FLCCC I-CARE Early Treatment Protocol Review (2023)
The I-Care protocol has been updated and below is their latest version (March 30, 2023).
First Line Therapies
(In order of priority; not all required.)
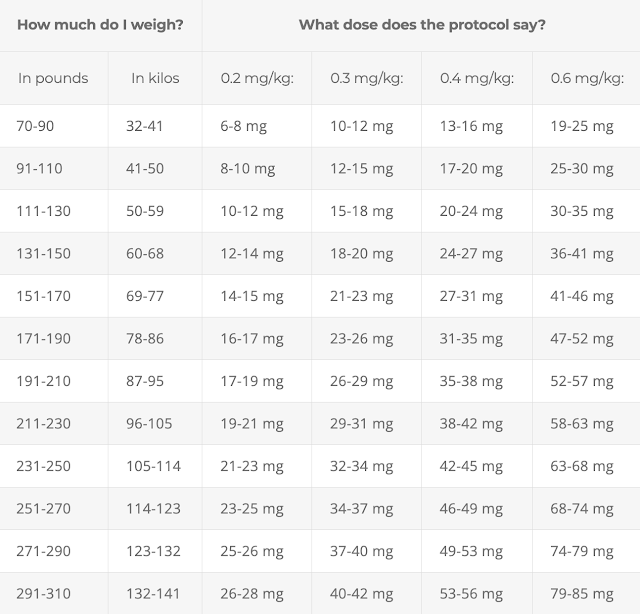
- Ivermectin: 0.4 to 0.6 mg/kg – one dose daily for at least 5 days or until symptoms resolve. If symptoms persist longer than 5 days, consult a healthcare provider. See Table 1 (below) for help with calculating correct dose. Due to a possible interaction between quercetin and ivermectin, these drugs should be staggered throughout the day (see Table 2 below). For COVID treatment, ivermectin is best taken with a meal or just following a meal, for greater absorption.
- Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ): 200 mg twice a day for 5 to 10 days. Best taken with zinc. HCQ may be taken in place of, or together with, ivermectin. While ivermectin should be avoided in pregnancy, the FDA considers HCQ safe in pregnancy. Given the pathway used by the Omicron variant to gain cell entry, HCQ may be the preferred drug for this variant.
- Mouthwash: three times a day. Gargle three times a day (do not swallow) with an antiseptic-antimicrobial mouthwash containing chlorhexidine, cetylpyridinium chloride (e.g., Scope™, Act™, Crest™) or povidone-iodine (e.g. Betadine® Antiseptic Sore Throat Gargle™).
- Nasal spray with 1% povidone-iodine: 2-3 times a day. Do not use for more than 5 days in pregnancy. If 1% product is not available, dilute the more widely available 10% solution (see box) and apply 4-5 drops to each nostril every 4 hours.
- Pour 1 ½ tablespoons (25 ml) of 10% povidone-iodine solution into a 250 ml nasal irrigation bottle.
- Fill bottle to top with distilled, sterile, or previously boiled water.
- To use: tilt head back, apply 4-5 drops to each nostril. Keep head tilted for a few minutes, then let drain.
- Quercetin (or a mixed flavonoid supplement): 250-500 mg twice a day. Due to a possible interaction between quercetin and ivermectin, these drugs should not be taken simultaneously (i.e., should be staggered at different times of day.) As supplemental quercetin has poor solubility and low oral absorption, lecithin-based and nanoparticle formulations are preferred.
- Nigella sativa: If using seeds, take 80 mg/kg once a day (or 400 to 500 mg of encapsulated oil twice a day).
- Honey: 1 g/kg one to two times a day.
- Melatonin: 5-10 mg before bedtime (causes drowsiness). Slow- or extended-release formulations preferred.
- Curcumin (turmeric): 500 mg twice a day. Curcumin has low solubility in water and is poorly absorbed by the body; consequently, it is traditionally taken with full fat milk and black pepper, which enhance its absorption.
- Zinc: 75-100 mg daily. Take with HCQ. Zinc supplements come in various forms (e.g., zinc sulfate, zinc citrate and zinc gluconate).
- Aspirin: 325 mg daily (unless contraindicated).
- Kefir and/or Bifidobacterium Probiotics. Depending on the brand, these products can be very high in sugar, which promotes inflammation. Look for brands without added sugar or fruit jellies and choose products with more than one strain of lactobacillus and bifidobacteria. Try to choose probiotics that are also gluten-free, casein-free and soy-free.
- Vitamin C: 500-1000 mg twice a day.
- Home pulse oximeter. Monitoring of oxygen saturation is recommended in symptomatic patients, due to asymptomatic hypoxia. Take multiple readings over the course of the day and regard any downward trend as ominous. Baseline or ambulatory desaturation under 94% should prompt consultation with primary or telehealth provider, or evaluation in an emergency room. (See box for further guidance.)
- Only accept values associated with a strong pulse signal
- Observe readings for 30–60 seconds to identify the most common value
- Warm up extremities prior to taking a measurement
- Use the middle or ring finger
- Remove nail polish from the finger on which measurements are made
Second Line Therapies
(In order of priority/importance.)
Add to first line therapies above if: 1) more than 5 days of symptoms; 2) poor response to first line agents; 3) significant comorbidities).
Treatment of BA.4/BA.5/BQ.1.1 and XBB1 Variants
Treatment of Current Circulating Omicron variants
Limited data are available on the clinical implications of the current circulating Omicron ‘subvariants’, however these variants have demonstrated ‘neutralization escape’, meaning they have evolved to escape neutralizing antibodies from previous infections or from mRNA injection. Indeed, vaccination appears to be a risk factor for symptomatic disease.
The newer variants seem to differ from previous variants due to the early onset of bacterial pneumonia. While the optimal treatment approach to the symptomatic patient is unclear, it is best to risk-stratify symptomatic patients. Risk factors for hospitalization and death include advanced age (over 60), comorbidities (especially obesity and metabolic syndrome, poor ambulatory status, delayed treatment, high D-dimer), recently vaccinated, and severe symptoms.
High-risk patients should consider:
- The combination of both HCQ and ivermectin
- Nattokinase 2000-4000 FU/day for 15 days OR Apixaban 5 mg daily for 15 days OR Rivaroxaban 10 mg daily for 15 days. The escalated use of anticoagulants should only be considered in patients with a low risk of bleeding. Furthermore, the risk of serious bleeding increases as the number of anticoagulant drugs is increased.
- Spironolactone: 200 mg once daily for 7 days (avoid in patients with impaired renal function)
If symptoms have not markedly improved by day 3 of treatment, one of the following antibiotics should be started. NOTE: providers should prescribe an antibiotic at the first visit.
Hypoxia/shortness of breath: If the patients develop hypoxia or shortness of breath Prednisolone 60 mg daily for 5 days should be prescribed.
About Ivermectin
Ivermectin is a well known, FDA-approved drug that has been used successfully around the world for more than four decades. One of the safest drugs known, it is on the WHO’s list of essential medicines, has been given over 3.7 billion times, and won the Nobel Prize for its global and historic impacts in eradicating endemic parasitic infections in many parts of the world.
To review the totality of supporting evidence for ivermectin in COVID-19, visit our Ivermectin information page.
Ivermectin is a remarkably safe drug with minimal adverse reactions (almost all minor), however its safety in pregnancy has not been definitively established. Talk to your doctor about use in pregnancy, particularly in the first trimester.
Potential drug-drug interactions should be reviewed before prescribing ivermectin.
Ivermectin has been demonstrated to be highly effective against the Omicron variant at a dose of 0.3 to 0.4 mg/kg, when taken early.
Higher doses (0.6 mg/kg) may be required: in regions with more aggressive variants; if treatment starts on or after 5 days of symptoms; in patients in advanced stage of the disease or who have extensive risk factors (i.e., older age, obesity, diabetes, etc.)Table 1. How to calculate ivermectin dose
Note that ivermectin is available in different strengths (e.g., 3, 6 or 12 mg) and administration forms (tablets, capsules, drops, etc.). Note that tablets can be halved for more accurate dosing, while capsules cannot.

Ordinary Vitamin D3 Does not work in Acute Illness
d.velop Vitamin D Supplements 2400 IU, 20 mcg – High Potency Vitamin D3
 |
| Check Price on Amazon |




.png)



.png)

Comments
Post a Comment