Ferroptosis vs Apoptosis vs Pyroptosis: What are the Differences?
Ferroptosis, apoptosis, and pyroptosis are different ways that cells in our body can die.
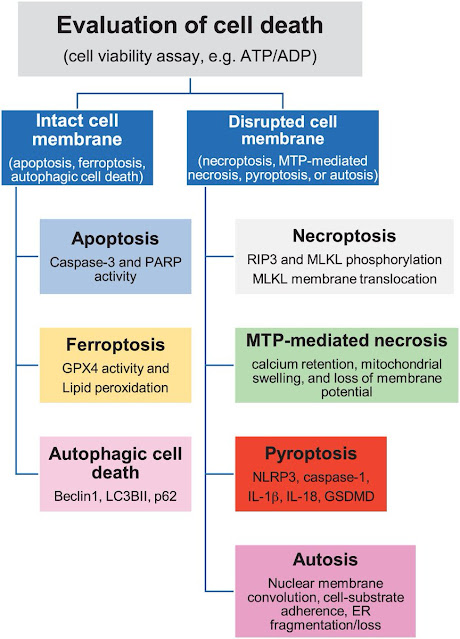
Ferroptosis is a newly discovered type of cell death. It happens when cells accumulate harmful substances called lipid peroxides, which cause damage to the cell. Iron and lipid metabolism are important factors in ferroptosis. Iron helps produce reactive oxygen species that lead to the peroxidation of lipids, eventually resulting in cell death. Unlike the other two processes, ferroptosis doesn't involve the activation of specific proteins or the release of inflammatory chemicals.
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is a natural process that occurs during development and to maintain the balance of cells in our bodies. It is characterized by certain changes in the cell's appearance, such as shrinkage, condensation of the genetic material, and the formation of small blebs on the cell membrane. Apoptosis can be triggered by various signals, both from inside and outside the cell. It is executed by a group of proteins called caspases, which act like molecular scissors, breaking down the cell's components in an orderly manner. Importantly, apoptosis does not cause inflammation or an immune response.
Pyroptosis is a type of cell death that is associated with inflammation. It serves as a defense mechanism against microbial infections. When cells undergo pyroptosis, they swell and burst open, releasing substances that trigger an immune response. Pyroptosis is mainly controlled by specific protein complexes called inflammasomes, which activate caspases. The activated caspases cleave a protein called gasdermin D, leading to the formation of pores in the cell membrane and causing the cell to rupture. While pyroptosis helps fight infections, it can also contribute to inflammatory diseases.
To summarize, ferroptosis, apoptosis, and pyroptosis are different ways in which cells die. Ferroptosis is driven by harmful substances and doesn't involve specific proteins or inflammation. Apoptosis is a controlled process important for development and maintaining cell balance, and it doesn't cause inflammation. Pyroptosis, on the other hand, is associated with inflammation and serves as a defense against infections but can also contribute to inflammatory diseases.
Cell death is an essential process for maintaining homeostasis in multicellular organisms. Throughout life, cells undergo various forms of programmed cell death, each serving distinct purposes. Among these forms, ferroptosis, apoptosis, and pyroptosis have emerged as prominent mechanisms with unique characteristics. Understanding the differences between these cell death pathways is crucial for unraveling their roles in physiological and pathological contexts.
In this article, we will explore the contrasting features of ferroptosis, apoptosis, and pyroptosis.
Ferroptosis is a newly discovered type of cell death. It happens when cells accumulate harmful substances called lipid peroxides, which cause damage to the cell. Iron and lipid metabolism are important factors in ferroptosis. Iron helps produce reactive oxygen species that lead to the peroxidation of lipids, eventually resulting in cell death. Unlike the other two processes, ferroptosis doesn't involve the activation of specific proteins or the release of inflammatory chemicals.
Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, is a natural process that occurs during development and to maintain the balance of cells in our bodies. It is characterized by certain changes in the cell's appearance, such as shrinkage, condensation of the genetic material, and the formation of small blebs on the cell membrane. Apoptosis can be triggered by various signals, both from inside and outside the cell. It is executed by a group of proteins called caspases, which act like molecular scissors, breaking down the cell's components in an orderly manner. Importantly, apoptosis does not cause inflammation or an immune response.
Pyroptosis is a type of cell death that is associated with inflammation. It serves as a defense mechanism against microbial infections. When cells undergo pyroptosis, they swell and burst open, releasing substances that trigger an immune response. Pyroptosis is mainly controlled by specific protein complexes called inflammasomes, which activate caspases. The activated caspases cleave a protein called gasdermin D, leading to the formation of pores in the cell membrane and causing the cell to rupture. While pyroptosis helps fight infections, it can also contribute to inflammatory diseases.
To summarize, ferroptosis, apoptosis, and pyroptosis are different ways in which cells die. Ferroptosis is driven by harmful substances and doesn't involve specific proteins or inflammation. Apoptosis is a controlled process important for development and maintaining cell balance, and it doesn't cause inflammation. Pyroptosis, on the other hand, is associated with inflammation and serves as a defense against infections but can also contribute to inflammatory diseases.
Related: Best Anti Aging Supplements 2023




.png)

.png)

Comments
Post a Comment