant anti-tumor effects, effectively shrinking tumors in mice. However, TBP1901 did not have strong effects in preventing cancer cell growth in a dish (in vitro). Still, regular curcumin had anti-tumor effects in vitro.
Cellular senescence occurs when cells stop dividing. As you age, senescent cells accumulate, which is believed to accelerate aging and disease progression (
Source,
Source).
Research demonstrates that curcumin activates certain proteins, including sirtuins and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which helps delay cellular senescence and promotes longevity (
Source,
Source).
Plus, curcumin has been shown to combat cellular damage and significantly increase the lifespan of fruit flies, roundworms, and mice. This compound has been shown to postpone age-related disease and alleviate age-related symptoms as well (
Source,
Source).
This may be why turmeric intake has been associated with a reduced risk of age-related mental decline in humans (
Source). You can increase your curcumin intake by using turmeric in recipes or taking curcumin supplements.
Recent studies have come forward that in addition to its anti-aging and anti-inflammatory properties, it may also have anti-tumor properties. However, the bioavailability — ability to be used in the body — of curcumin may not be ideal. Thus, to help enhance its known positive benefits, researchers out of Kyoto University in Japan modified curcumin into a prodrug – an inactive compound that requires metabolism by the body before becoming biologically active.
6. CoQ10
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is an antioxidant that your body produces. It plays an essential role in energy production and protects against cellular damage (
Source).
Research suggests that levels of CoQ10 decline as you age. Supplementing with it has been shown to improve certain aspects of health in older individuals.
For instance, a 4-year study in 443 older adults demonstrated that supplementing with CoQ10 and
selenium improved overall quality of life, reduced hospital visits, and slowed physical and mental deterioration (
Source).
CoQ10 supplements may work by reducing oxidative stress, a condition characterized by an accumulation of free radicals that accelerates the aging process and the onset of age-related disease (
Trusted Source).
Additionally, CoQ10 supplements may benefit heart health by reducing stiffness in your arteries, lowering blood pressure, and preventing the buildup of oxidized cholesterol in your arteries (
Trusted Source).
CoQ10 is also part of Dr.
David Sinclair’s supplement list.
However, various studies show that coenzyme Q10 does not extend lifespan
(R,R,R,R). Some studies show that coenzyme Q10 can actually shorten lifespan
(R).
There are of course also some studies showing that co-enzyme Q10 can extend lifespan, but often these studies have not been well conducted, or they use organisms that are not ideal representation of normal aging, like using co-enzyme Q10 deficient mice.
Lastly, the interventions testing program (ITP) tested a similar compound, MitoQ (a better absorbable nutrient based on coQ10), and didn’t find a life extension effect (
R).
That said, CoQ10 decline as you age and it plays an essential role in energy production and protects against cellular damage. Supplementing with CoQ10 might allow for more physical activity and therefore more likely to have a protective effect than a negative one.
Related: Best CoQ10 Supplements
7. Vitamin C and Calcium Alpha-KetoGlutarate (AKG)
Vitamin C can help to maintain a proper epigenome, especially in combination with another longevity ingredient, alpha- ketoglutarate.
An
umbrella review* (Xu 2022) to assess the existing systematic reviews and meta-analyses for the association between vitamin C intake and multiple health outcomes; showed that vitamin C intake was associated with reduced risk of all-cause mortality, cardiovascular disease (CVD), oesophageal cancer, gastric cancer, cervical cancer and lung cancer with an increment of 50–100 mg per day. Beneficial associations were also identified for respiratory, neurological, ophthalmologic, musculoskeletal, renal and dental outcomes. A
total of 76 meta-analyses (51 papers) of randomised controlled trials and observational studies with 63 unique health outcomes were identified. Harmful associations were found for breast cancer and kidney stones for vitamin C supplement intake.
Alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) extends lifespan and healthspan in different species. In humans, alpha-ketoglutarate has shown to protect cells against damage and stressors. Alpha-ketoglutarate supports a healthy metabolism and a healthy epigenome.
Alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) is a small molecule naturally present in our body. During aging, levels of AKG decline.
Alpha-ketoglutarate is used by the mitochondria, which convert this substance into energy, but alpha-ketoglutarate has various other functions in the body.
Numerous studies show that alpha-ketoglutarate can extend lifespan in various organisms. AKG extended lifespan in C elegans worms (
R) and fruit flies (
R,
R,
R) and mice.
Alpha-ketoglutarate also plays a role in maintaining stem cell health (
Nature 2015), and in bone and gut metabolism (
R).
Calcium alpha-ketoglutarate is also involved in collagen production, can reduce fibrosis, and can thus play a role in maintaining healthy, youthful skin (
R,
R).
Ascorbic acid vs whole food vitamin C: What's the Difference?
Synthetic Ascorbic acid is NOT the same as whole food vitamin C. If you were to compare the two to a car, vitamin C would be the whole car, fully functional, and the engine is an enzyme called tyrosinase, while ascorbic acid is the car frame, with no moving parts.
Whole food vitamin C can also boost your copper level, as vitamin C contains an enzyme called tyrosinase, which has 2 atoms of copper in it. Ascorbic acid is prooxidant, while vitamin C complex is actually an antioxidant. Anything that has copper is going to be antioxidant.
8. Fisetin
Quercetin and Fisetin have been grouped together due to their similar molecular structure, with only minor differences. Both are flavonoids and senolytics.
Fisetin, a molecular cousin to the more popular Quercetin, is also a naturally occurring substance found in fruits and vegetables, such as strawberries, apples, grapes, onions, and cucumbers.
Fisetin is a flavonoid. Flavonoids are substances that give fruits and vegetables their bright colors (like yellow, orange and blue) and play a major role in conferring the health benefits that we get from eating more vegetables and fruits.
Fisetin is probably most known for its impact on senescent cells: studies showed that this substance can reduce the accumulation of senescent cells (
R). Fisetin is a
senolytic, a compound that can clear away senescent cells.
Senescent cells accumulate everywhere in the body during aging. Senescent cells were previously normal cells that became too damaged. Normally, when a cell is too damaged, it kills itself, but senescent cells don’t do that.
Instead of dying, they keep lingering around in the body.
Senescent cells secrete all kinds of substances that damage the healthy surrounding cells, like inflammatory substances (cytokines and chemokines), substances that break down the glue that holds the cells together (matrix metalloproteinases), and growth factors that accelerate aging (
R). Not only do senescent cells damage healthy surrounding cells, but they also damage stem cells, which are the foundational cells that create new cells, which build up and repair our organs and tissues.
Reducing the senescent cell burden can lead to reduced inflammaging (low-grade inflammation that increases during aging) and enhanced function of stem cells.
Substances that can eliminate senescent cells are called “senolytics”. Fisetin is a well-studied senolytic substance.
Fisetin versus quercetin
Besides fisetin, another senolytic is quercetin. Quercetin and fisetin look very similar. However, fisetin seems to be the most potent and safest of natural senolytics (
Lancet 2018).
The conclusion of the researchers was the following:
“Fisetin had the most potent senotherapeutic effects in several cell types in vitro and showed strong anti-geronic effects in vivo”.
Quercetin reduces glutathione and inhibits sirtuin-6 and NRF-2. All of these will hurt your longevity (see this
clip, 2:30).
Lifespan extension effects of fisetin
Scientists demonstrated that fisetin can extend median and maximum lifespan in mice, even when taken late in a mouse’s life (equivalent to 50 or 60 years old for a human) (
R).
More than a senolytic: other anti-aging effects of fisetin
Fisetin has many other beneficial effects on the aging process besides eliminating senescent cells.
For example, fisetin inhibits the mTOR pathway (
R), which plays an important role in aging and is where many of the health benefits behind fasting are derived. Fisetin can also reduce oxidative stress (
R).
Fisetin can reduce inflammaging (aging-related low-grade inflammation) by inhibiting pro-inflammatory enzymes and substances, like lipoxygenases and NF-kB (
R,
R).
Interestingly, fisetin can also have various beneficial effects on the skin. For example, fisetin can reduce the formation of skin wrinkles and appearance of skin aging.
Fisetin also has a positive impact on brain functioning and brain aging (
R). For example, fisetin can improve memory formation in mice (
R,
R).
9. EGCG (Green Tea Extract)
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is a well-known polyphenol compound concentrated in green tea.
Best Evidence: The
Minnesota Green Tea Trial (MGTT 2015) is the largest and longest double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized intervention study that specifically evaluated the effects of oral GTE (green tea extract) containing defined quantities of EGCG on established biomarkers of breast cancer risk.
They randomized and stratified 1075 healthy postmenopausal women at high risk of breast cancer according to their breast tissue density and catechol-O-methyltransferase genotypes and divided them into two groups: 537 placebo and 538 green tea groups. Green tea group participants took 4 capsules that contained 843 mg EGCG, whereas the placebo group took capsules without green tea extracts.
Researchers measured changes in percent mammographic density, circulating endogenous sex hormones, and proteins of the insulin-like growth factor axis. Their results showed that supplementation with green tea extract could modify and reduce mammographic density (MD) and protect against breast cancer, even though it was only significant in younger women (50–55 years) and had no effect in older women (
R), an age-dependent effect similar to those of tamoxifen.
Studies have confirmed numerous health benefits of green tea including prevention of cancer (
R,
R) and cardiovascular disease, as well as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiarthritic, antibacterial, and antiviral effects. (
R,
R,
R,
R). Plus, animal studies have shown that it can protect against skin aging and wrinkles caused by ultraviolet (UV) light (
Source).
As human clinical evidence is still limited, future research needs to define the actual magnitude of health benefits, establishes the safe range of tea consumption associated with these benefits, and elucidates the mechanisms of action.
Among EGCG’s diverse array of potential health-promoting properties is its ability to promote longevity and protect against age-related disease development.
EGCG may slow aging by restoring mitochondrial function in cells and acting on pathways involved in aging, including the AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway (AMPK). It also induces autophagy, the process by which your body removes damaged cellular material (
Source).
Green tea may protect against EMF exposure as well. A
2011 study published in Neurotoxicity Research reported that green tea can protect neurons in the brain against cell phone radiation. Cell phone exposure for 24 hours resulted in neuronal cell death in cultured rat cells. Green tea, however, prevented cell death.
EGCG can be consumed by drinking green tea or taking concentrated supplements.
Because scientists aren’t sure how much EGCG is safe to take in pill form, the best way to incorporate it into the diet is by drinking green tea. One cup of green tea usually contains about 50 to 100 mg of EGCG.
10. Resveratrol and Pterostilbene
Resveratrol and pterostilbene have been grouped together due to their similar molecular structure, with only minor differences.
A
2021 research review suggests that resveratrol supplements may help protect against age-related cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and diabetic disorders. Unfortunately, confirmation of the therapeutic efficacy of Resveratrol concentration in humans is still needed to mitigate the research.
Resveratrol is a polyphenol in grapes, berries, peanuts, and red wine that may promote longevity by activating certain genes called sirtuins. It has been shown to increase the lifespan of fruit flies, yeasts, and nematodes (
Source).
It displays powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor properties in clinical trials. Resveratrol also enhances sirtuin function (
R).
Nearly two decades ago, it was discovered that resveratrol slowed the process of cellular aging in yeast. In 2003, Harvard Medical School Professor David Sinclair, PhD, found that resveratrol activated a class of sirtuin proteins called SIRT1.
Note: You might have heard of “skinny genes” — genetic components that can help us stay thin, age well, and live longer. Sirtuins are a family of proteins that might do just that. Sirtuins aren’t genes at all, they’re proteins. Humans have seven of them, called SIRT1, SIRT2, SIRT3, and so on.
Then, the same mechanism was studied and found to be true in mice. An
animal study published in 2013 found that resveratrol does extend the life of obese mice, but not of mice that maintain a healthy weight. Not even if they’re give more resveratrol from a very young age. That suggests that resveratrol can help reduce the damage caused by lifestyle factors like diet and fitness levels, but it doesn’t add any extra benefit you can’t already get from leading a healthy lifestyle in the first place.
Investigations into resveratrol then turned toward its effects on human health. Resveratrol was found to support cardiovascular health, antioxidant defenses, glucose metabolism, healthy inflammatory balance, and more. As results of these reported studies, people became more interested in drinking resveratrol-rich red wine and taking resveratrol supplements.
The efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of resveratrol have been documented in over 244 clinical trials, with an additional 27 clinical trials currently ongoing (
Pratap Singh 2019). Resveratrol is reported to potentially improve the therapeutic outcome in patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, obesity, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, multiple myeloma, metabolic syndrome, hypertension, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, cardiovascular diseases, kidney diseases, inflammatory diseases, and rhinopharyngitis.
The polyphenol is reported to be safe at doses up to 5 g/d, when used either alone or as a combination therapy. Although the clinical utility of resveratrol is well documented, the rapid metabolism and poor bioavailability have limited its therapeutic use. In this regard, the recently produced micronized resveratrol formulation called SRT501, shows promise (
Pratap Singh 2019).
Pterostilbene vs Resveratrol
Some of the biggest hurdles for reaping the benefits of resveratrol in humans appear to be its limited bioavailability and rapid elimination from the body. But those hurdles might be overcome by a compound that has more recently gained some notice.
PubMed has indexed more than 12,000 research studies on resveratrol, but only 500 on pterostilbene. However, the sheer number of scientific studies on a compound doesn’t necessarily mean the compound is superior. It’s also important to note that pterostilbene research lags about 10 years behind resveratrol research.
The slight difference in molecular structure between resveratrol and pterostilbene provides a sound rationale for the superiority of pterostilbene. Pterostilbene should be more stable and bioavailable in theory, and preclinical studies so far validate the assumption.
Other ways to manage aging symptoms
Besides exploring the best supplements with some anti-aging benefits, there are specific methods you should consider to prevent aging symptoms from appearing prematurely. We share some expert-validated tips to help in your efforts to preserve youthfulness and vitality.
Skin protection
Skin protection goes beyond cosmetics. To keep your skin vibrant and healthy, consider constant protection from UV rays by applying sunscreen even in winter. UV protection may help maintain skin elasticity, hinder premature aging, and lower the risk of developing skin cancer.
Healthy lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle includes such aspects as a balanced diet, adequate sleep patterns, and quitting harmful habits such as smoking and excess alcohol consumption.
Nourish your body with food rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Drink an adequate amount of water a day to stay hydrated for skin and overall body health.
As the saying goes, “Resting is rusting.” Yet, regular physical activity can be a cornerstone for well-being. At least 30 minutes of daily exercise can help preserve flexibility and healthy weight — important for graceful aging.
Stress management
Stress and anxiety are other caveats for the accelerated aging process. Learn the most suitable methods to cope with stress — yoga, meditation, and social interaction.Living with chronic stress can be devastating and lead to the premature appearance of aging signs. It is fundamental to find help from a therapist to manage stress and gain holistic anti-aging results.
Best anti-aging supplements — conclusion
It's important to remember that supplements are not a replacement for
a healthy diet and lifestyle, engaging in regular exercise, and
reducing stress. It's always best to talk to your doctor before
starting any new supplement program.
Certain supplements may help slow the aging process and promote a long,
healthy life. A good anti-aging supplement is one that contains
substances that are based on science and that acts on aging mechanisms.
This also enables these supplements to have an additional important
benefit: synergy.
After all, aging is a complex process
caused by various different mechanisms, such as epigenetic
dysregulation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and accumulation of
proteins.
If you have an anti-aging supplement that only
focuses on a single dimension such as “improving mitochondrial health”,
you are not addressing other important aging mechanisms, like epigenetic
dysregulation or accumulation of proteins.
Therefore, this
supplement, even if it could improve mitochondrial health, will have
little impact on extending lifespan given it only tackles one facet of
the aging process.
As such, it’s very important for a good
anti-aging supplement stack or combination to contain substances that
act on different aging mechanisms in a synergistic way.
For
example, alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) can maintain the epigenome and
improve mitochondrial health. AKG can work together with other
substances that improve mitochondrial health, like fisetin and malate,
or that improve the epigenome, like NMN and glycine.
But
addressing the aging epigenome and mitochondria is not enough. You also
need to tackle many other aging mechanisms, like protein accumulation
and DNA damage.
So the ideal anti-aging supplement contains
not just one or two substances that focus on one aging mechanism (like
mitochondrial health or the NAD+ metabolism), but contains many
substances that act on many aging pathways, and in a synergistic way.
In real medicine, results are not guaranteed and there are no cure-alls.
Real research is published in peer-reviewed journals, and you can search the
journals via PubMed or Google Scholar.
Related:
Can Diet and Lifestyle Strategies Reverse Your Aging? 1,000+ Studies Analyzed
Does Nicotinamide Riboside cause Cancer?











.png)



Comments
Post a Comment