9 Best Supplements for Knee Osteoarthritis 2024
Arthritis is the swelling and tenderness of one or more of your joints. The main symptoms of arthritis are joint pain and stiffness, which typically worsen with age. The most common types of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
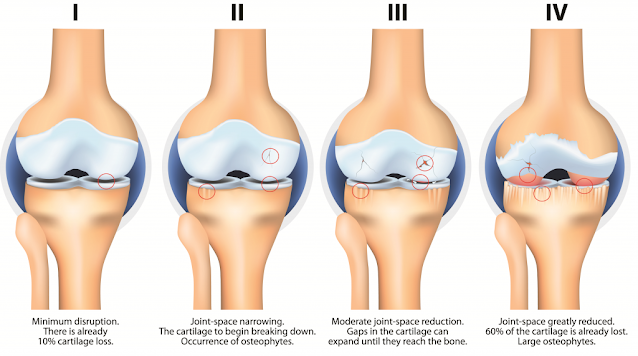
Osteoarthritis causes cartilage to break down. Rheumatoid arthritis is a
disease in which the immune system attacks the joints, beginning with the
lining of joints.
Knee osteoarthritis means that your knee hurts and your doctor does not know the cause. With aging, a person wears away the shock-absorbing cartilage in the knees, which increases risk for pain and swelling. Often people with knee osteoarthritis have perfectly normal MRIs of their knee cartilage, and people with MRI evidence of torn cartilage often have no pain or swelling.
Best Supplements for Knee Osteoarthritis
Of late, there are also dozens of supplements and ways that claim to treat
joint pain, but which ones actually work? Here’s a look at the best options
and what the existing research says about them.
1. Glucosamine
Glucosamine is a natural component of cartilage, a substance
that prevents bones from rubbing against each other and causing pain and
inflammation. It might also help prevent the cartilage breakdown that can
happen with arthritis.
Many supplements aimed at treating joint pain contain glucosamine, which is one of the most well-studied supplements for osteoarthritis. But despite this research, there are still some questions about how well it works.
There are two types of glucosamine found in supplements: glucosamine hydrochloride and glucosamine sulfate.
One meta-analysis found that products containing glucosamine hydrochloride don’t do much to improve joint pain caused by osteoarthritis. Another study shows that glucosamine sulfate does improve these symptoms, so it may be a better option than glucosamine hydrochloride.
When taken over a long period of time, glucosamine sulfate may also help to slow down the progression of osteoarthritis. Studies suggest that it slows down narrowing of the joint space, a marker of the condition getting worse, when taken for up to three years.
Many supplements aimed at treating joint pain contain glucosamine, which is one of the most well-studied supplements for osteoarthritis. But despite this research, there are still some questions about how well it works.
There are two types of glucosamine found in supplements: glucosamine hydrochloride and glucosamine sulfate.
One meta-analysis found that products containing glucosamine hydrochloride don’t do much to improve joint pain caused by osteoarthritis. Another study shows that glucosamine sulfate does improve these symptoms, so it may be a better option than glucosamine hydrochloride.
When taken over a long period of time, glucosamine sulfate may also help to slow down the progression of osteoarthritis. Studies suggest that it slows down narrowing of the joint space, a marker of the condition getting worse, when taken for up to three years.
Try it: Glucosamine sulfate is typically taken once daily in a dose of 1,500
milligrams (mg). If this upsets your stomach, try spreading it out over
three doses of 500 mg each. You can find glucosamine sulfate supplements
on Amazon.
2. Chondroitin
Like glucosamine, chondroitin is a building block of
cartilage. It may also help prevent cartilage breakdown from
osteoarthritis.
Many clinical studies have found that chondroitin can reduce joint pain and stiffness in people with osteoarthritis. About 53 percent of people who take chondroitin have a 20 percent or greater improvement in knee pain.
Chondroitin sulfate may also slow down the progression of osteoarthritis when taken long-term. Studies show that it slows down narrowing of the joint space when taken for up to 2 years.
Joint supplements often combine chondroitin with glucosamine. But it’s still unclear if taking a combination supplement is any better than taking one or the other on their own.
Try it: Chondroitin is typically taken in a dose of 400 to 800 mg two or three times per day. You can find chondroitin supplements on Amazon.
Many clinical studies have found that chondroitin can reduce joint pain and stiffness in people with osteoarthritis. About 53 percent of people who take chondroitin have a 20 percent or greater improvement in knee pain.
Chondroitin sulfate may also slow down the progression of osteoarthritis when taken long-term. Studies show that it slows down narrowing of the joint space when taken for up to 2 years.
Joint supplements often combine chondroitin with glucosamine. But it’s still unclear if taking a combination supplement is any better than taking one or the other on their own.
Try it: Chondroitin is typically taken in a dose of 400 to 800 mg two or three times per day. You can find chondroitin supplements on Amazon.
3. Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM)
Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) is another common ingredient in
supplements said to help with joint pain. One of the most popular uses of
MSM is to decrease joint or muscle pain. It has been shown to benefit
those with joint degeneration, a common cause of pain in the knees, back,
hands and hips.
In one randomised controlled study, MSM improved pain and functioning compared to a placebo in people with osteoarthritis.
A study in 100 people over the age of 50 found that treatment with a supplement containing 1,200 mg of MSM for 12 weeks decreased pain, stiffness and swelling in the joints, compared to a placebo (Int J Biomed Sci. 2015).
The group receiving the supplement also reported improved overall quality of life and less difficulty walking and getting out of bed (Int J Biomed Sci. 2015).
Another study in 32 people with lower back pain found that taking a glucosamine supplement containing MSM significantly reduced lumbar stiffness and pain upon movement, plus greatly increased quality of life (Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2005).
Try it: Typical MSM doses range from 1,500 to 6,000 grams per day, sometimes divided into two doses.
In one randomised controlled study, MSM improved pain and functioning compared to a placebo in people with osteoarthritis.
A study in 100 people over the age of 50 found that treatment with a supplement containing 1,200 mg of MSM for 12 weeks decreased pain, stiffness and swelling in the joints, compared to a placebo (Int J Biomed Sci. 2015).
The group receiving the supplement also reported improved overall quality of life and less difficulty walking and getting out of bed (Int J Biomed Sci. 2015).
Another study in 32 people with lower back pain found that taking a glucosamine supplement containing MSM significantly reduced lumbar stiffness and pain upon movement, plus greatly increased quality of life (Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2005).
Try it: Typical MSM doses range from 1,500 to 6,000 grams per day, sometimes divided into two doses.
You can find MSM supplements on Amazon.
For the omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil to work against arthritis, it’s necessary to consume a fairly large quantity of it each day. Fish oil — or cod liver oil — enclosed in capsules makes this fairly easy.
Fish Oil vs Cod Liver Oil
On the other hand, because cod liver oil contains very high amounts of vitamin A and vitamin D, taking too much can be toxic. For the purpose of treating arthritis, fish oil is the safer choice.
EPA and DHA can reduce inflammation, which causes swelling and pain. Research has indicated that both acids might suppress the body’s immune system. However, a 2016 study suggests that DHA might enhance immune function instead. DHA is more effective at reducing inflammation than EPA, but both have a role.
All of these effects makes fish oil potentially beneficial for people with arthritis.
EPA and DHA come with other health benefits: They can help prevent heart attacks by making it harder for blood to clot. They help lower blood triglyceride levels and blood pressure. As well, EPA taken with statin medication is more effective in reducing the inflammation of arteriosclerosis than medication alone.
For the omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil to work against arthritis, it’s necessary to consume a fairly large quantity of it each day. Fish oil — or cod liver oil — enclosed in capsules makes this fairly easy.
On the other hand, because cod liver oil contains very high amounts of vitamin A and vitamin D, taking too much can be toxic. For the purpose of treating arthritis, fish oil is the safer choice as compared to cod liver oil.
Shop for fish oil supplement.
In 2019, some researchers found that curcumin capsules had a similar effect on the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis as diclofenac, an NSAID.
In the study, 139 people with OA of the knee took either a 50-milligram tablet of diclofenac twice a day for 28 days or a 500-milligram curcumin capsule three times a day.
Both groups said their pain levels improved, but those who took curcumin had fewer negative effects. The research suggested that people who can’t take NSAIDs may be able to use curcumin instead.
So, at least in theory, improvement in bone health should reduce the risk of knee joint pain.
This is because the two are closely related. For example, a thigh bone fracture due to osteoporosis will make you prone to knee pain.
And in knee osteoarthritis, collagen supplementation may help promote healthy cartilage growth. Some forms of collagen may also protect the joints from inflammation-induced breakdown. (R)
Glucosamine chondroitin and turmeric are some of the most helpful and better-researched supplements for knee conditions. (J Orthop Surg Res. 2018)
Do supplements work for knee pain?
Yes, some of them do – glucosamine, chondroitin, turmeric, and many more can help relieve knee pain.
Is it safe to take supplements for knee pain daily?
Yes, just make sure to follow the manufacturer’s recommendation on dosage. Also, discuss with your doctor before taking supplements if you are taking other medications.
4. Fish Oil and Omega-3s
The two types of omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil are
eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
For the omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil to work against arthritis, it’s necessary to consume a fairly large quantity of it each day. Fish oil — or cod liver oil — enclosed in capsules makes this fairly easy.
Fish Oil vs Cod Liver Oil
On the other hand, because cod liver oil contains very high amounts of vitamin A and vitamin D, taking too much can be toxic. For the purpose of treating arthritis, fish oil is the safer choice.
EPA and DHA
EPA and DHA can reduce inflammation, which causes swelling and pain. Research has indicated that both acids might suppress the body’s immune system. However, a 2016 study suggests that DHA might enhance immune function instead. DHA is more effective at reducing inflammation than EPA, but both have a role.
All of these effects makes fish oil potentially beneficial for people with arthritis.
In one study, people said their pain levels decreased after taking fish oil
supplements.
Those who reported the improvement had taken a low dose rather than a high dose. They saw the improvement after 2 years. After 1 year, there was no significant improvement.
Commenting on this study, other scientists expressed further concerns. They noted that consuming more than 3 grams of fish oil a day could be hazardous.
Potential hazards include increased mercury consumption and bruising and bleeding.
Those who reported the improvement had taken a low dose rather than a high dose. They saw the improvement after 2 years. After 1 year, there was no significant improvement.
Commenting on this study, other scientists expressed further concerns. They noted that consuming more than 3 grams of fish oil a day could be hazardous.
Potential hazards include increased mercury consumption and bruising and bleeding.
EPA and DHA come with other health benefits: They can help prevent heart attacks by making it harder for blood to clot. They help lower blood triglyceride levels and blood pressure. As well, EPA taken with statin medication is more effective in reducing the inflammation of arteriosclerosis than medication alone.
For the omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil to work against arthritis, it’s necessary to consume a fairly large quantity of it each day. Fish oil — or cod liver oil — enclosed in capsules makes this fairly easy.
On the other hand, because cod liver oil contains very high amounts of vitamin A and vitamin D, taking too much can be toxic. For the purpose of treating arthritis, fish oil is the safer choice as compared to cod liver oil.
Shop for fish oil supplement.
5. Curcumin / Turmeric
Curcumin is an antioxidant that may offer a variety of anti-inflammatory
benefits. It’s present in turmeric, a mild spice that can add color and
flavor to sweet and savory dishes, as well as teas.
It’s also available as a supplement.
Curcumin, present in turmeric, has long played a role in Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine, due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
It’s also available as a supplement.
Curcumin, present in turmeric, has long played a role in Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine, due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
This new meta-analysis on curcumin was published in 2021 by researchers at the University of Miami
(1). After reviewing 10 different studies on curcumin and knee arthritis
with almost thirteen hundred patients, the researchers concluded that:
“Although limitations exist within the 10 RCTs reviewed, this small
set of studies show a reduction in pain and improvement in function
similar to that of NSAIDs but with a reduced incidence of adverse
events. Turmeric appears to be a safe adjunct to NSAID therapy
allowing for additional analgesic benefit as well as a reduced dosage
requirement for NSAIDs. “
Meaning that Curcumin was shown to be as good as NSAIDs like Motrin,
Alleve, or Celebrex with far fewer side effects!
In 2019, some researchers found that curcumin capsules had a similar effect on the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis as diclofenac, an NSAID.
In the study, 139 people with OA of the knee took either a 50-milligram tablet of diclofenac twice a day for 28 days or a 500-milligram curcumin capsule three times a day.
Both groups said their pain levels improved, but those who took curcumin had fewer negative effects. The research suggested that people who can’t take NSAIDs may be able to use curcumin instead.
You can find curcumin supplements on Amazon.
www.onedaymd.com
6. Resveratrol
Resveratrol is another nutrient that has antioxidant and
anti-inflammatory properties.
In a 2018 study, scientists gave 110 people with mild to moderate OA of the knee a 500-milligram dose of resveratrol or a placebo.
They took this combination alongside a 15-gram dose of the NSAID meloxicam every day for 90 days.
People who took resveratrol found that their pain levels dropped significantly, compared with those who took the placebo.
More research is needed to confirm that resveratrol can benefit people with OA.
However, if you’re already taking another NSAID and it doesn’t reduce your pain as much as you’d like, the research suggests resveratrol may be a useful add-on.
In a 2018 study, scientists gave 110 people with mild to moderate OA of the knee a 500-milligram dose of resveratrol or a placebo.
They took this combination alongside a 15-gram dose of the NSAID meloxicam every day for 90 days.
People who took resveratrol found that their pain levels dropped significantly, compared with those who took the placebo.
More research is needed to confirm that resveratrol can benefit people with OA.
However, if you’re already taking another NSAID and it doesn’t reduce your pain as much as you’d like, the research suggests resveratrol may be a useful add-on.
Food sources of resveratrol include:
In a 2020 randomized controlled trial, mineral rich algae with pine bark improved pain, physical function
and analgesic use in mild-knee joint osteoarthritis, compared to
Glucosamine.
Yet, its role in bone health is extremely important. Getting the required vitamin D can sustain normal calcium levels, thus promoting bone health and preventing osteoporosis.
- grapes
- tomatoes
- red wine
- peanuts
- soy
- some teas
You can find resveratrol supplements on Amazon.
7. Pine Bark Extract (Pycnogenol)
Pine bark acts as a local anti-inflammatory in synovial fluid (R) and three publications have shown it to improve KOA (knee
osteoarthritis) pain and stiffness, NSAID (non steroidal anti
inflammatory drug) use, physical and emotional well-being (R, R, R). Pine bark preparations have recently been “strongly recommended”
to the rheumatology community as early and additive treatment for
OA, likely based on the following meta-analysis (R, R).
8. Vitamin D
Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining bone health and bone density, but its role in joints is less clearly understood. So far, studies show no added benefit of taking it, at least for joint pain.Yet, its role in bone health is extremely important. Getting the required vitamin D can sustain normal calcium levels, thus promoting bone health and preventing osteoporosis.
So, at least in theory, improvement in bone health should reduce the risk of knee joint pain.
This is because the two are closely related. For example, a thigh bone fracture due to osteoporosis will make you prone to knee pain.
Therefore, it could be argued that vitamin D may potentially improve knee osteoarthritis pain indirectly by promoting bone health.
9. Collagen
Collagen is a natural substance widely taken for its advocated benefits in joint and skin health. All connective tissue, including the joint cartilage, contains large amounts of collagen.And in knee osteoarthritis, collagen supplementation may help promote healthy cartilage growth. Some forms of collagen may also protect the joints from inflammation-induced breakdown. (R)
FAQs
What is the best supplement for knee pain?Glucosamine chondroitin and turmeric are some of the most helpful and better-researched supplements for knee conditions. (J Orthop Surg Res. 2018)
Do supplements work for knee pain?
Yes, some of them do – glucosamine, chondroitin, turmeric, and many more can help relieve knee pain.
Is it safe to take supplements for knee pain daily?
Yes, just make sure to follow the manufacturer’s recommendation on dosage. Also, discuss with your doctor before taking supplements if you are taking other medications.
Conclusion: The best supplements for osteoarthritis of the knee
However, if you are taking medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that suppress the immune system, blood thinners, or blood pressure drugs, it's important to speak with your doctor before taking any supplements. It's also advisable to consult with your doctor before trying any other alternative or complementary remedies as they may interact with your medications. Your doctor should be able to provide you with advice on any potential drug interactions.
Comments
Post a Comment