NMN’s Potential to Rejuvenate Stem Cells for Stem Cell Therapy Enhancement : Study
Key Points:
- NMN enhances the ability of stem cells to migrate, suggesting they can better target damaged tissues once injected into the body.
- Stem cells are hindered by excessive levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which NMN diminishes.
- NMN prevents stem cells from entering a dysfunctional pro-inflammatory state called senescence.
Stem cells are now being implemented in the clinic to treat degenerative, metabolic, and inflammatory diseases. However, as living cells, they lose their ability to target and repair injured tissues after being cultivated in a laboratory dish for too long. For this reason, scientists have been searching for ways to keep stem cells in top form to maintain their healing efficacy when injected into humans for therapy.
Now, researchers from the East China University of Science and Technology in China show that nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) — an NAD+ precursor known to elevate NAD+ levels — helps to maintain the functional longevity of stem cells in a dish, which can lead to improved effectiveness of stem cell therapies. As published in Antioxidants, Zheng and colleagues report that NMN enhances stem cell migration, diminishes stem cell ROS, and prevents stem cell senescence.
NMN Rejuvenates Therapy-Purposed Stem Cells
To study the effects of NMN on stem cells, Zheng and colleagues isolated a type of stem cell called mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cords donated by consenting mothers. Umbilical cord stem cells are the most commonly used for therapy (after bone marrow stem cells) because they are easy to acquire and do not elicit much of an immune response when injected into humans.
In addition to NMN, the researchers also tested a naturally occurring molecule essential for mitochondrial function called coenzyme Q10 (Q10). Both NMN and Q10 were tested because of their antioxidant — ROS-neutralizing — effects. Indeed, the researchers found a 67% increase in ROS production from cultivated stem cells. Furthermore, both NMN and Q10 elevated stem cell growth.
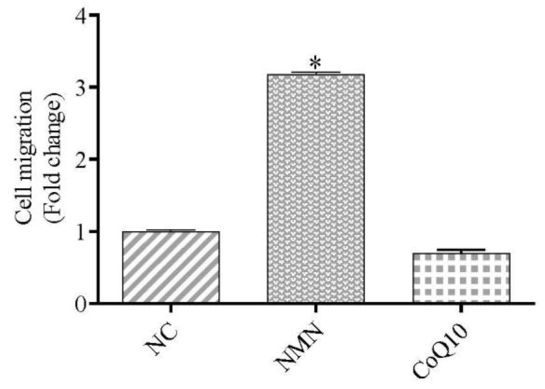
Since stem cells need to home in on injured tissue sites for therapies to work, the researchers tested the effect of NMN and Q10 on stem cell migration. It was found that NMN increased stem cell migration 3-fold, while Q10 had no effect. These findings suggest that NMN can enhance the homing-in effects of stem cells for stem cell therapies.
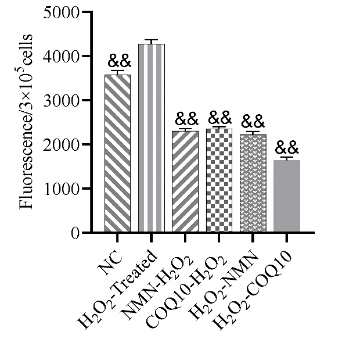
To study the effects of NMN and Q10 on stem cell ROS levels, Zheng and colleagues exposed the stem cells to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which is toxic to cells. Upon treating the H2O2-exposed stem cells with NMN or Q10, ROS levels were diminished. This occurred whether the H2O2 was applied before or after NMN or Q10 treatment. These findings suggest that NMN and Q10 act as potent antioxidants.
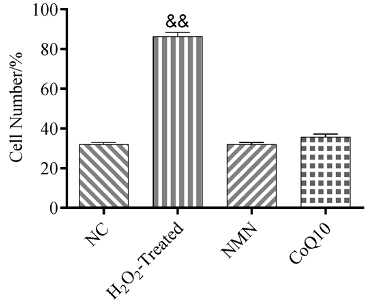
Two hours after exposing the stem cells to H2O2, Zheng and colleagues saw that about 86% of them entered into a senescent state. However, both NMN and Q10 prevented the stem cells from entering senescence. These findings suggest that NMN and Q10 can prolong the replicative lifespan of cultivated stem cells, increasing the potential of stem therapy efficacy.
NMN & Stem Cells: The Anti-Aging Duo of the Future?
Today, the FDA only approves therapies utilizing a class of blood stem cells called hematopoietic stem cells. Therefore, clinics operating in the United States that use mesenchymal stem cells like the ones in this study are currently considered illegal. The FDA has been very cautious about approving stem cell therapies, considering one individual became blind after receiving stem cells into the eye. In another case, stem cell injections into the spinal cord of one individual led to tumor growth. Therefore, more research is needed before we may see FDA-approved stem cell therapy clinics sprout across the country.
Whenever this occurs, we may see NMN or other cell-rejuvenating compounds routinely used in the clinic to keep stem cells fresh. NMN has previously been shown to enhance stem cell therapy for heart attack repair, so the body of research reinforcing NMN as a support compound for stem cell therapy is growing. When it comes to treating age-related chronic diseases, like heart and brain disorders, which are largely degenerative diseases, it may only be a matter of time before stem cell therapies are the go-to, while pharmacological interventions will be a thing of the past.
Zheng, Z., Wang, X., Ouyang, L., Chen, W., Zhang, L., & Cao, Y. (2023). Antioxidants Improve the Proliferation and Efficacy of hUC-MSCs against H2O2-Induced Senescence. Antioxidants, 12(7), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071334


.png)




.png)

Comments
Post a Comment